Preparation of carbon nanotube doped fenbufen molecularly imprinted polymer sustained-release material
A molecular imprinting and carbon nanotube technology, which can be used in medical preparations without active ingredients, medical preparations containing active ingredients, drug combinations, etc., and can solve problems such as poor dispersion and difficulty in carbon nanotube composites.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
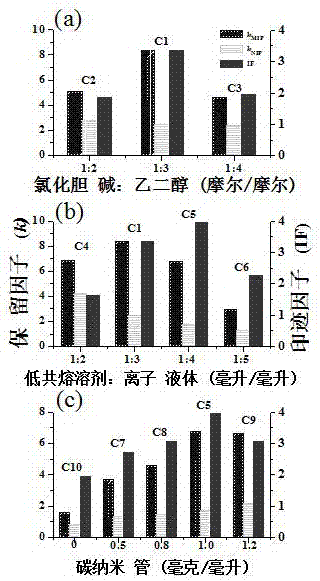
[0031] In order to obtain the best synthesis formula of fenbufen carbon nanotube doped controlled-release molecularly imprinted polymer, we optimized the synthesis formula of fenbufen imprinted monolithic column, the specific operation steps are as follows:
[0032] Preparation method of fenbufen molecularly imprinted monolithic column doped with single-walled carbon nanotubes using ionic liquid and deep eutectic solvent as binary porogen:
[0033] a. Mix 0.75% of the template molecule fenbufen (both in mass percentages), 0.29% of the initiator azobisisobutyronitrile, and 0.06% of single-walled carbon nanotubes, and add a mass fraction of 54.03% [BMIM]BF 4Dissolve and mix with mass fraction 21.76% ChCl (choline chloride) / EG (ethylene glycol) at room temperature by ultrasonic (40KHz, 10min), then add mass fraction 2.71% 4-vinylpyridine and mass fraction 20.40% Ethylene glycol methacrylate continues to be ultrasonically mixed to remove the oxygen in the mixed reaction liquid, in...
Embodiment 2
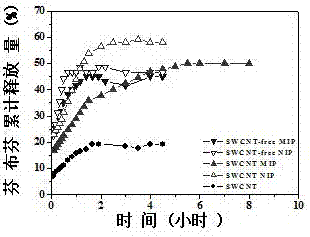
[0041] Drug Release Experiments A model to study the kinetics of drug release from fenbufen molecularly imprinted polymers. In order to investigate the drug release model, the total amount of drug released by fenbufen molecularly imprinted polymers and non-imprinted polymers within a certain period of time was determined. The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0042] a. Mix template molecule fenbufen 0.75% (both mass percentages), initiator azobisisobutyronitrile 0.29%, single-walled carbon nanotubes 0.06%, add mass fraction 54.03% [BMIM]BF 4 With the mass fraction of 21.76% ChCl / EG (mol / mol, 1:3), ultrasonically dissolve and mix at room temperature, and then add the mass fraction of 2.71% 4-vinylpyridine and the mass fraction of 20.40% ethylene glycol dimethacrylate Continue to sonicate to make it evenly mixed, remove the oxygen in the mixed reaction solution, seal it, and react in a water bath at 60°C for 14 h;
[0043] b. The molecularly imprinted polymer obtained...
Embodiment 3
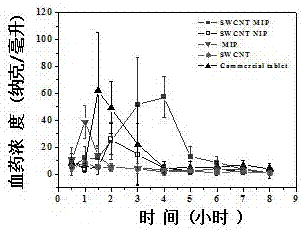
[0049] Pharmacokinetic experiments to study the blood concentration of fenbufen molecularly imprinted polymer in rats over time. In order to investigate the controlled-release effect of the drug in rats, the blood drug concentration in rats was determined within a certain period of time after oral administration of different types of fenbufen carrier materials.
[0050] The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0051] a. Synthesize molecularly imprinted polymers containing carbon nanotubes, molecularly imprinted polymers without carbon nanotubes, and non-imprinted polymers containing carbon nanotubes by the same method as above (Example 2).
[0052] b. Fenbufen Tablets (Zhejiang Weikang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.), a commercial drug in the control group, was purchased from Tianjin Laomin Pharmacy Chain Co., Ltd.; single-walled carbon nanotubes were purchased from Nanjing Xianfeng Nano Technology Co., Ltd.
[0053] c. Soak the above prepared material in the acetonitrile sol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com