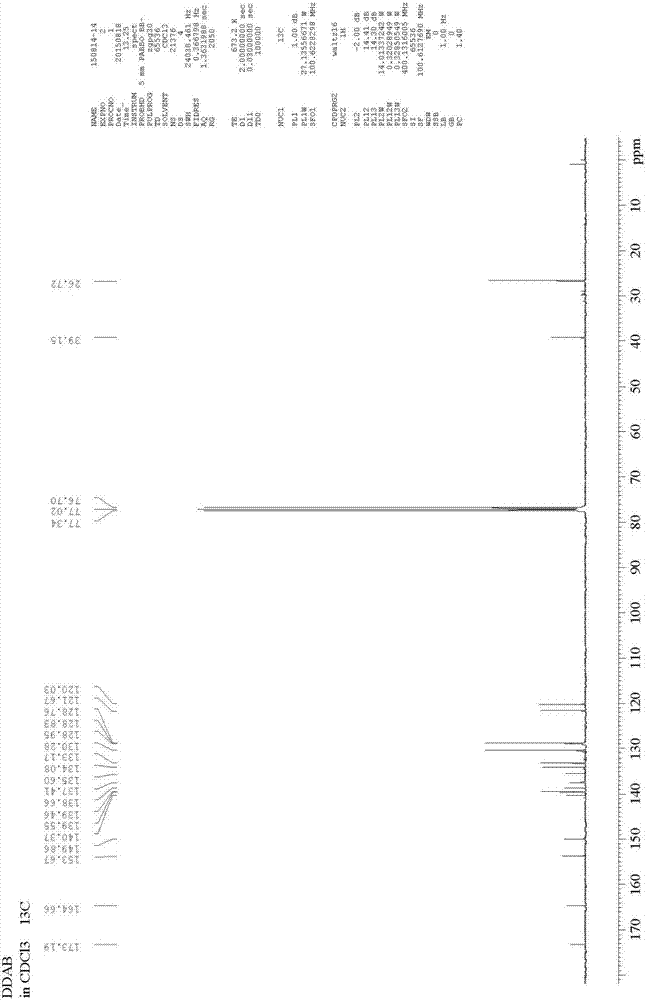
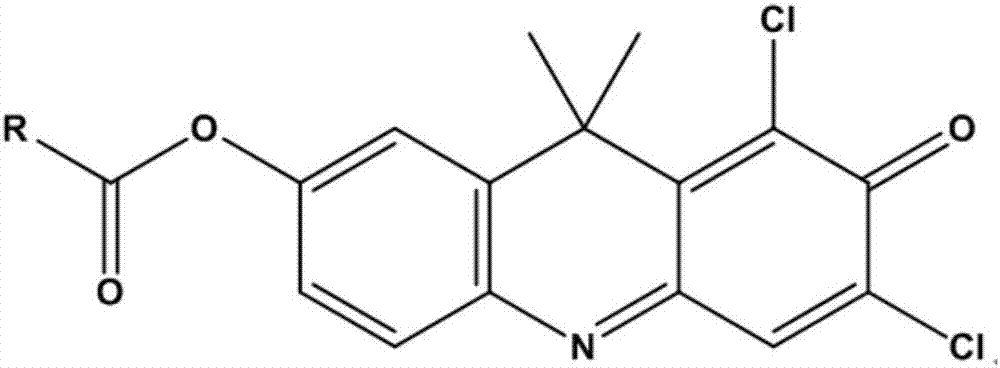
Near infrared fluorescence probe substrate of carboxylesterase2 and application of substrate
A carboxylesterase and fluorescent probe technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of large quantitative error, short emission wavelength, and large interference of biological matrix autofluorescence, and achieve high sensitivity, simple and easy synthesis process, and good fluorescence properties. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
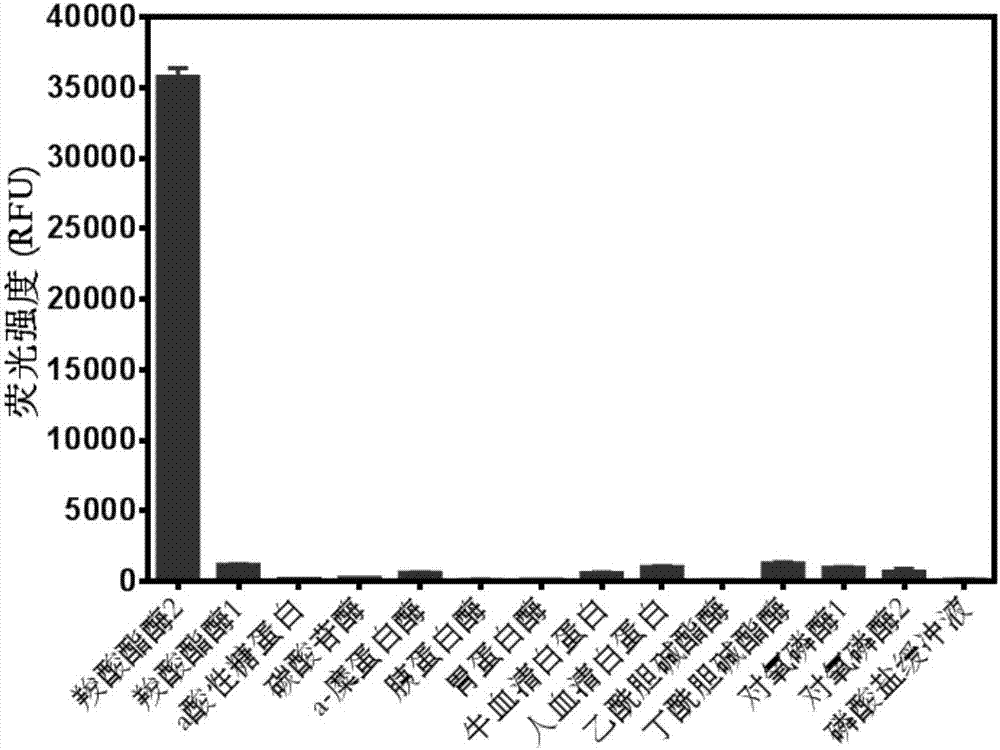
[0040] Probe specificity evaluation
[0041] (1) Contains carboxylesterase 1, carboxylesterase 2, trypsin, pepsin, trypsin, carbonic anhydrase, a-chymotrypsin, paraoxonase 1, paraoxonase 2, a acid glycoprotein 198μL of phosphate of acetylcholinesterase (5μg / mL), butyrylcholinesterase (20U / L), human serum albumin (50μg / mL), bovine serum albumin (50μg / mL), at 37℃ Pre-incubate with shaking for 5 minutes;
[0042] (2) Add 2μL of 1,3-dichloro-7-hydroxy-9,9-dimethyl-2(9H)-acridone benzoyl ester (final concentration 5μM) to start the reaction, 37°C Shaking incubation;
[0043] (3) After 30 minutes, add 200 μL of acetonitrile and shake vigorously to terminate the reaction;
[0044] (4) Detection of hydrolysate (λ ex =600nm, λ em =662nm) the fluorescence intensity value at the collection wavelength (see figure 2 ).
Embodiment 2
[0046] Drawing of carboxylesterase 2 quantitative standard curve
[0047] (1) Using 5mg / mL carboxylesterase 2 (CE2) standard solution, dilute with phosphate buffer into different concentrations of single enzyme working solution (0,0.5,1,2,3,4,5,6 ,7,8,9,10μg / mL), pre-incubate at 37℃ for 5min;
[0048] (2) Add 2 μL of 1,3-dichloro-7-hydroxy-9,9-dimethyl-2(9H)-acridone benzoyl ester (198 μL) to each solution sample (198 μL) The final concentration is 10μM), incubate with shaking at 37°C for 15min, add 200μL of acetonitrile and shake vigorously for 15 seconds to stop the reaction;
[0049] (3) Detection of hydrolysate DDAO (λ ex =600nm, λ em =662nm) The fluorescence intensity value at the acquisition wavelength, the fluorescence intensity value of DDAO is linearly fitted to the CE2 concentration, and the quantitative standard curve of human carboxylesterase 2 is established; the curve equation is Y=2521*X–72.24, The square of the correlation coefficient is 0.997 (see image 3 ).
Embodiment 3
[0051] Loperamide inhibition test
[0052] (1) Recombinantly express 198μL of CE2 single enzyme (2μg / mL), human liver microsomes (4μg / mL), and human intestinal microsomes (4μg / mL), pre-incubate at 37℃ for 5 minutes with shaking;
[0053] (2) Add 1 μL of CE2 positive inhibitor loperamide final concentration (0-100 μM) to the reaction system, and incubate for 5 minutes;
[0054] (3) Add 2μL of 1,3-dichloro-7-hydroxy-9,9-dimethyl-2(9H)-acridone benzoyl ester (final concentration 5μM) to start the reaction;
[0055] (3) After 15 minutes, add 200 μL of acetonitrile and shake vigorously to terminate the reaction;
[0056] (4) Perform fluorescence detection (λ ex =600nm, λ em =662nm), calculate the inhibitory intensity of CE2 based on the ratio of the fluorescence intensity of each group at 662nm to the DMSO group (see Figure 4 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com