Preparation method of lipopeptide biosurfactant
A biological surface and active agent technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of hindering industrialization, low output, high production cost, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing operation steps, reducing production cost and saving pretreatment cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
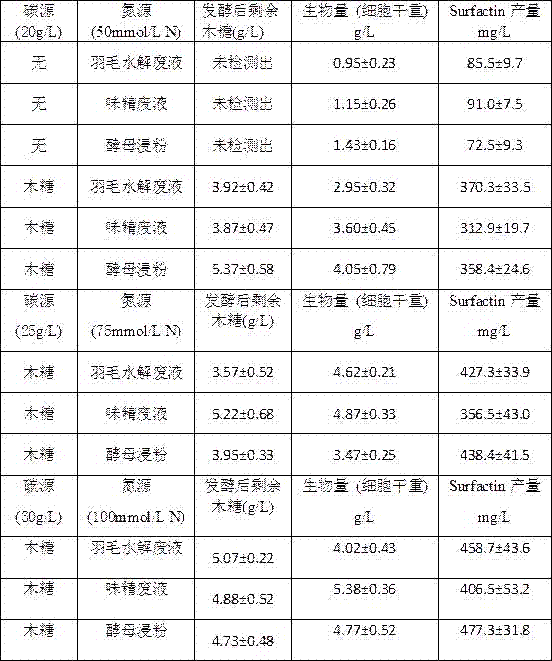
[0026] This example demonstrates that Bacillus subtilis Bacillus subtilis G-34 utilizes xylose to produce lipopeptide biosurfactants.
[0027] (1) Preparation of seed medium: yeast extract powder 5g / L, peptone 10g / L, sodium chloride 10g / L; sterilize at 121°C for 20min, cool down for later use.
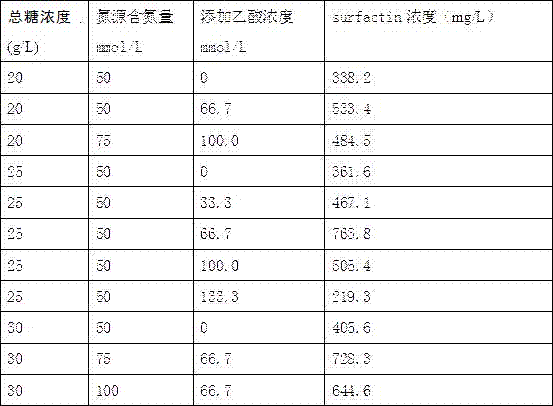
[0028] (2) Fermentation medium preparation: xylose 20-30g / L, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.2g / L, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate 0.02g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 10g / L, nitrogen source: feather hydrolysis Waste liquid, MSG fermentation waste liquid, or yeast extract powder (N content of nitrogen source is 50-100mmol / L), use NaOH solution (6mol / L) to adjust the pH to 7.5. Sterilize at 115°C for 20min. Let cool and set aside.
[0029] Feather hydrolysis waste liquid is provided by Jiangsu New Hanling Bioengineering Co., Ltd. (Jiangsu, Xinyi). The ingredients contain 18-20% of total amino acids, NH 4 Cl 20-25%, small peptide and ash 2%.
[0030] The monosodium glutamate ferme...
Embodiment 2
[0038] This example illustrates and common Ca(OH) 2Compared with neutralization and detoxification, NaOH neutralization is a better method for pretreatment of corncob / corn stalk acid hydrolysis solution.
[0039] (1) The seed medium is the same as that in Example 1, and the cultivation method adopts the method adopted in Example 1 for cultivation.
[0040] (2) Fermentation medium: corn cob acid hydrolysis solution or corn stalk acid hydrolysis solution (containing 20g / L of total sugar), feather hydrolysis waste liquid (containing N content of 50mmol / L), magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.2g / L, Ferrous sulfate heptahydrate 0.02g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 10g / L, use NaOH solution (6mol / L) to adjust the pH to 8.0. Sterilize at 115°C for 20min. Let cool and set aside.
[0041] The preparation method of corn cob / corn stalk acid hydrolysis solution is: crush corn cob or corn stalk into granules, mix corn cob or corn stalk granules with dilute sulfuric acid with a concentrati...
Embodiment 3
[0047] This example shows that Bacillus subtilis G-34 has strong tolerance to various inhibitory components in corncob acid hydrolysis solution.
[0048] (1) The seed medium is the same as that in Example 1, and the cultivation method adopts the method adopted in Example 1 for cultivation.
[0049] (2) Fermentation medium: corn cob acid hydrolysis solution (total sugar 30g / L), magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.2g / L, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate 0.02g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 10g / L, nitrogen source is Feather hydrolysis waste liquid (N content of nitrogen source is 50mmol / L), using NaOH solution (6mol / L) to adjust the pH to 7.8. Sterilize at 115°C for 20min. Let cool and set aside. Formic acid (65mmol / L), acetic acid (45mmol / L), furfural (12mmol / L), 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (12mmol / L) and other biomass produced in the dilute acid hydrolysis process were added to experimental groups 1-4. Inhibit ingredients.
[0050] The sample in Example 1 was used as a control group....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com