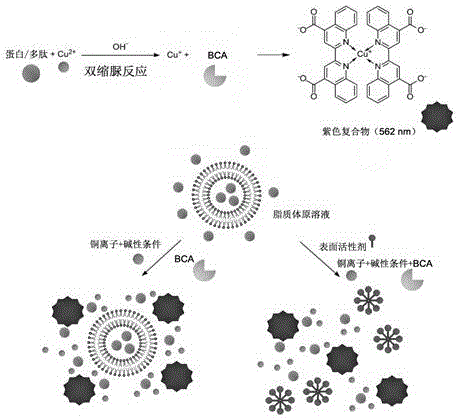
Method for detecting entrapment rate of protein or polypeptide drugs in lipid vesicles
A technology of lipid vesicles and encapsulation efficiency, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, biological tests, material inspection products, etc., to achieve the effect of strong light absorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
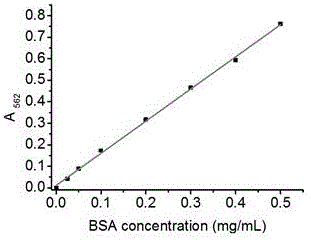
[0034] Prepare liposomes encapsulating bovine serum albumin (BSA) according to the conventional reverse-phase evaporation method, as follows: Weigh 20 mg soybean lecithin and 5 mg cholesterol, dissolve them in 9 mL ether, add them to a round-bottomed flask, add 3 mL 1 mg / mL bovine serum albumin (BSA) solution, sonicated in a water bath for 2 to 5 minutes to form a stable white emulsion suspension, evaporated to dryness with a rotary evaporator to remove the organic solvent, took out the remaining liquid, and ultrasonically treated with an ice-water bath probe until the solution became After clarification, a liposome solution is obtained. The liposome solution was diluted 10 times to a concentration of 0.1 mg / mL. Take a 96-well plate, add the diluted liposome solution at 20 μL per well; take another diluted liposome solution, add Triton X-100 to a final concentration of 0.5%, and add 20 μL per well Add 0.5 mg / mL BSA standard to each well of the standard well, add samples accor...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Prepare the transfer body wrapped with bovine serum albumin (BSA) according to the conventional film dispersion method, as follows: Weigh 30 mg soybean lecithin, 6 mg cholesterol, and 2 mg sodium deoxycholate, dissolve them in an appropriate amount of chloroform, and add them to a round bottom flask , evaporate to dryness with a rotary evaporator to remove the organic solvent, so that a uniform film is formed at the bottom of the flask; place the flask in a vacuum desiccator for at least 3 hours to completely remove the residual organic solvent, and add 5 mL of 1 mg / mL BSA solution , oscillating to hydrate the film, ultrasonic treatment in a water bath for 30 minutes, until the solution becomes clear to obtain the transfer body solution, take an appropriate amount of transfer body solution and dilute it 10 times for later use. Take a 96-well plate, add the diluted transfersome solution at 20 μL per well; take another diluted transfersome solution, add Triton X-100 to a f...
Embodiment 3
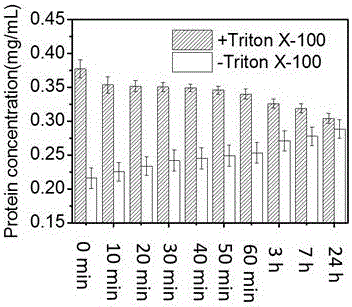
[0040] Prepare the liposome solution according to Example 1, take 1 mL of the liposome solution and use an ultrafiltration centrifuge tube with a molecular weight cut-off of 100 kD to remove the free protein by centrifugation, and then use a final concentration of 0.1% Triton X-100 to separate the For liposome demulsification, take 20 μL each, add 200 μL BCA reaction reagent, place it at 50°C for 20 min, place it in a microplate reader quickly, and read the absorbance value at 562 nm. Also scan the plate once every 10 minutes, record continuously for one hour, and then scan again at room temperature, 3, 7, and 24 hours after color development, and record the absorbance changes at different times. Calculate the concentration of each porin according to the standard curve obtained from each measurement, as shown in the attached Figure 4 Shown is the time change curve of the initial total protein concentration (Initial+Triton) and the total protein concentration after ultrafiltrat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com