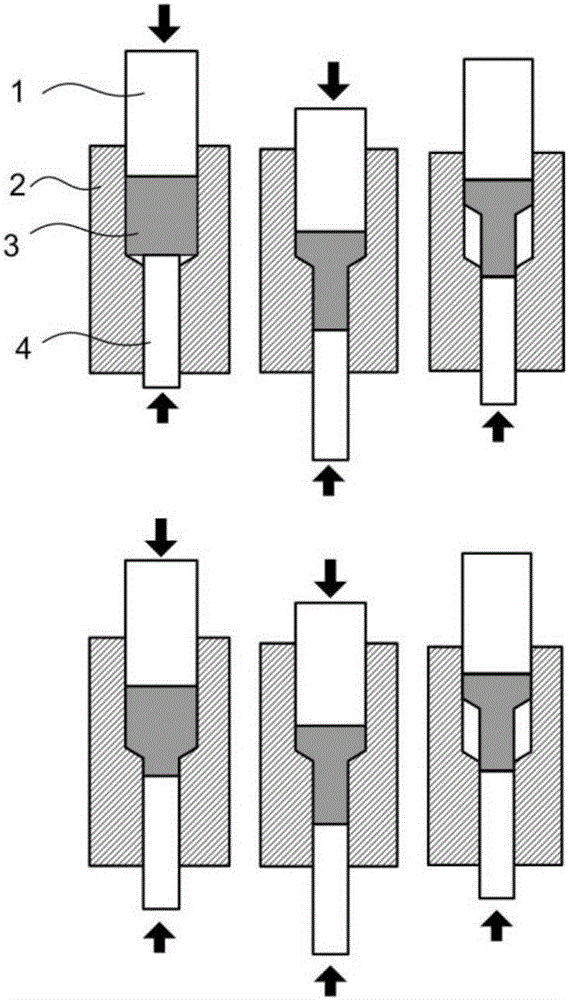
Ball grinding-diameter shrinkage reciprocating extruding method for circular curing of waste titanium chips
A reciprocating extrusion and chipping technology, applied in the field of metal material processing, can solve the problems of ECAP strain accumulation rate to be improved, weaken the mechanical properties of materials, and difficult microstructure refinement, so as to eliminate pore defects and prevent continuous distribution and aggregation , fast processing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0020](1) Ti swarf recovery pretreatment: use the swarf generated by end milling grade 2 Ti (ASTM Grade 2) as the raw material, collect the swarf, and use Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES for short) ) to analyze its chemical composition (mass percentage, wt.%), and the analysis results are shown in Table 1. It can be seen from Table 1 that the chemical composition (oxygen content) of the milled grade 2 Ti chips meets the ASTM standard range. At the same time, 99.9% ethanol is used to clean Ti chips in an ultrasonic vibration tank to remove oil and impurities in raw materials.
[0021] (2) BM treatment of Ti chips: Put the Ti chips obtained in step (1) into a steel BM container, and the mass ratio between chips and steel balls (10 mm in diameter) was 15:1. At the same time, 1 wt.% stearic acid was added as a process control agent, and the BM container was filled with argon as a protective atmosphere to prevent excessive oxidation of chips during...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com