Preparation method for biological chip for detecting food-borne pathogenic bacteria
A technology of food-borne pathogenic bacteria and biochips, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, measurement/testing of microorganisms, organic compound libraries, etc., can solve heavy preparation and finishing work, long detection cycle, lack of specificity, etc. problems, avoiding the interaction between primers and products, ensuring specificity, and reducing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
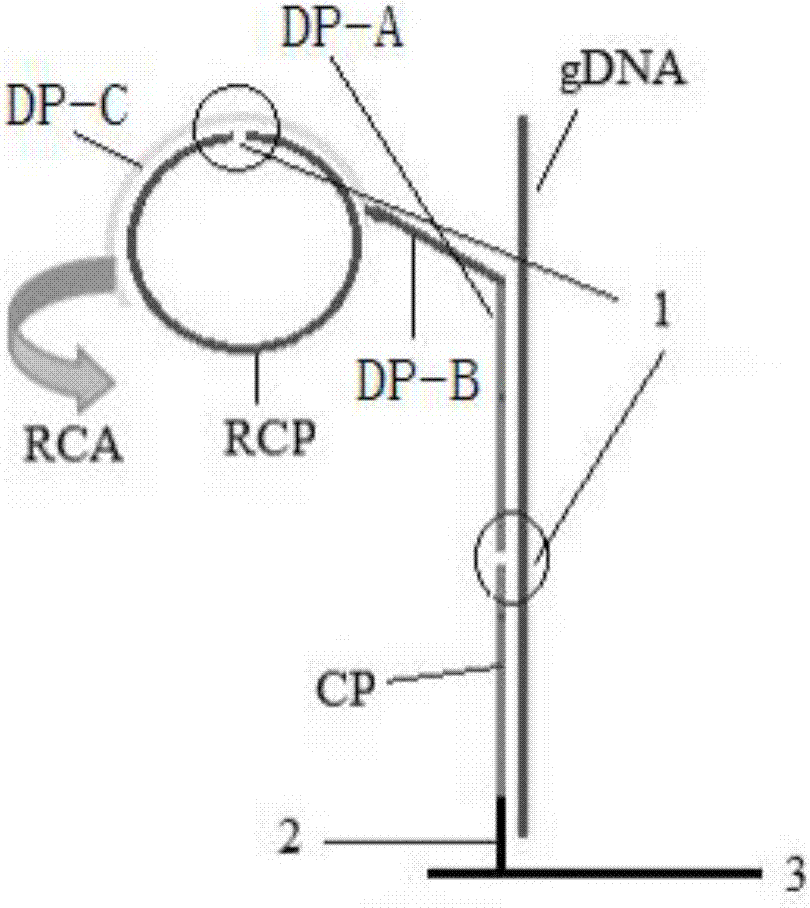
[0028] A method for preparing a chip for detecting food-borne pathogenic microorganisms, the specific steps are as follows:
[0029] (1): Soak the silanized glass slide in 5% glutaraldehyde (50% aqueous solution, Amresco) phosphate buffer solution (0.1M PH7.4) for 2 hours, wash with acetone, ethanol, deionized distilled water Thoroughly wash each twice, blow dry with nitrogen, and store at 4°C for later use;
[0030] (2): Design and synthesis of probes:
[0031] TP: 5′-GCCTTTACAGATAGCATGCCATACAGTCATTTCACGC-3′
[0032] CP: 5′-NH 2 -TTTTTTTTGCGTGAAATGACTGTATGG-3′
[0033] DP: 5′-CATGCTATCTGTAAAGGCTTTCGTTTCACGACGAAATAACGGGATACAGGAC-3′
[0034] RCP: 5′-CGTTATTTCGTCTATTCTACTGTATTCTGTATGTCTCCGTATCGCTGTCACCTGTGTATCTTTGATTCGTCAGTCCTGTATCC-3′
[0035] PC:5′-NH 2 -TTTTTTTTTTGCATATGAGCGTCTCGACTTT-biotin-3'
[0036] NC: 5′-NH 2 -TTTTTTTTTTTCGTTACTAGTACATGCTTCGGTTT-3′
[0037] (3): CP, PC and NC were prepared as a 100 μM stock solution using TE buffer and stored at -20°C. Before ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Embodiment 2: Verify the feasibility and specificity of the microarray chip detection method:
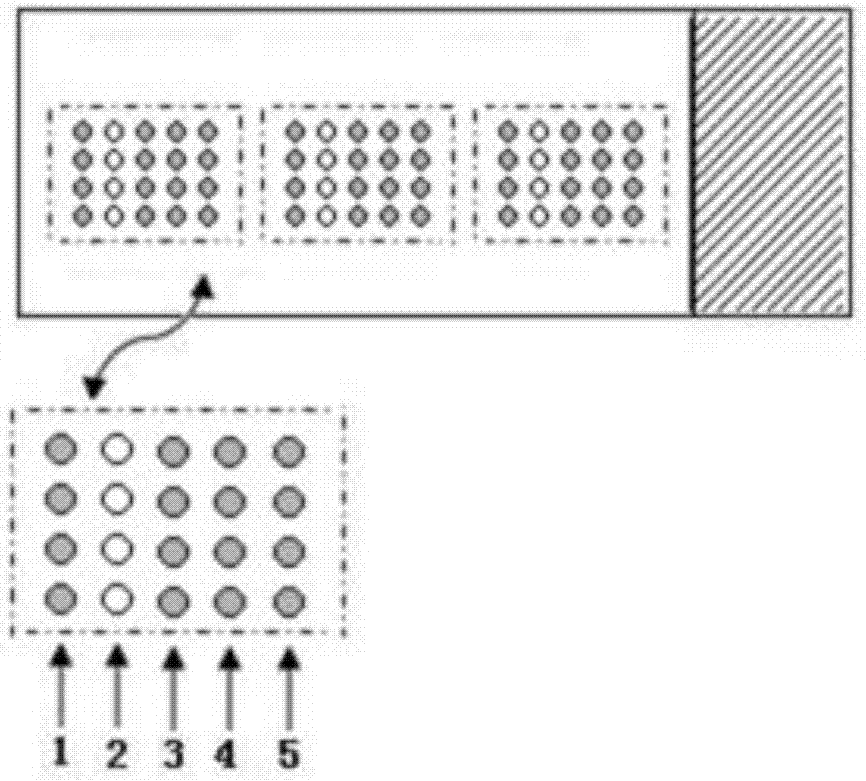
[0051] (1) Spot PC, NC and CP onto the aldehyde-based substrate using a spotting instrument, with a probe concentration of 2 μM.
[0052] (2) The probe fixing process is the same as (1)-(4) in Example 1.
[0053] (3)(3) Add TP, DP (final concentration 0.05μM) and RCP (5μL) into the hybridization solution in the EP tube, heat at 95°C, denature for 5min, and quickly transfer 25μL of the hybridization reaction system in the EP tube to the aldehyde In the 25 μL Gene Frame of the substrate, cover the cover glass, place it in a hybridization oven to start the hybridization reaction, and hybridize at 50°C for 4 hours.
[0054] (4) connection, RCA, washing and scanning, the steps are the same as (6)-(12) of Example 1.
[0055] Taking TP as the detection object, TP was directly added to the hybridization reaction system for microarray chip rolling circle amplification detection, and...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Embodiment 3: Detection effect of Staphylococcus aureus
[0057] Staphylococcus aureus (CMCC26003) was cultured, and gDNA of Staphylococcus aureus was extracted.
[0058] The sampling steps are the same as (1)-(12) of Example 1.
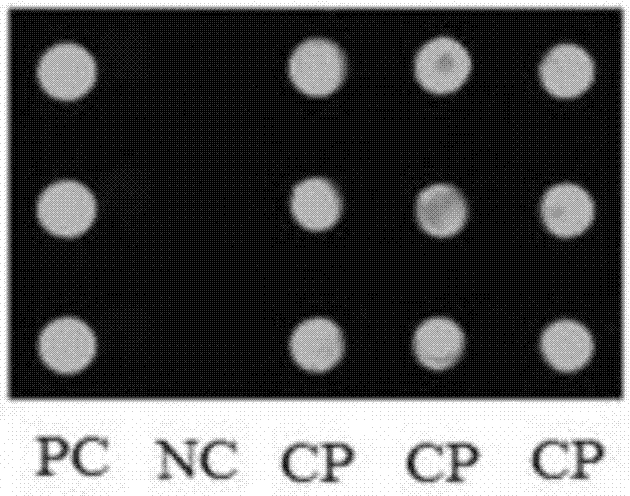
[0059] Cultivate Staphylococcus aureus (CMCC26003), extract its gDNA, prepare 2μM CP, PC and NC, and array, and perform sRCA reaction. The detection results are as follows: Figure 4 As shown, both PC and CP have fluorescence signals, and NC has no fluorescence signals, indicating that the method of the present invention can specifically detect Staphylococcus aureus gDNA, indicating that the detection method has high specificity.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com