Accelerator for anaerobic fermentation of antibiotic antibacterial residue and preparation and application of accelerator
An antibiotic slag, anaerobic fermentation technology, applied in fermentation, biochemical equipment and methods, bacteria and other directions, can solve the mismatch between processing capacity and production, low organic load of anaerobic fermentation of bacterial slag, gas production efficiency and comprehensive problems such as poor efficiency, to achieve the effect of promoting sustainable development, promoting the growth of methane bacteria, and improving gas production efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] Example 1 Preparation of Anaerobic Fermentation Accelerator
[0016] (1) Functional microbial culture
[0017] Both Y10 and Z13 were cultured in LB medium with shaking at 30 °C for 72 h in an anaerobic bottle. It was detected that 80% of the bacteria in the fermentation liquid formed spores, and they were placed at 4 °C for later use. Centrifuge at 8000 rpm / min for 15 min before use, collect the bacteria separately, dilute with a small amount of sterile water, and adjust the concentration of spores to (1.0-5.0)×10 11 cfu / mL.
[0018] LB medium: 5.0 g of yeast extract, 10.0 g of tryptone, 10.0 g of sodium chloride, 15.0 g of agar, 1000 mL of water, pH7.0-7.4.
[0019] (2) Trace element stock solution configuration: FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O, NiCl 2 ·6H 2 O and CoCl 2 ·6H 2 O is prepared to a relatively high concentration, such as a stock solution of 1-10 mol / L for later use.
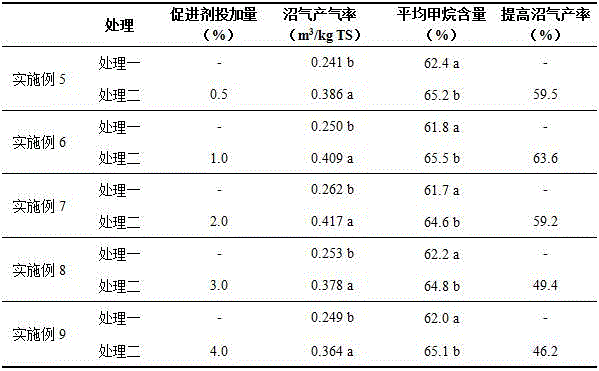
[0020] (3) Take an appropriate amount of biochar, dry it in an oven, and pulverize it. Mix func...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Example 2 Anaerobic fermentation of cephalosporin C bacteria residue
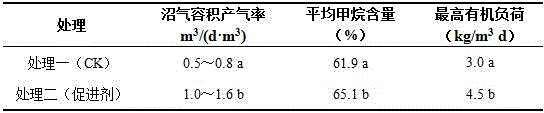
[0022] A 250 mL anaerobic bottle was used, with cephalosporin C residue as raw material, and a medium-temperature full-mix anaerobic fermentation process. Two treatments were set up: treatment one: blank control; treatment two: adding 1.5% of the present invention accelerators. The organic load TS is 2%, (TS is also called the dry matter concentration, which refers to placing a certain amount of fermentation feed liquid in an oven at 100~105 °C and drying it to a constant weight, and the percentage of the dried material to the total weight). The biogas slurry in the fermentation biogas digester was used as the inoculum, the inoculum amount was 20-30% (volume ratio), the fermentation temperature was 35±2°C, the fermentation time was 30 days, and 5 parallels were used for each treatment. The specific results are shown in Table 1.
[0023] Table 1 Biogas production situation
[0024]
[0025] As c...
Embodiment 3
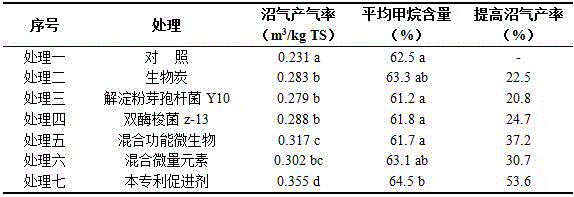
[0026] Embodiment 3 Batch type anaerobic fermentation experiment
[0027] A 250 mL anaerobic bottle was used, with penicillin residue as raw material, and a medium-temperature full-mix anaerobic fermentation process. Seven treatments were set up: treatment 1: blank control; treatment 2: adding biochar with a mass fraction of 1%; treatment 3: Add Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Y10 1.0 x 10 7 cfu / mL; treatment four: add bienzyme Clostridium Z-13 1.0×10 7 cfu / mL; treatment five: add mixed functional microorganisms, in which Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Y10 and Clostridium bienzyme Z-13 are mixed at a ratio of 1:1, and the dosage is 1.0×10 7 cfu / mL; treatment six: mixed trace elements, of which Fe 2+ 300 mg / L, Ni 2+ 0.5 mg / L, Co 2+ 50 mg / L. Treatment seven: Add the accelerator prepared by the present invention with a mass fraction of 1% (after adding, the fermentation system will contain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Y100.5×10 7 cfu / mL, Bienzyme Clostridium Z-130.5×10 7 cfu / ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com