A kind of negative electrode active material of sodium ion battery, negative electrode, battery and preparation method
A technology for negative active materials and sodium-ion batteries, applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of poor rate performance and cycle performance of titanium-based materials, achieve good cycle stability, good rate performance, and good electrical conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0092] In this embodiment, the precursors of potassium source and titanium source are used as raw materials, and the negative electrode active material is prepared by a high-temperature carbothermal reduction method. The specific process is as follows:
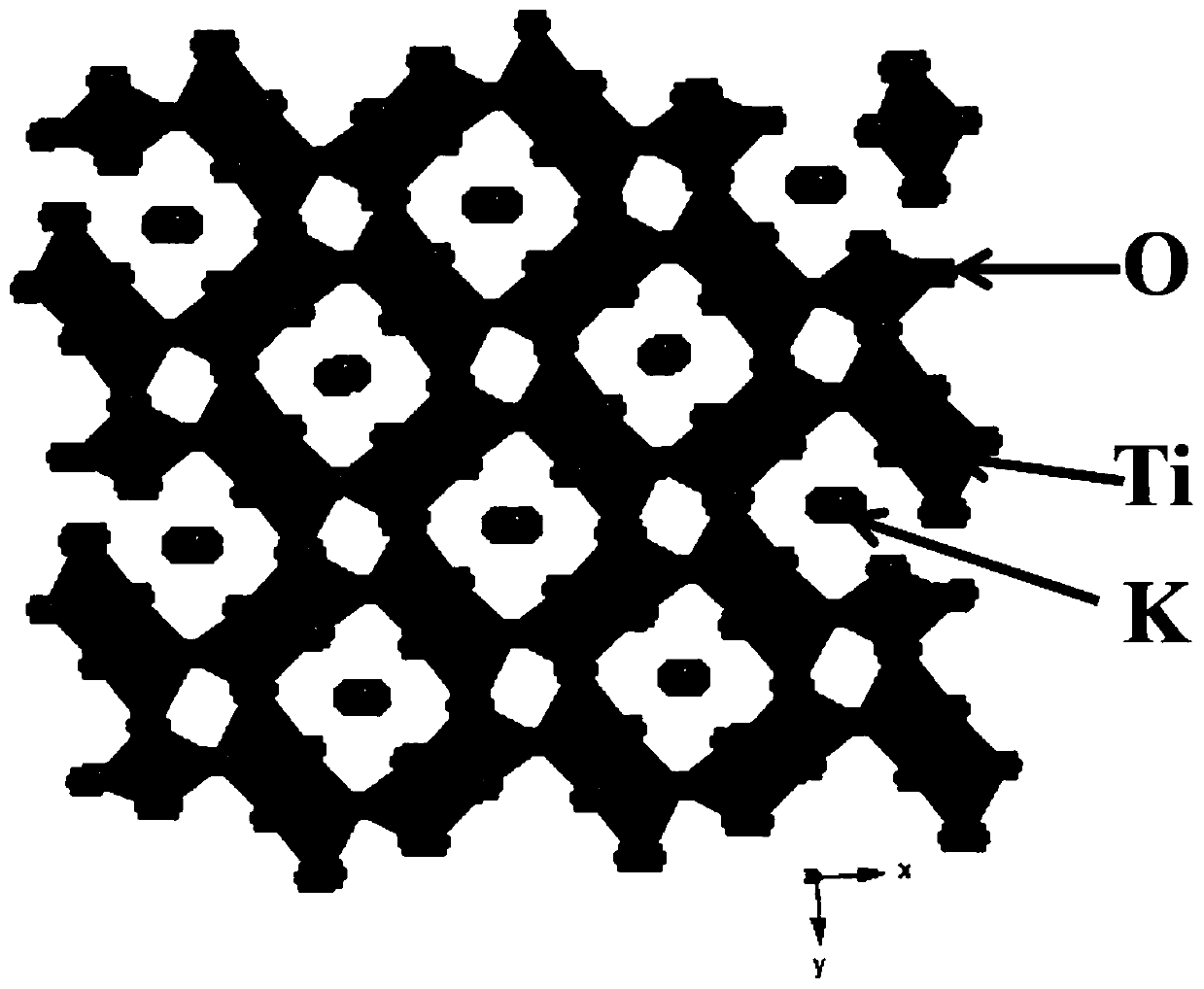
[0093] First, KOH and anatase TiO 2 As a precursor, the two are stoichiometrically mixed in a mixed solution of ethylene glycol and deionized water,
[0094] Then, the hydrothermal reaction gives K 2 Ti 6 o 13 Nanowires, the hydrothermally obtained product and glucose are mixed uniformly in absolute ethanol, wherein the carbon content accounts for K 2 Ti 6 o 13 The ratio to the total mass of carbon is 30%,
[0095] After drying, the resulting mixture was 2 Carbon-coated K x TiO 2 For nanorods, the reaction temperature of the high-temperature carbothermal reduction method is 800° C., and the holding time is 360 minutes.
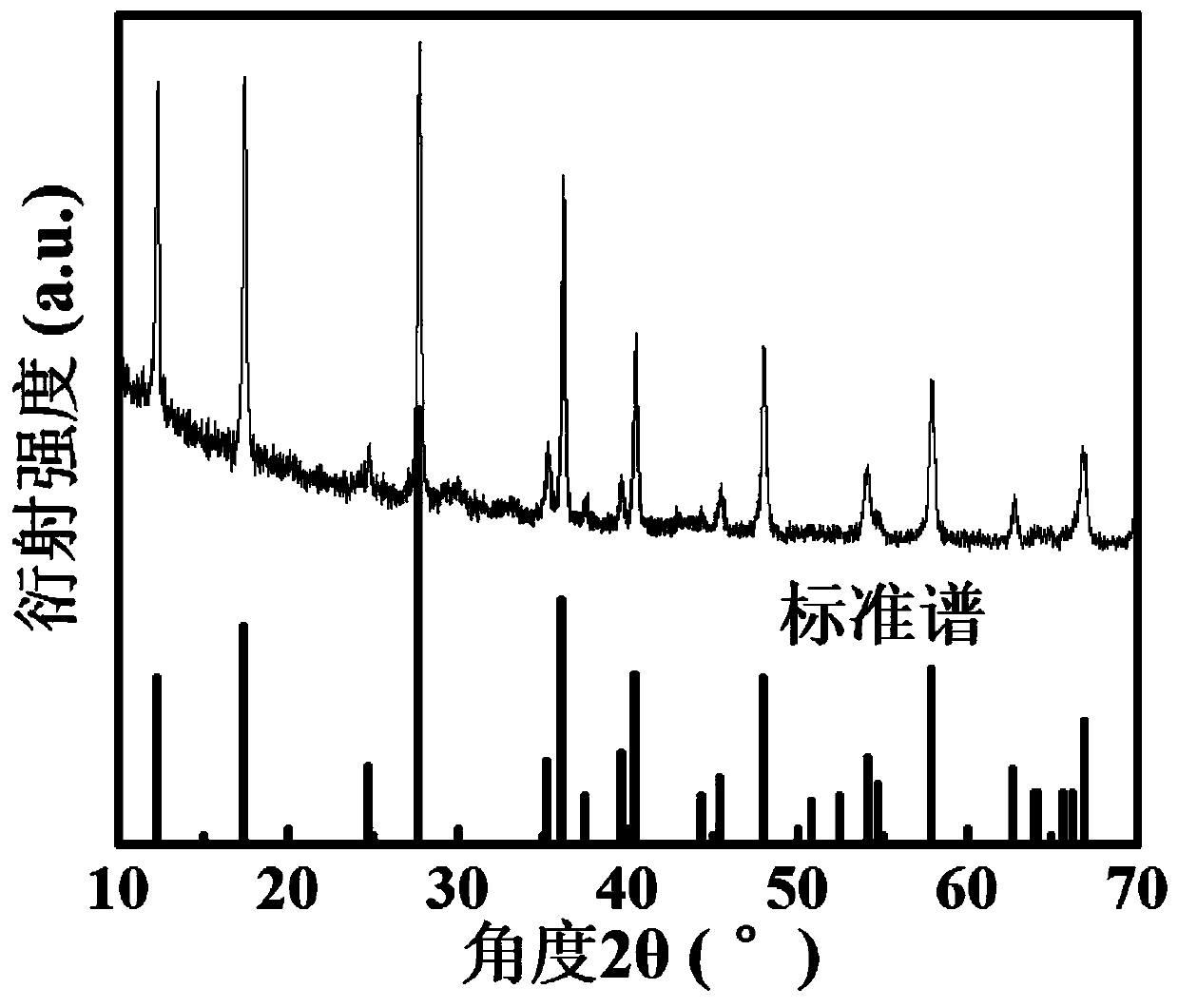
[0096] XRD test shows that the product is a single K x TiO 2 (0x TiO 2 (0<x<1) The nanorod su...
Embodiment 2
[0106] In this embodiment, the precursors of the potassium source and the titanium source are used as raw materials, and the negative electrode active material is prepared by chemical vapor deposition. The specific process is as follows:
[0107] First, KOH and anatase TiO 2 As the precursor, the two are mixed evenly in the mixed solution of ethylene glycol and deionized water according to the stoichiometric ratio. In practice, the selected medium is selected from water, ethanol, acetone, glycerin, isopropanol, ethylene glycol, n-butyl Alcohol, hydrazine hydrate, tetrahydrofuran, dimethyl sulfoxide, dimethylformamide, cyclohexane, n-hexane, octadecene, oleic acid, oleylamine or their mixture, and then hydrothermal reaction to obtain K 2 Ti 6 o 13 Nanowires,
[0108] Next, the hydrothermally obtained product is placed in a high-temperature reactor,
[0109] Finally, the organic carbon source toluene was brought into the high-temperature reactor by chemical vapor depositio...
Embodiment 3
[0113] In this embodiment, the precursors of the potassium source and the titanium source are used as raw materials, and the negative electrode active material is prepared by a solid-phase ball milling-assisted high-temperature calcination method. The specific process is as follows:
[0114] First, KOH and anatase TiO 2 As the precursor, glucose as the carbon source, the three are mixed uniformly by ball milling according to the stoichiometric ratio, and the carbon content accounts for 10% of the total mass of the mixture.
[0115] Then, the mixture was placed in a high-temperature reactor under N 2 Carry out high-temperature calcination under atmosphere protection, the holding temperature is 600-1000°C, and the holding time is 240-600min.
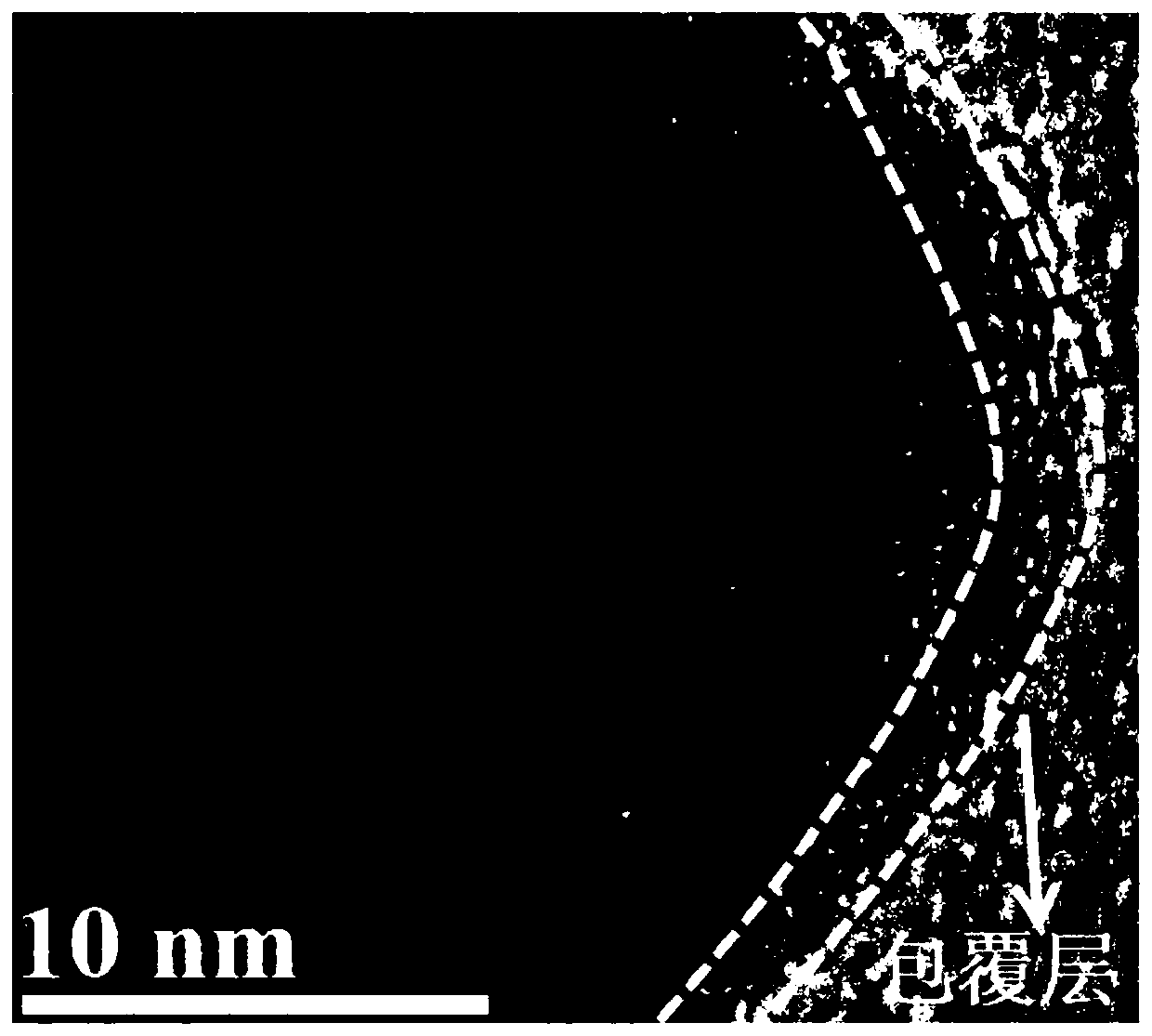
[0116] XRD test shows that the product is a single K x TiO 2 (0<x<1), through the observation of the scanning electron microscope and the transmission electron microscope, it is found that the thickness of the semi-graphitized carbon l...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com