Method for purifying bacterial capsular polysaccharide
A technology of capsular polysaccharide and purification method is applied in the field of purification of bacterial capsular polysaccharide crude product, can solve the problems of polysaccharide reduction, unfavorable production, solution volume limitation, etc., achieves reduction of protein and nucleic acid impurities, easy industrial production, and process Simple and fast effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1. Preparation of Streptococcus pneumoniae polysaccharide serotypes 1, 3, 4, 7F, 9v, 15B, 19A, 19F, 23F, 33F capsular crude polysaccharide
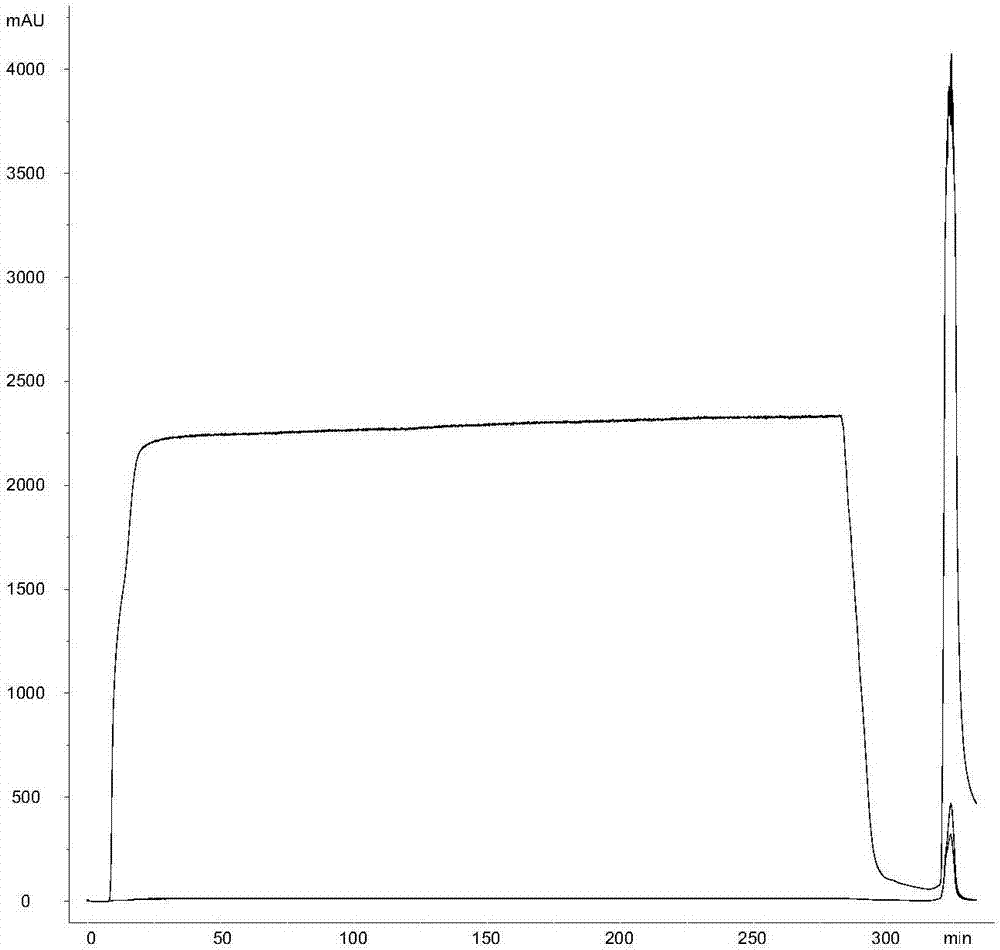
[0034] Streptococcus pneumoniae fermentation broth was dissolved with sodium deoxycholate (DOC) at 4°C for 12-24h. Then add acid directly to the bacterial lysate, adjust the pH value of the lysate containing capsular polysaccharide to 3-6.5, let it stand at room temperature for more than 1 hour, and centrifuge to remove impurities such as lysate, some proteins and nucleic acids, and a large number of cell debris. Centrifuge the acidified solution for one hour at 20° C. with a relative centrifugal force greater than 10,000 g, collect the supernatant and discard the precipitate. The obtained supernatant is ultrafiltered with a molecular cut-off of 50-100kD membrane, diafiltered with pure water to further remove small molecular impurities, and finally concentrated to obtain a crude capsular polysaccharide solution.
[0035] T...
Embodiment 2
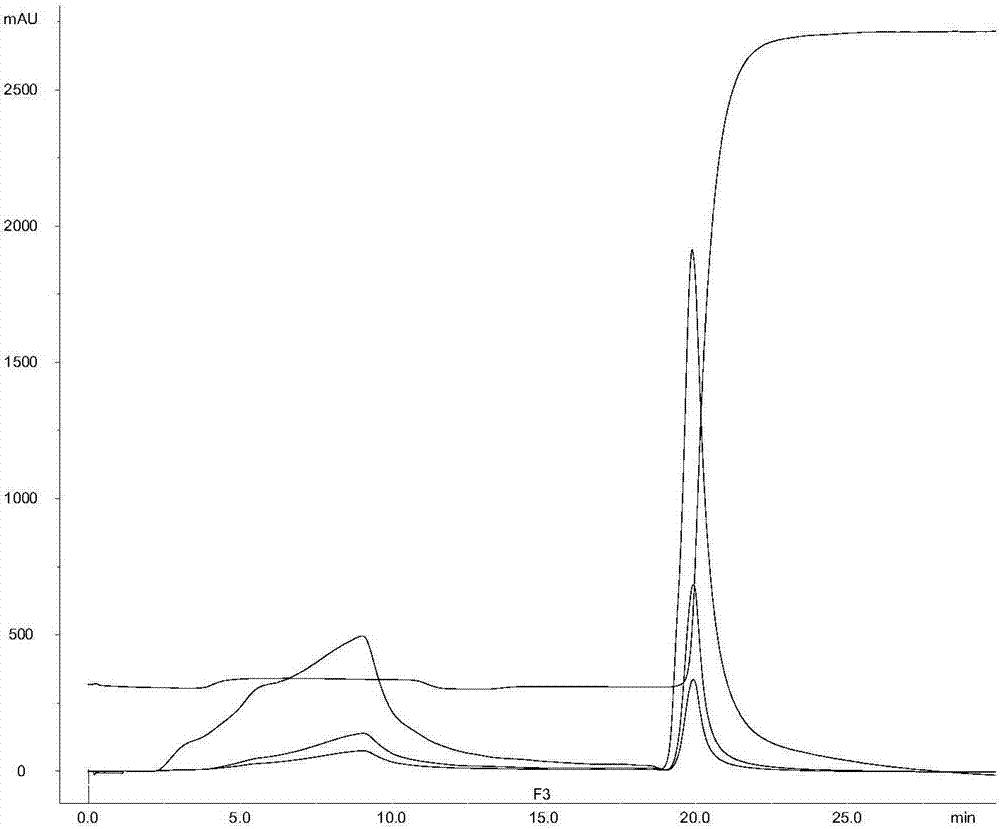
[0037]Example 2. Analysis of the treatment effect of 19F serotype capsular polysaccharide solution by different chromatography packing materials
[0038] Experimental operation
[0039] Ion-exchange chromatography (Capto DEAE, GE): The crude polysaccharide solution obtained after acidification treatment uses a membrane with a molecular weight cut-off of 10-100kD, and uses 5-50mM phosphate buffer solution at a pH of 6 to 8 to further ultrafilter and change the solution. until a constant conductance is reached. The Capto DEAE chromatographic column was equilibrated with the same buffer, and then the capsular polysaccharide solution after the exchange was applied to the column, and the flow-through was collected. After loading the samples, wash with 1-2 column volumes of 25 mM phosphate buffer, and the polysaccharides are recovered in the flow-through and washing solutions. Proteins, nucleic acids, and polysaccharides bound to the Capto DEAE column were eluted with 1M NaCl. ...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Example 3. Preparation of Streptococcus pneumoniae polysaccharide serotypes 1, 3, 4, 7F, 9v, 15B, 19A, 19F, 23F, 33F refined sugar
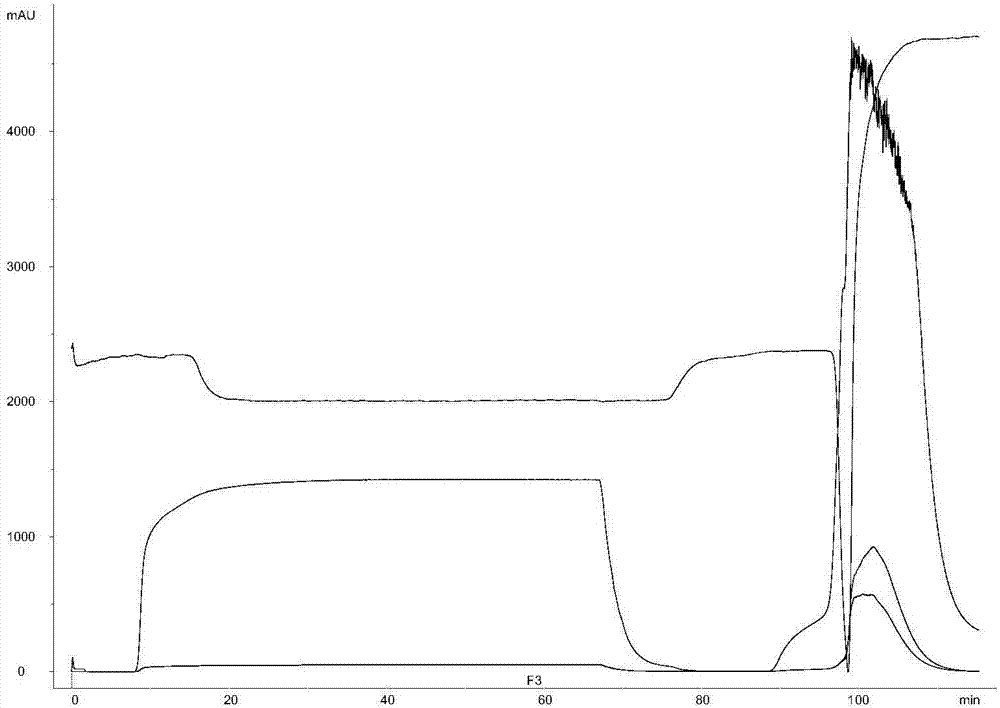
[0049] The crude polysaccharide solution obtained after the acidification treatment uses a membrane with a molecular weight cut-off of 10-100kD, uses 5-50mM phosphate buffer solution, and the salt ion concentration (NaCl) is preferably at 100-300mM, and is further ultrafiltered until a constant conductivity is achieved. The Hydroxyapatite chromatography column is preferably connected in series with the Capto adhere chromatography column and then equilibrated with the same buffer solution, and then the capsular polysaccharide solution after the liquid exchange is applied to the column to collect the flow-through. After the sample loading is completed, further wash with 1-2 column volumes of the same salt ion buffer, and the polysaccharides are recovered in the flow-through and wash solutions.
[0050] Table 3. Protein and nucleic acid conte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com