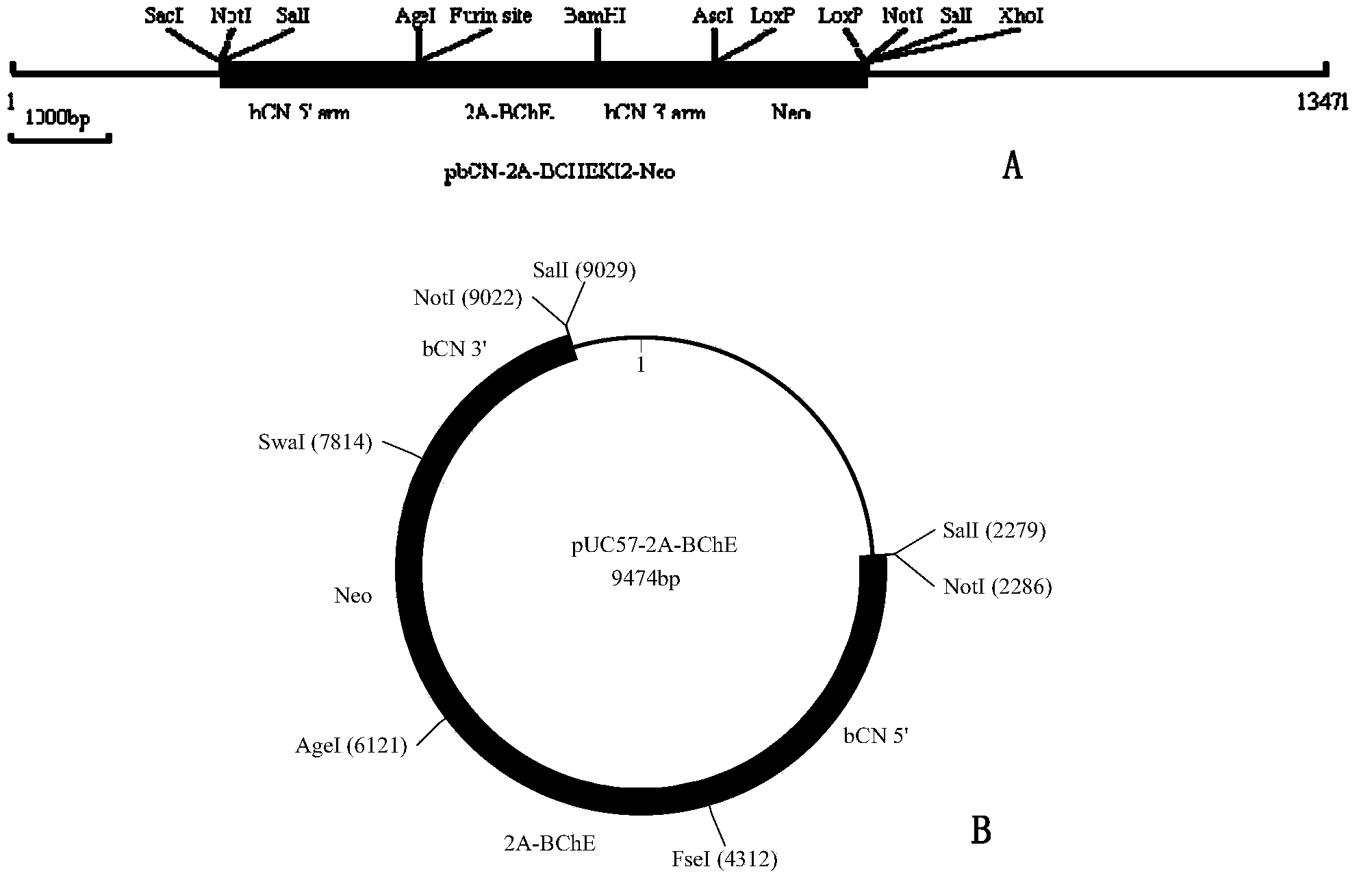
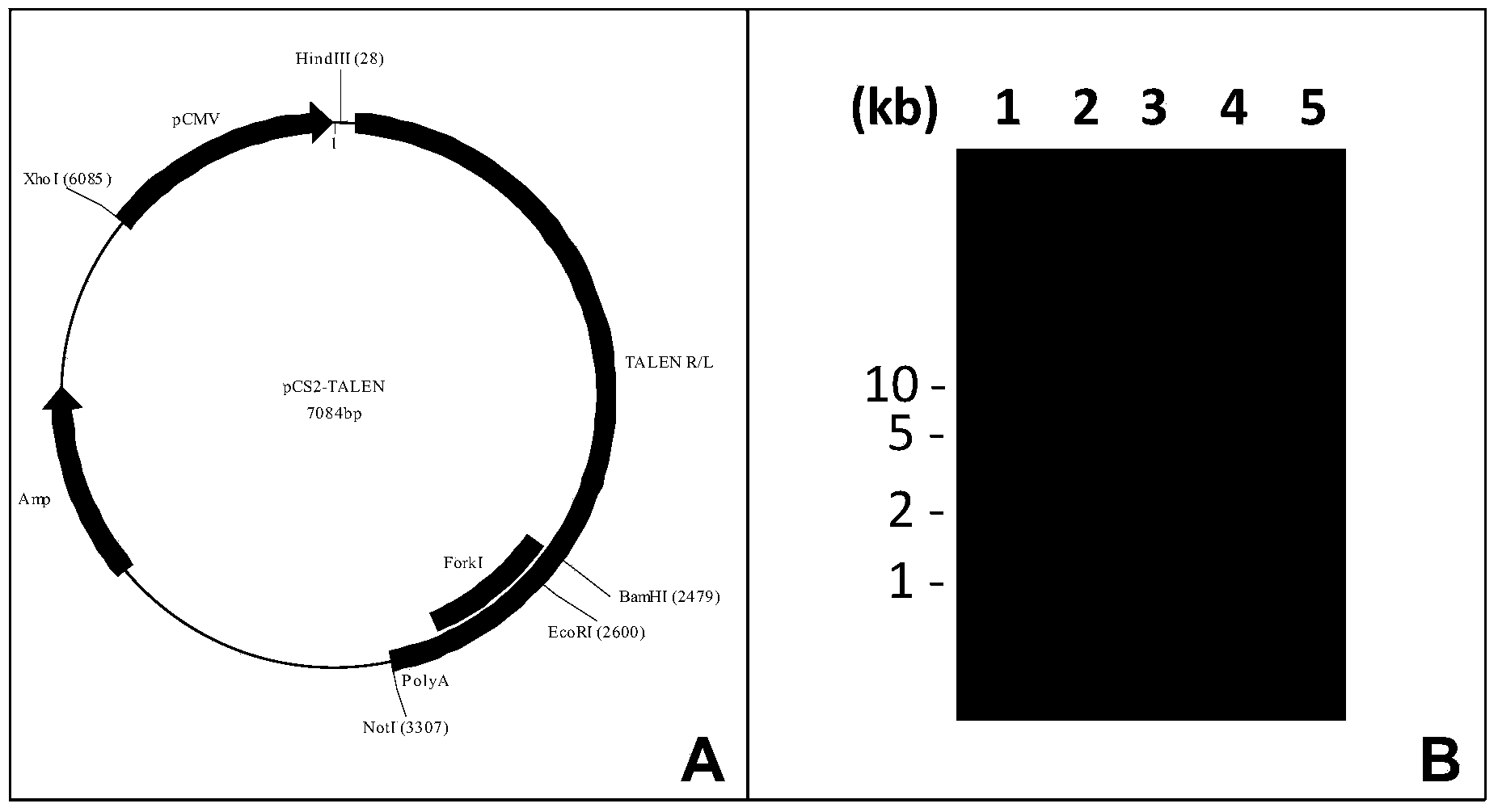
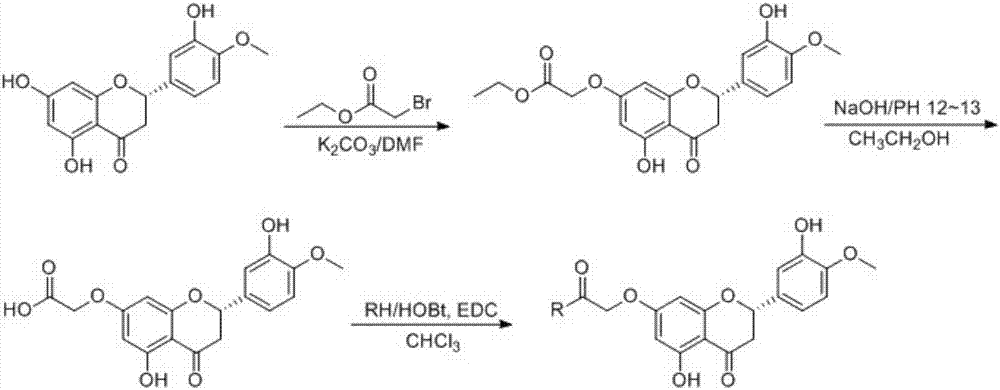
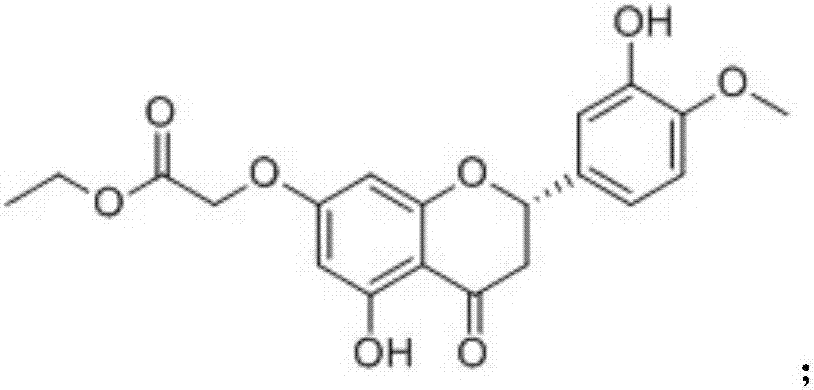
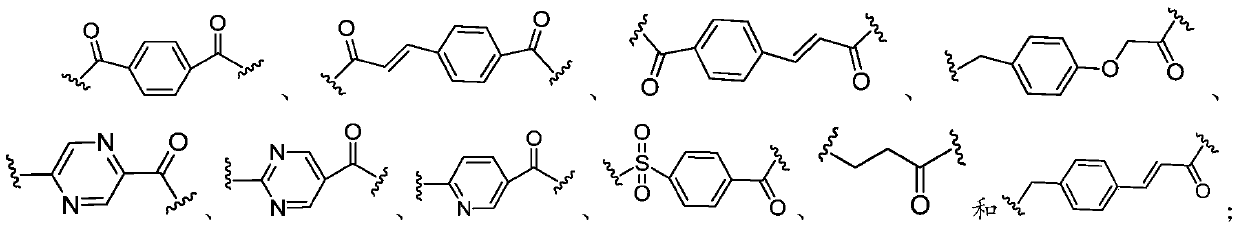
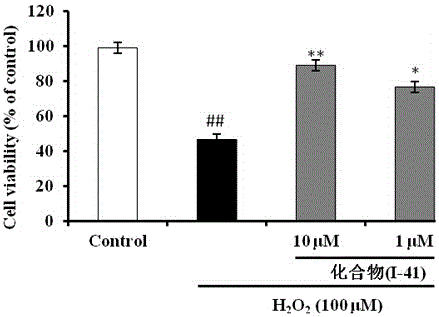
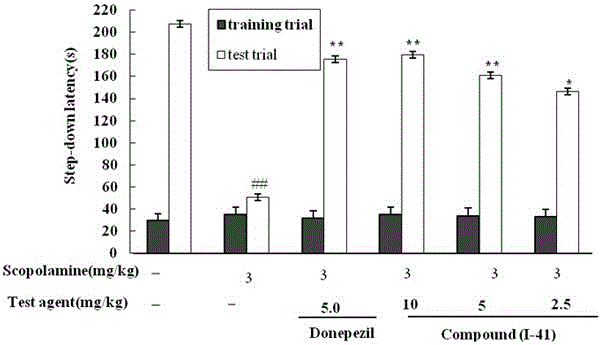
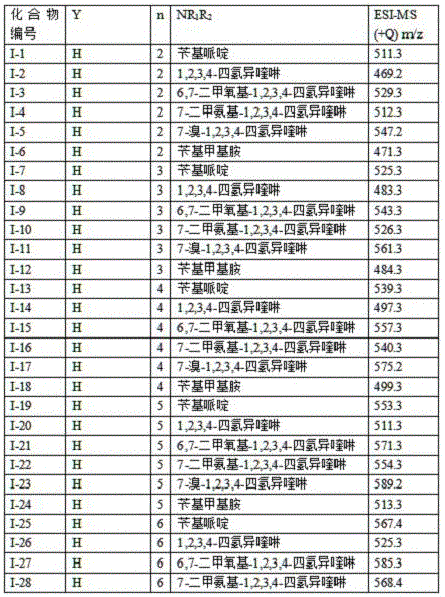
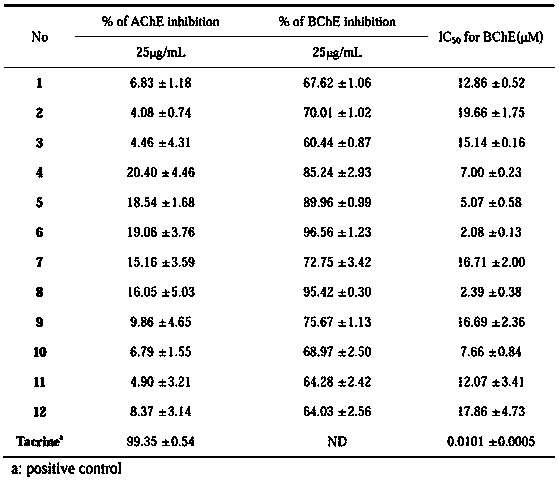
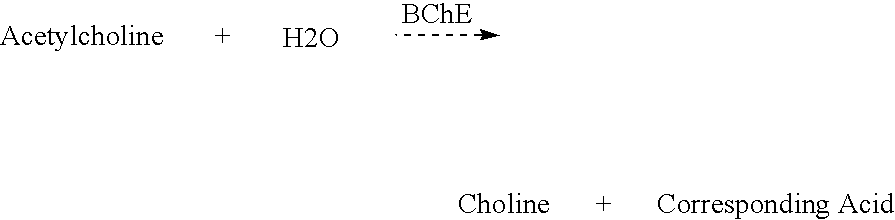
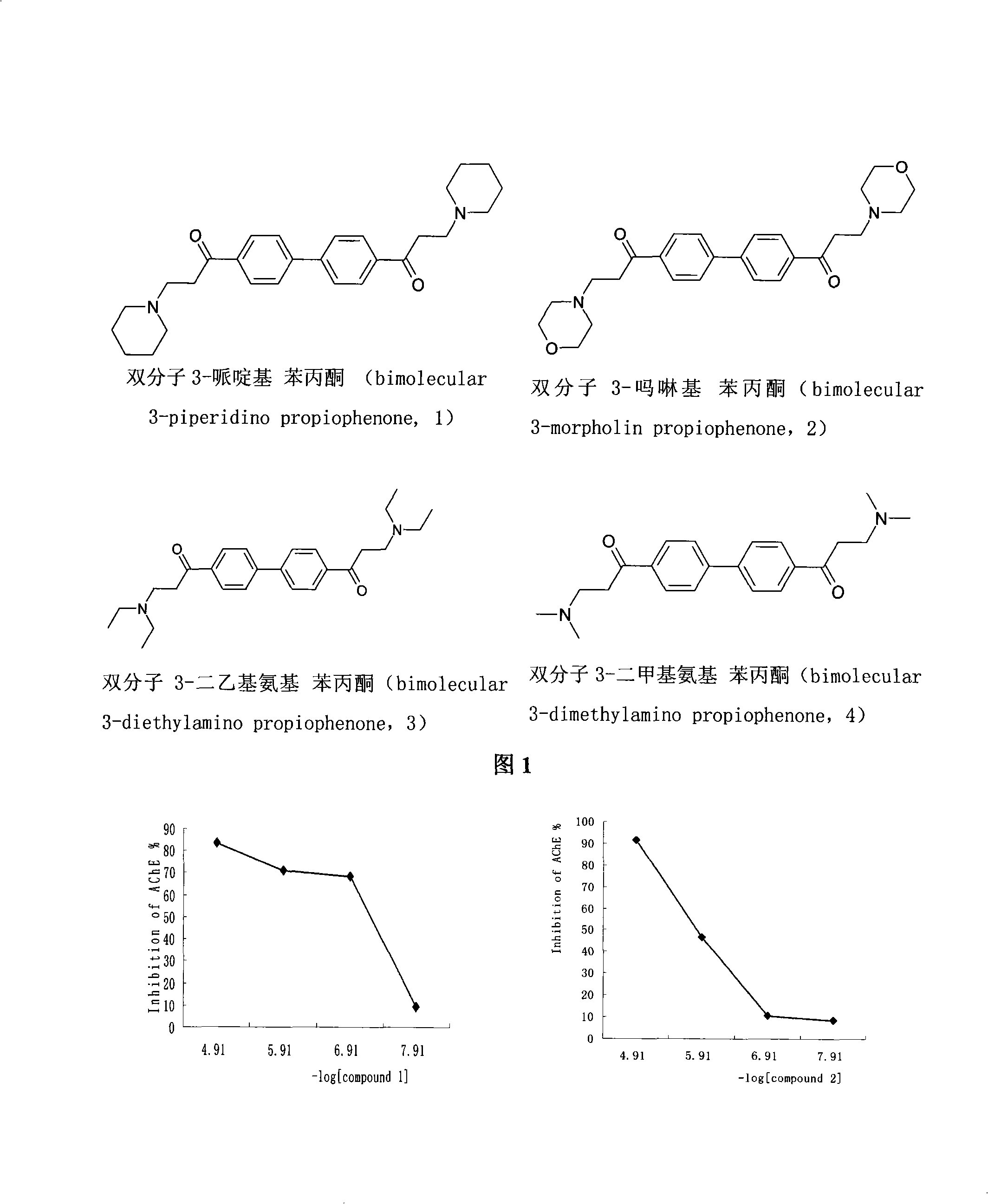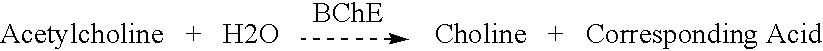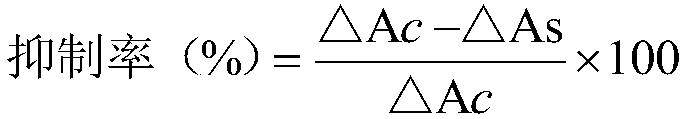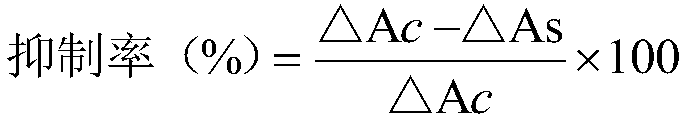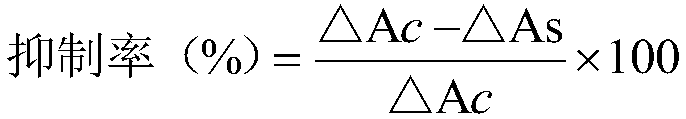Patents
Literature
147 results about "Butyrylcholinesterase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Butyrylcholinesterase (HGNC symbol BCHE; EC 3.1.1.8), also known as BChE, BuChE, pseudocholinesterase, or plasma (cholin)esterase, is a nonspecific cholinesterase enzyme that hydrolyses many different choline-based esters. In humans, it is made in the liver, found mainly in blood plasma, and encoded by the BCHE gene.
Production of hSA-linked butyrylcholinesterases in transgenic mammals
InactiveUS20060253913A1Promote formationImprove stabilityAnimal cellsVectorsMammalButyrylcholinesterase
The present invention provides methods for the large-scale production of recombinant butyrylcholinesterase fused to human serum albumin in cell culture, and in the milk and / or urine of transgenic mammals. The recombinant butyrylcholinesterase-albumin fusion protein of this invention can be used to treat and / or prevent organophosphate pesticide poisoning, nerve gas poisoning, cocaine intoxication, and succinylcholine-induced apnea.
Owner:PHARMATHENE
Large-Scale Production of Human Serum Butyrylcholinesterase as a Bioscavenger
InactiveUS20070184045A1Treating and preventing and inhibiting toxicityPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesCholinesteraseButyrylcholinesterase
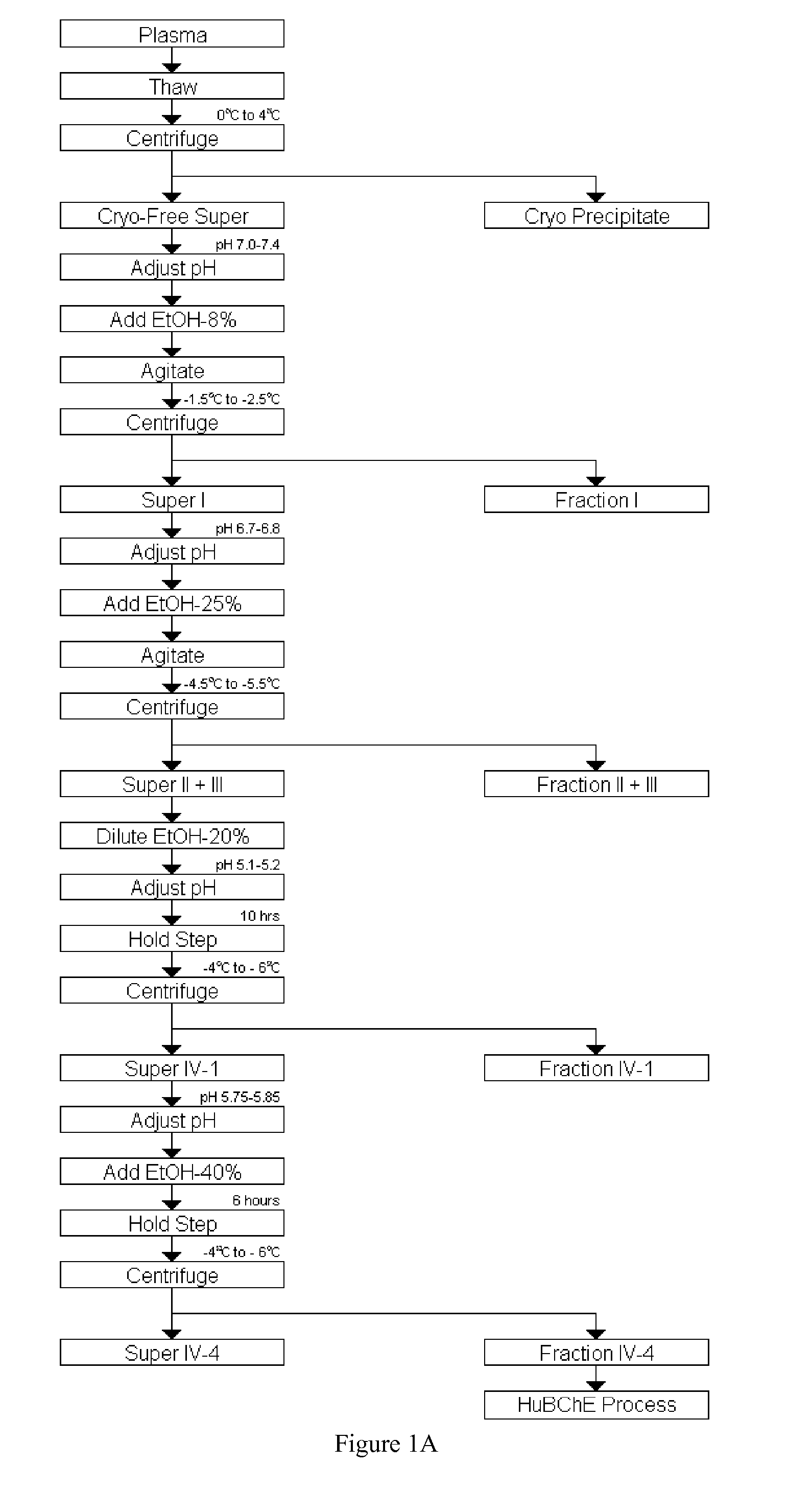
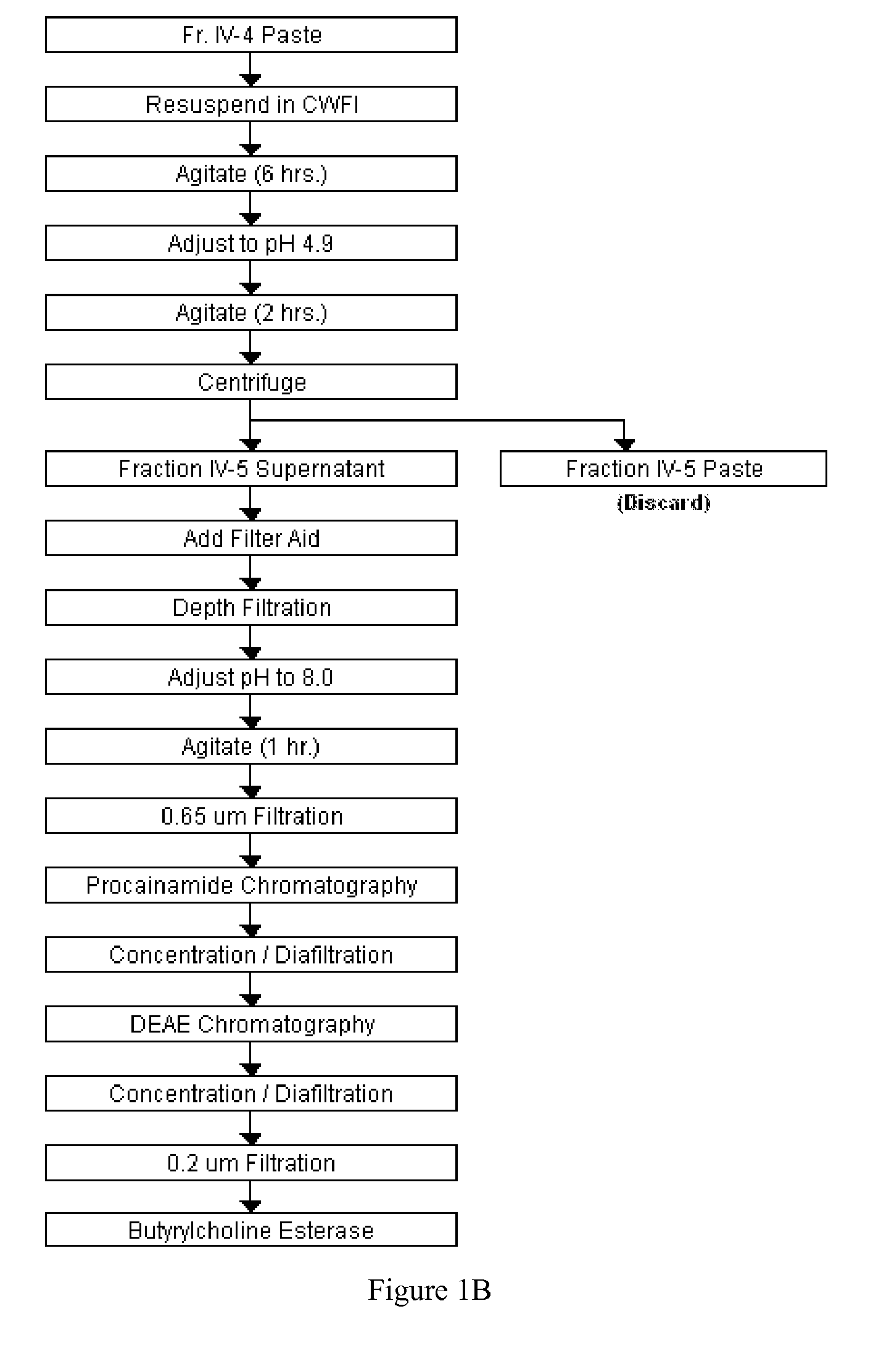
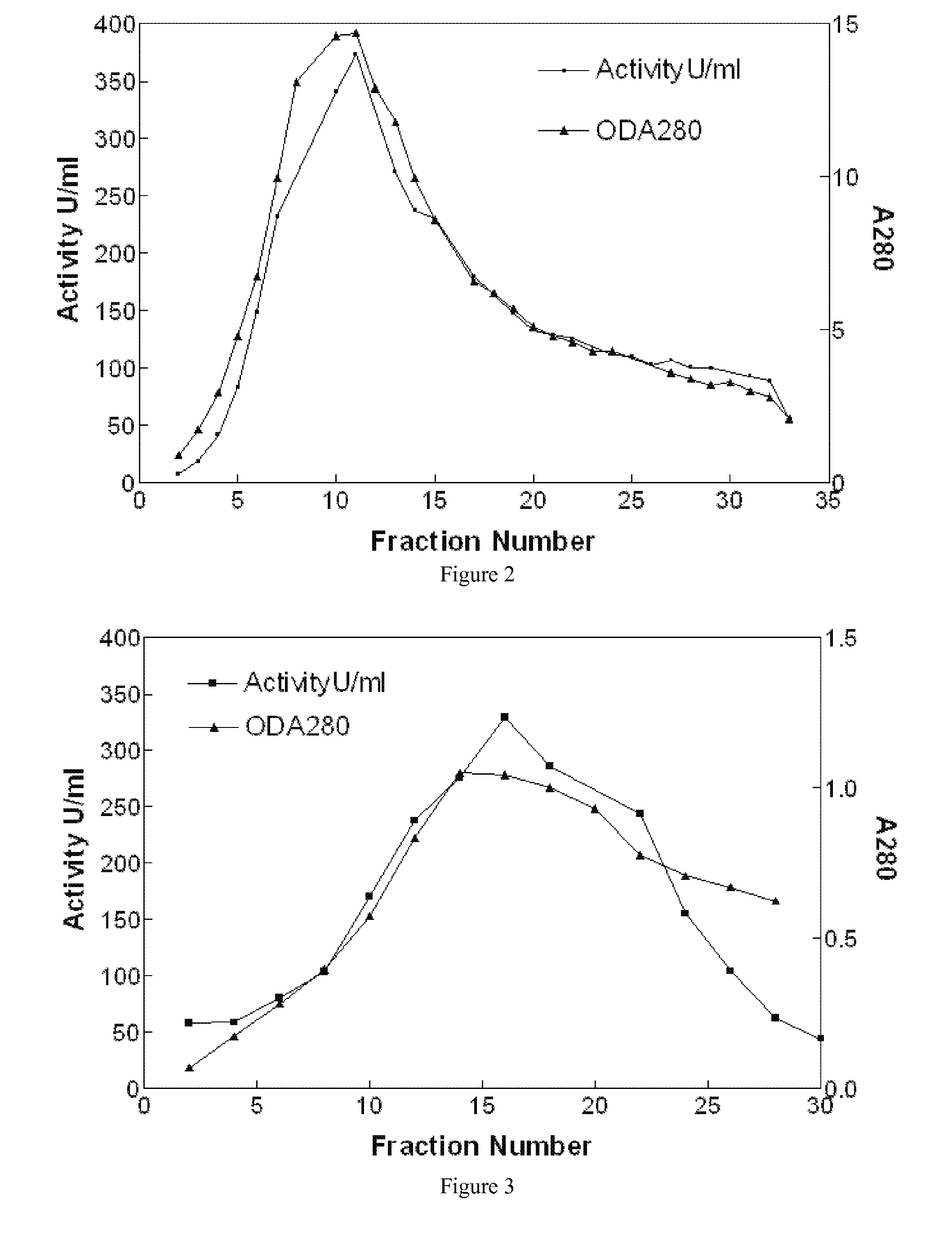
Disclosed herein are methods for the large-scale preparation of human butyrylcholinesterase (HuBChE) preparations from Cohn Fraction IV-4. As disclosed, the methods provide HuBChE preparations that are about 99% or more pure with recovery yields of about 60%. Also disclosed are the pharmacokinetics, safety and toxicity, stability and efficacy of the HuBChE preparations.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
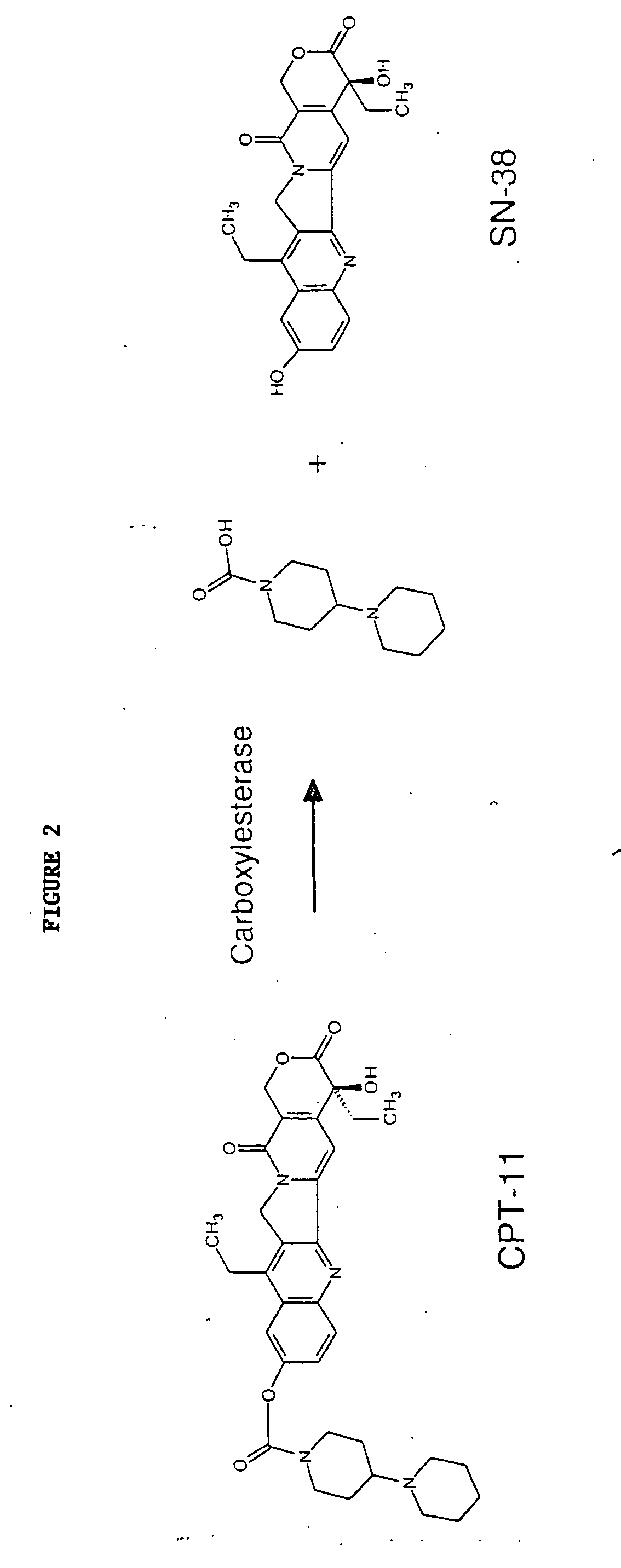
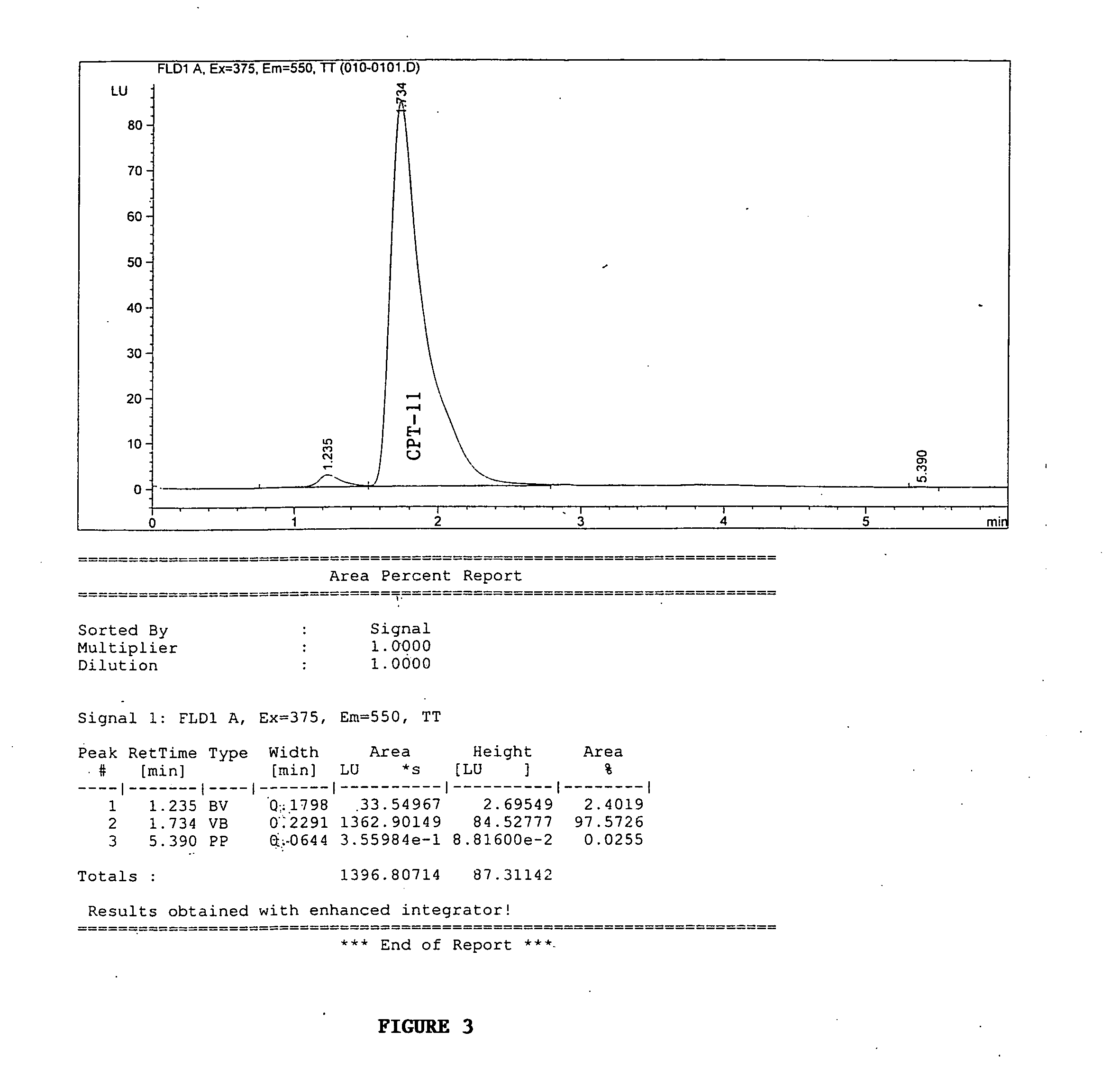
Butyrylcholinesterase variants that alter the activity of chemotherapeutic agents
The invention provides a butyrylcholinesterase variant having the amino acid sequence selected from SEQ ID NOS: 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 40, 42, 44, 46, 48, 50, 52, 54, 56, 58, 60, 62, 64, 66, 68, 70, 72, 74, 76, 78, 80, 82, 84, 86, 88, 90, 92, 94, 96, 98, 100, 102, 104, 106, 108, 110, 112, 114, 116, 118, 120, 122, 124, 126, 128, 130, 132, 134, 136, 138, 140, 142, 144, 146, 148, 150, 152, 154, 156, 158, 160, 162, 164, 166, 168, 170, 172, 174, 176, 178, 180, 182, 184, 186, 188, 190, 192, 194, and 196, or functional fragment thereof. In addition, the invention provides a method of converting a camptothecin derivative to a topoisomerase inhibitor by contacting the camptothecin derivative with a butyrylcholinesterase variant selected from SEQ ID NOS: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 40, 42, 44, 46, 48, 50, 52, 54, 56, 58, 60, 62, 64, 66, 68, 70, 72, 74, 76, 78, 80, 82, 84, 86, 88, 90, 92, 94, 96, 98, 100, 102, 104, 106, 108, 110, 112, 114, 116, 118, 120, 122, 124, 126, 128, 130, 132, 134, 136, 138, 140, 142, 144, 146, 148, 150, 152, 154, 156, 158, 160, 162, 164, 166, 168, 170, 172, 174, 176, 178, 180, 182, 184, 186, 188, 190, 192, 194, and 196, or functional fragment thereof, under conditions that allow conversion of a camptothecin derivative to a topoisomerase inhibitor. Further, the invention provides a method of treating cancer by administering to an individual an effective amount of a butyrylcholinesterase variant selected from SEQ ID NO: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 40, 42, 44, 46, 48, 50, 52, 54, 56, 58, 60, 62, 64, 66, 68, 70, 72, 74, 76, 78, 80, 82, 84, 86, 88, 90, 92, 94, 96, 98, 100, 102, 104, 106, 108, 110, 112, 114, 116, 118, 120, 122, 124, 126, 128, 130, 132, 134, 136, 138, 140, 142, 144, 146, 148, 150, 152, 154, 156, 158, 160, 162, 164, 166, 168, 170, 172, 174, 176, 178, 180, 182, 184, 186, 188, 190, 192, 194, and 196, or functional fragment thereof, exhibiting increased capability to convert a camptothecin derivative to a topoisomerase inhibitor compared to butyrylcholinesterase.
Owner:APPLIED MOLECULAR EVOLUTION
Enzyme conjugates for use as detoxifying agents
Disclosed are detoxifying enzyme conjugates, including conjugates of variants of such detoxifying enzymes. The detoxifying enzymes are preferably chlolinesterases, and more preferably, butyrylcholinesterase. Also disclosed are methods of making and using such conjugates.
Owner:BOLDER BIOTECH
Uses of chemically-modified cholinesterases for detoxification of organophosphorous compounds
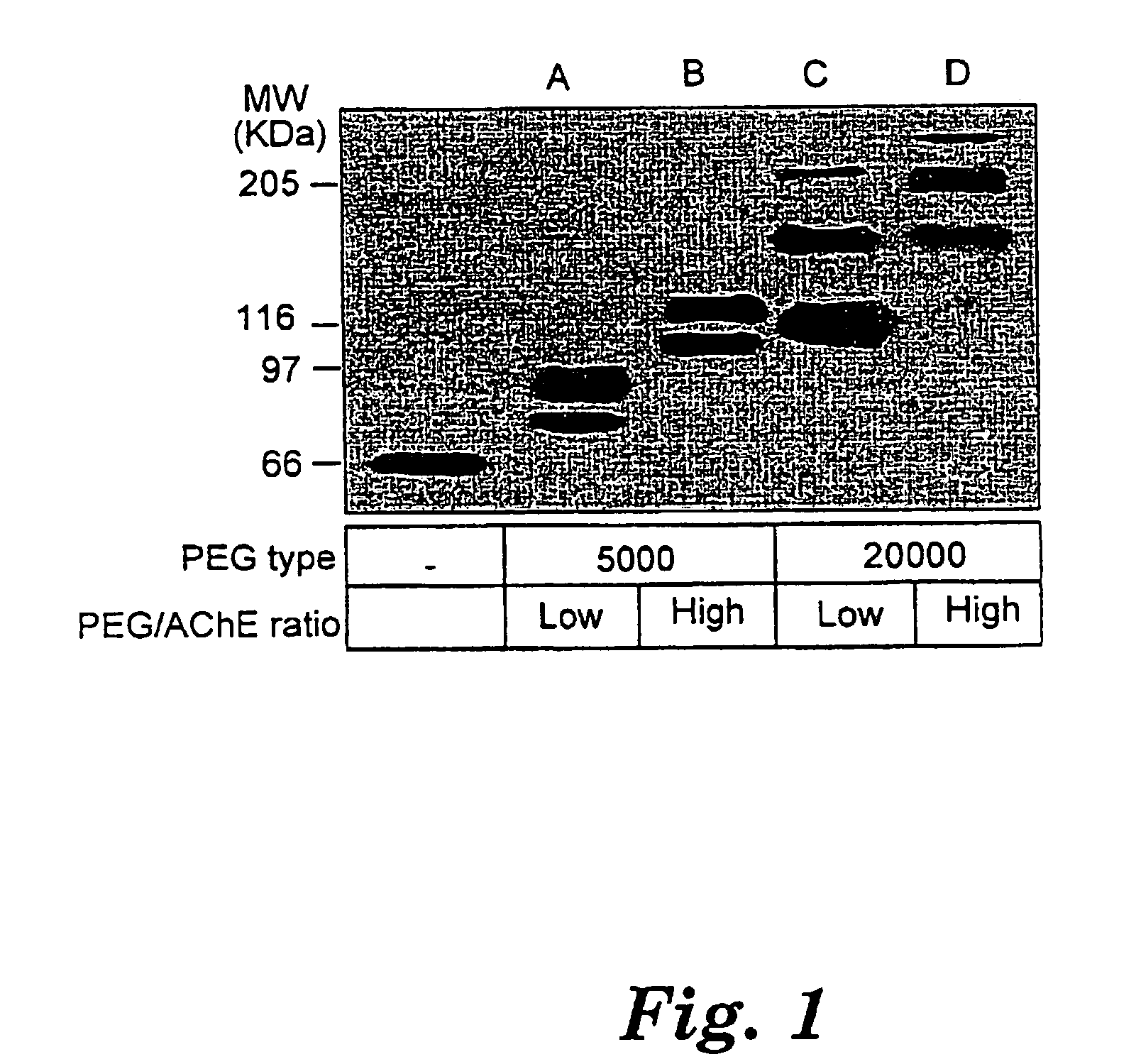
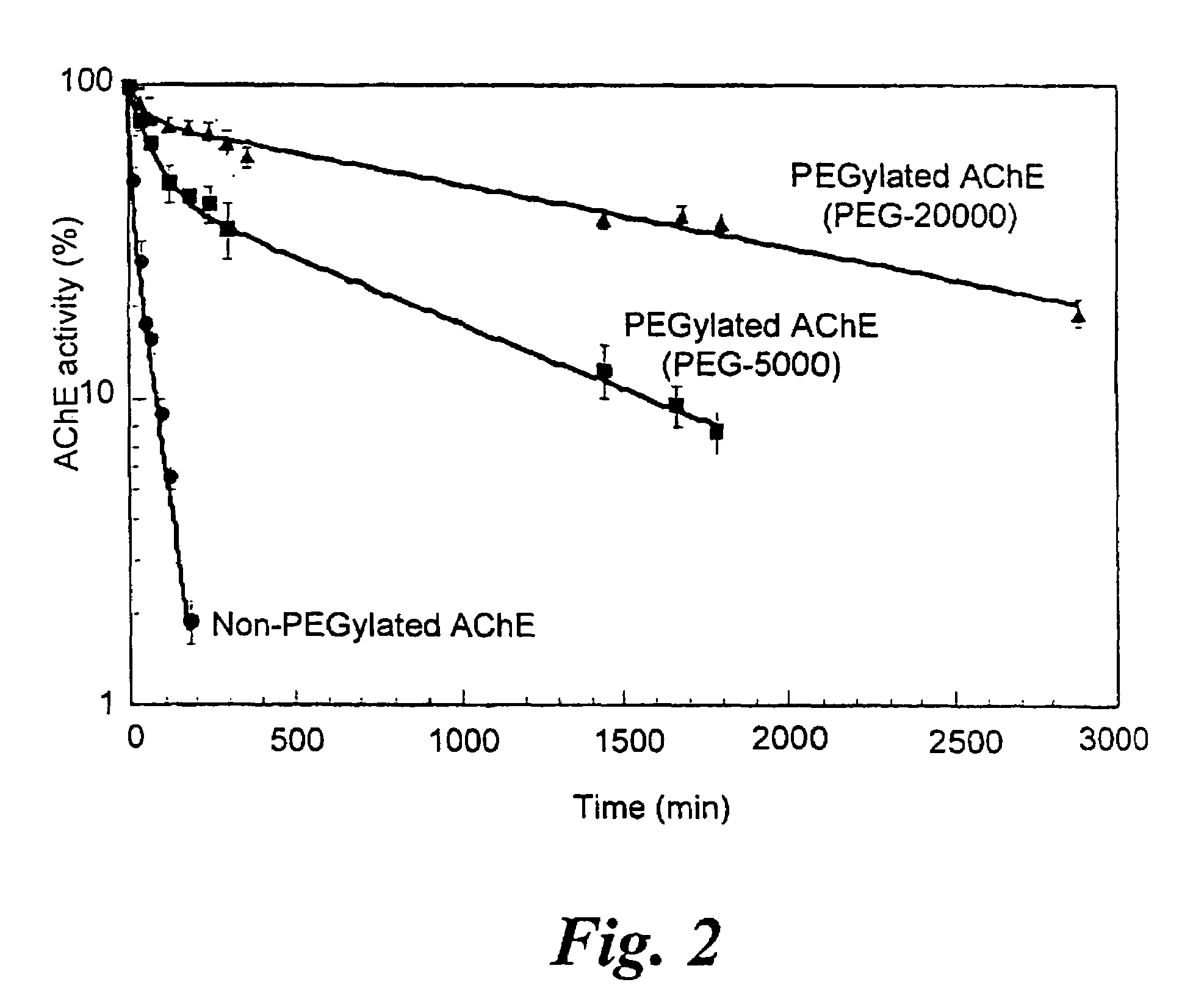
InactiveUS7572764B2Prolonged Circulatory Half-LifeBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCholinesteraseMammal
A circulatory long-lived cholinesterase (ChE) protein, such as acetylcholinesterase (AChE) or butyrylcholinesterase (BChE), which is a ChE protein modified with a non-antigenic polymer. The ChE may be AChE, such as native AChE of mammalian origin or of non-mammalian origin, or recombinant AChE. The recombinant AChE may be mutated at one or more amino-acid residues. The BChE may be native BChE of mammalian origin or of non-mammalian origin.
Owner:STATE OF ISRAEL MINIST OF AGRI & RURAL DEV AGRI RES ORG (A R O) (VOLCANI CENT)
Butyrylcholinesterase Variants that Alter the Activity of Chemotherapeutic Agents
InactiveUS20080213281A1Sugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsButyrylcholinesteraseTopoisomerase inhibitor
The invention provides a butyrylchinesterase variant, a method of converting a camptothecin derivative to a topoisomerase inhibitor by contacting the camptothecin derivative with a butyrylcholinesterase variant and a method of treating cancer by administering to an individual an effective amount a butyrylcholinesterase variant exhibiting increased capability to convert a camptothecin derivative to a topoisomerase inhibitor compared to butyrylcholinesterase.
Owner:APPLIED MOLECULAR EVOLUTION
Production and use of human butyrylcholinesterase
InactiveUS20090274679A1Peptide/protein ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesCountermeasureButyrylcholinesterase
The present invention concerns the production of human butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE) in transgenic plants and use of the derived BuChE as effective countermeasures against toxic agents such as pesticides, toxins, certain drugs and non-conventional warfare agents, as well as treatments for diseases and conditions associated with depressed cholinesterase levels.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
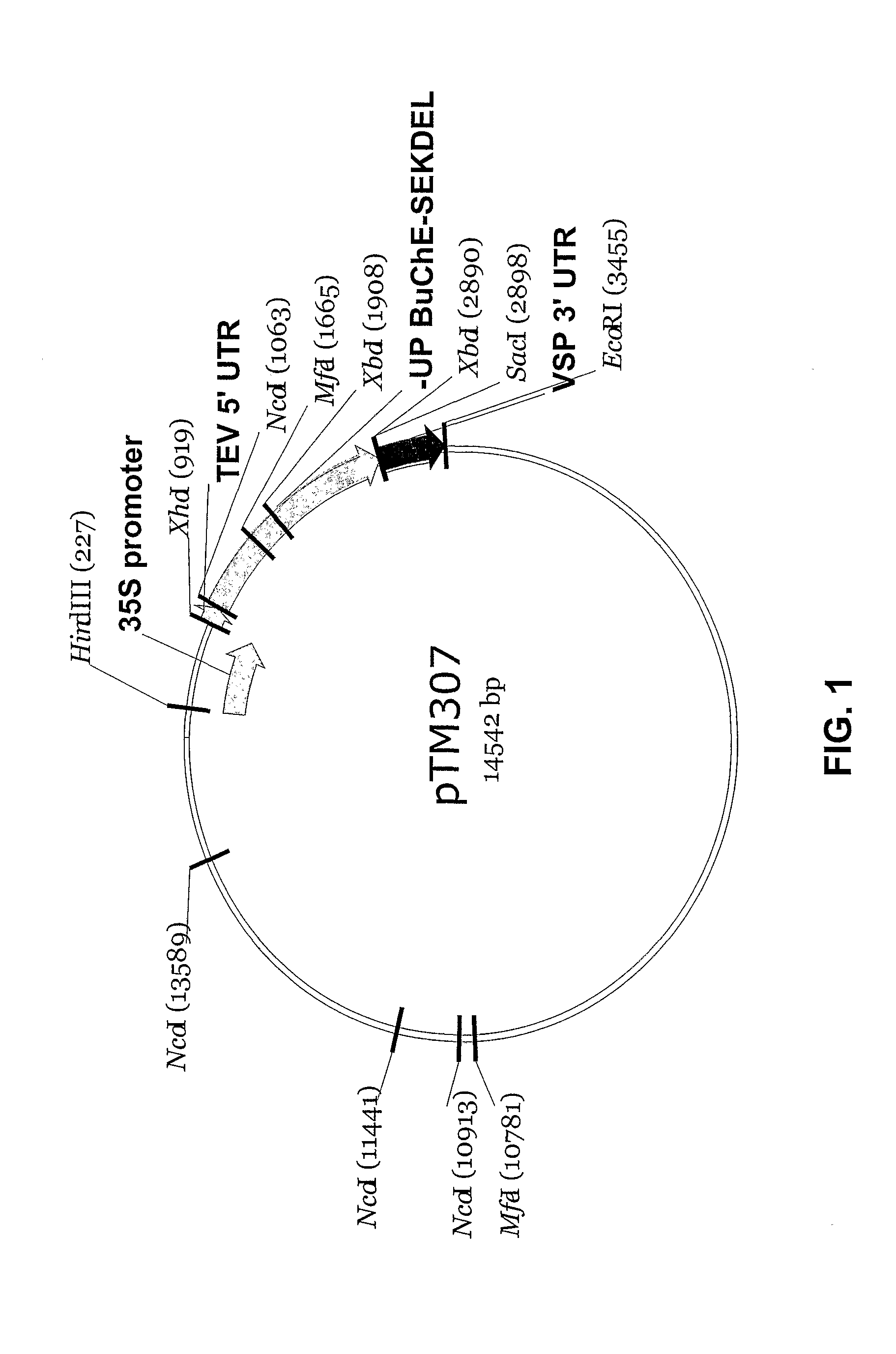
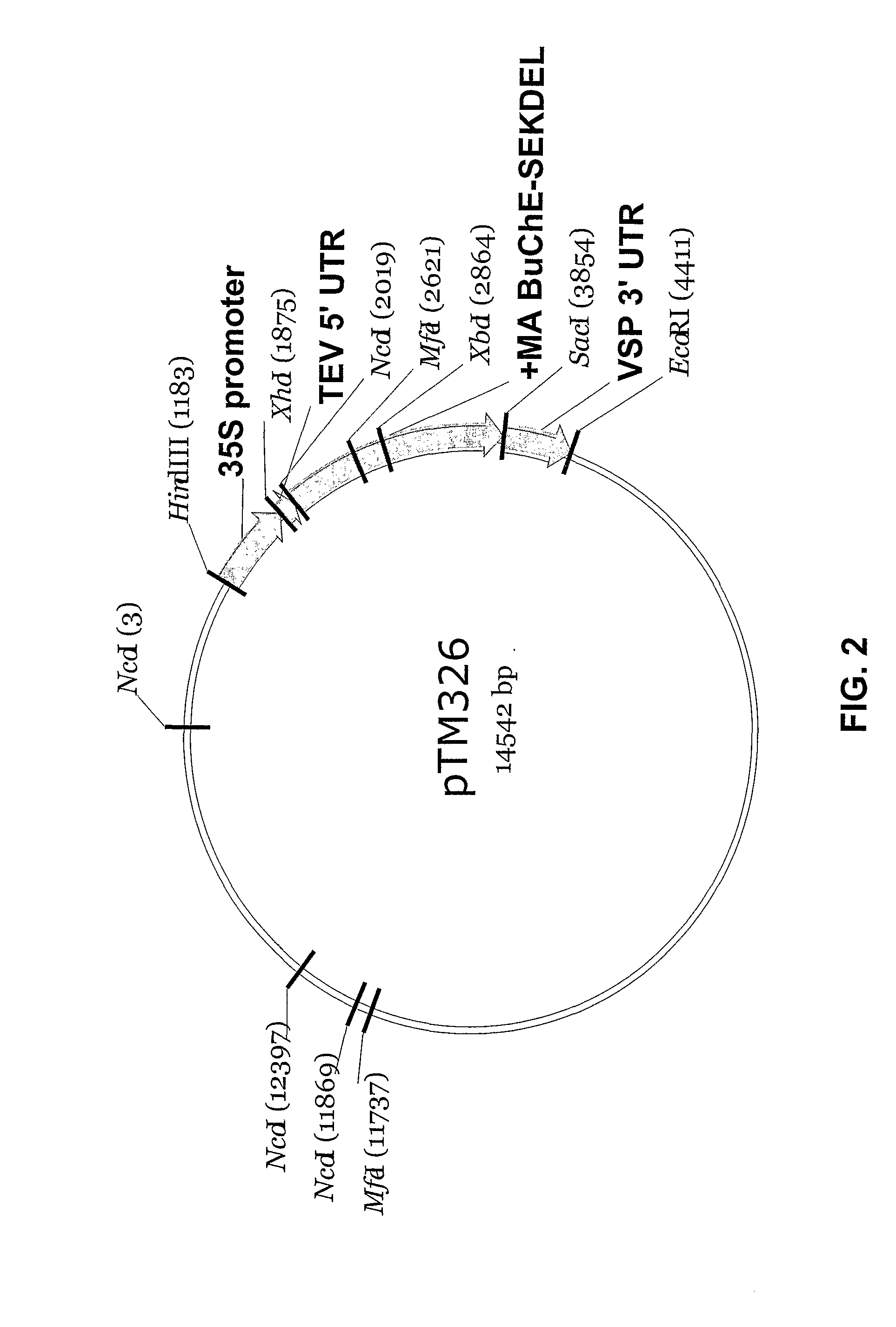
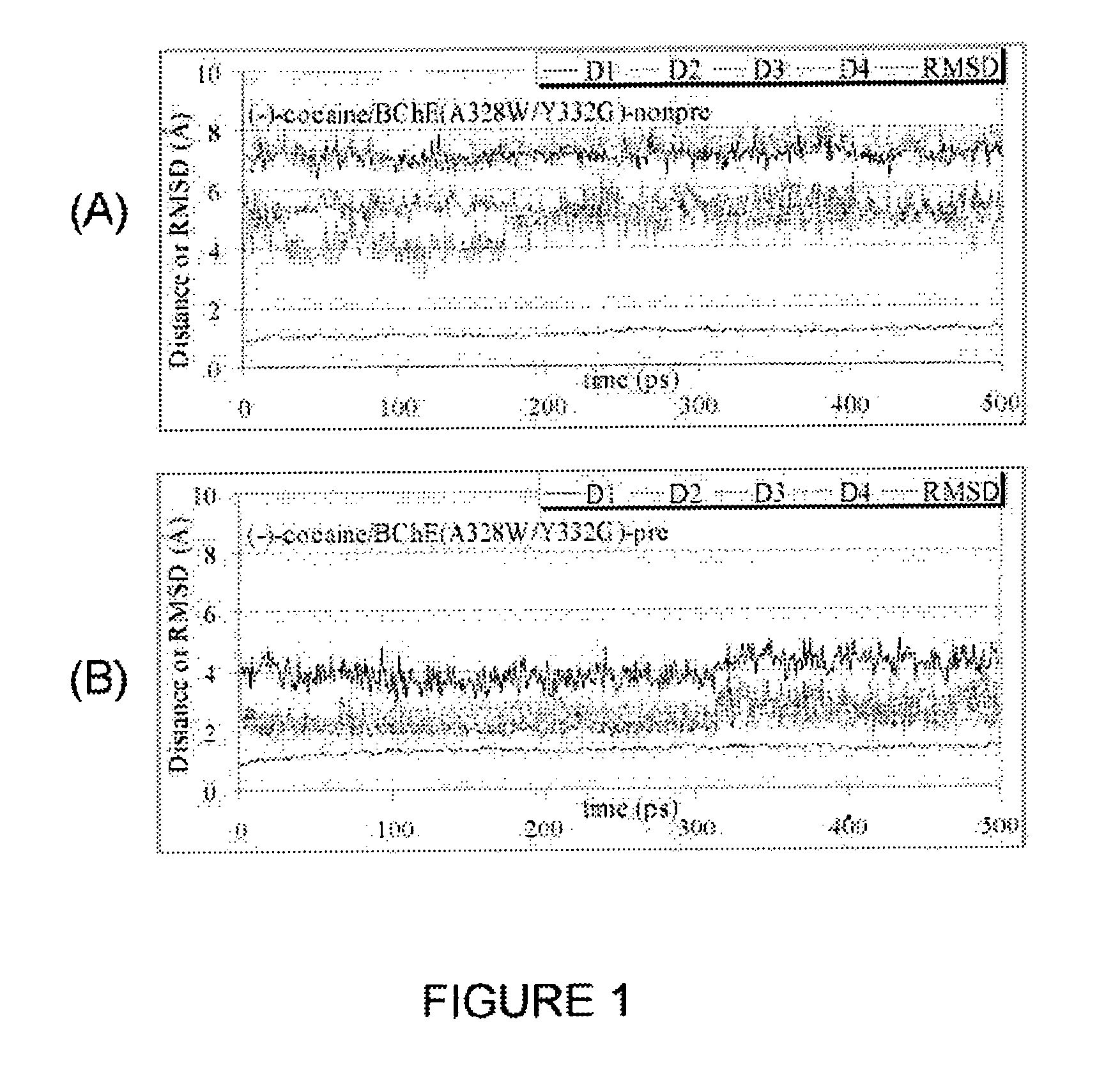
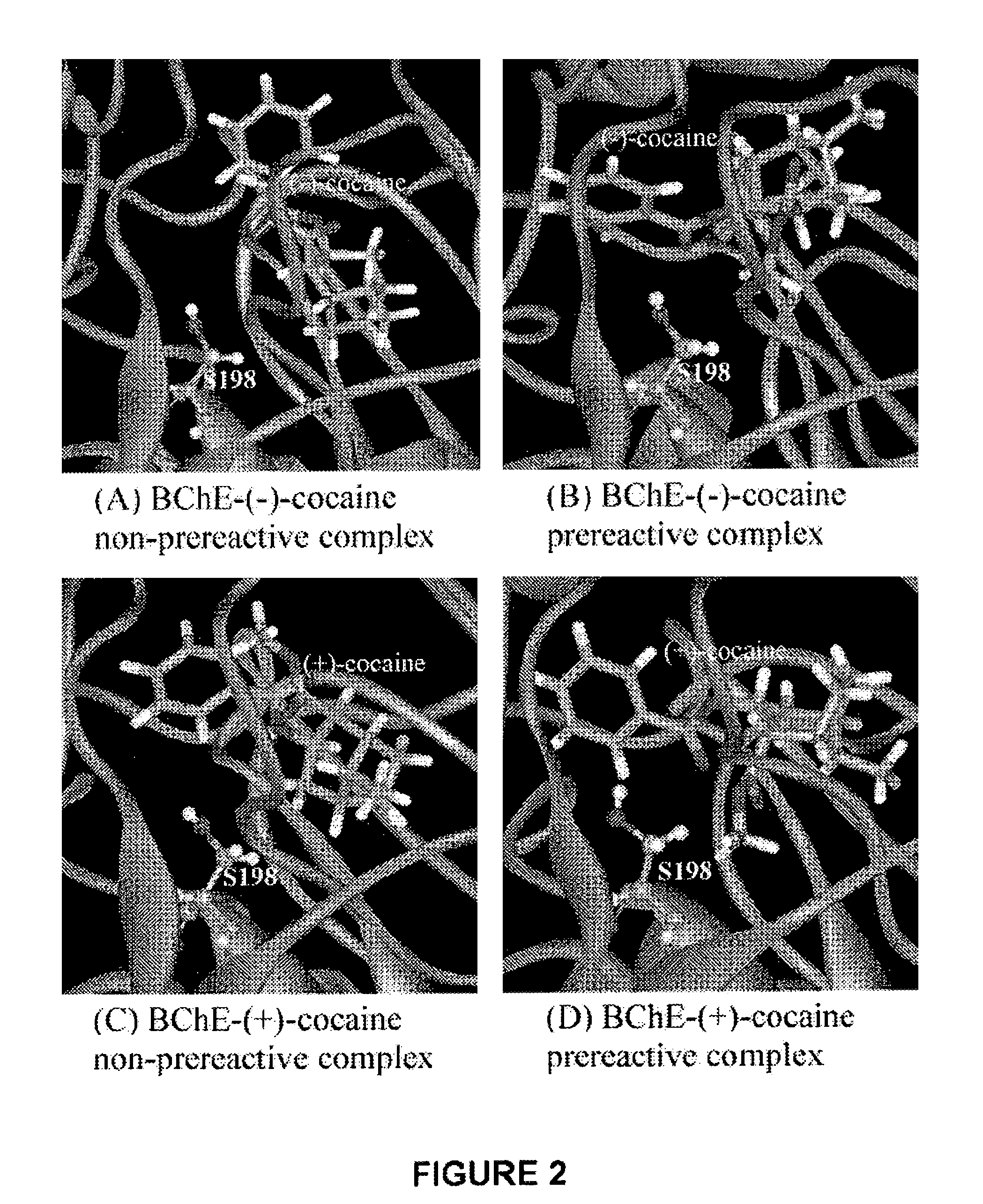
High-activity mutants of butyrylcholinesterase for cocaine hydrolysis and method of generating the same
ActiveUS7438904B1High catalytic efficiencyHigh catalytic activityHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsButyrylcholinesteraseCatalytic efficiency
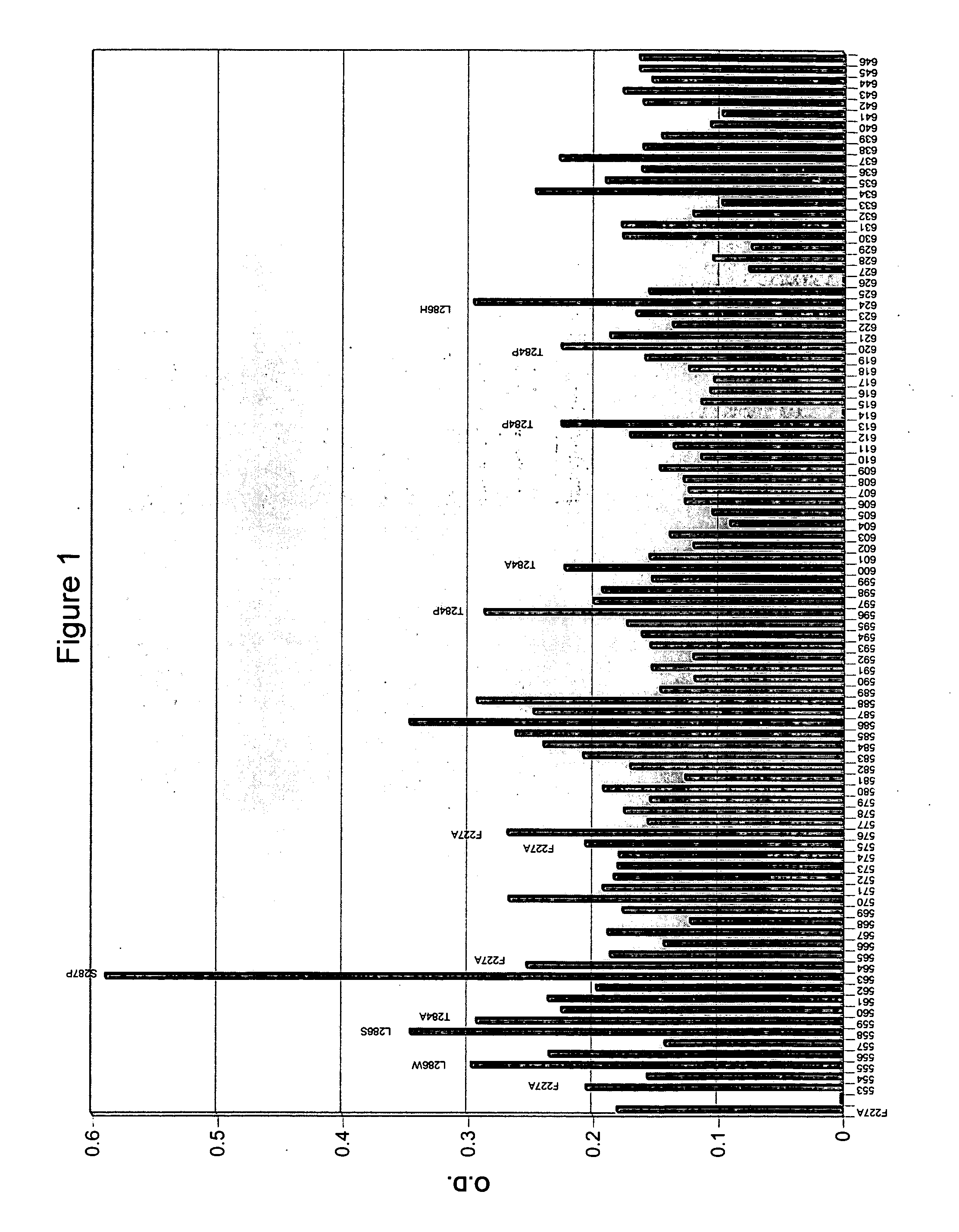
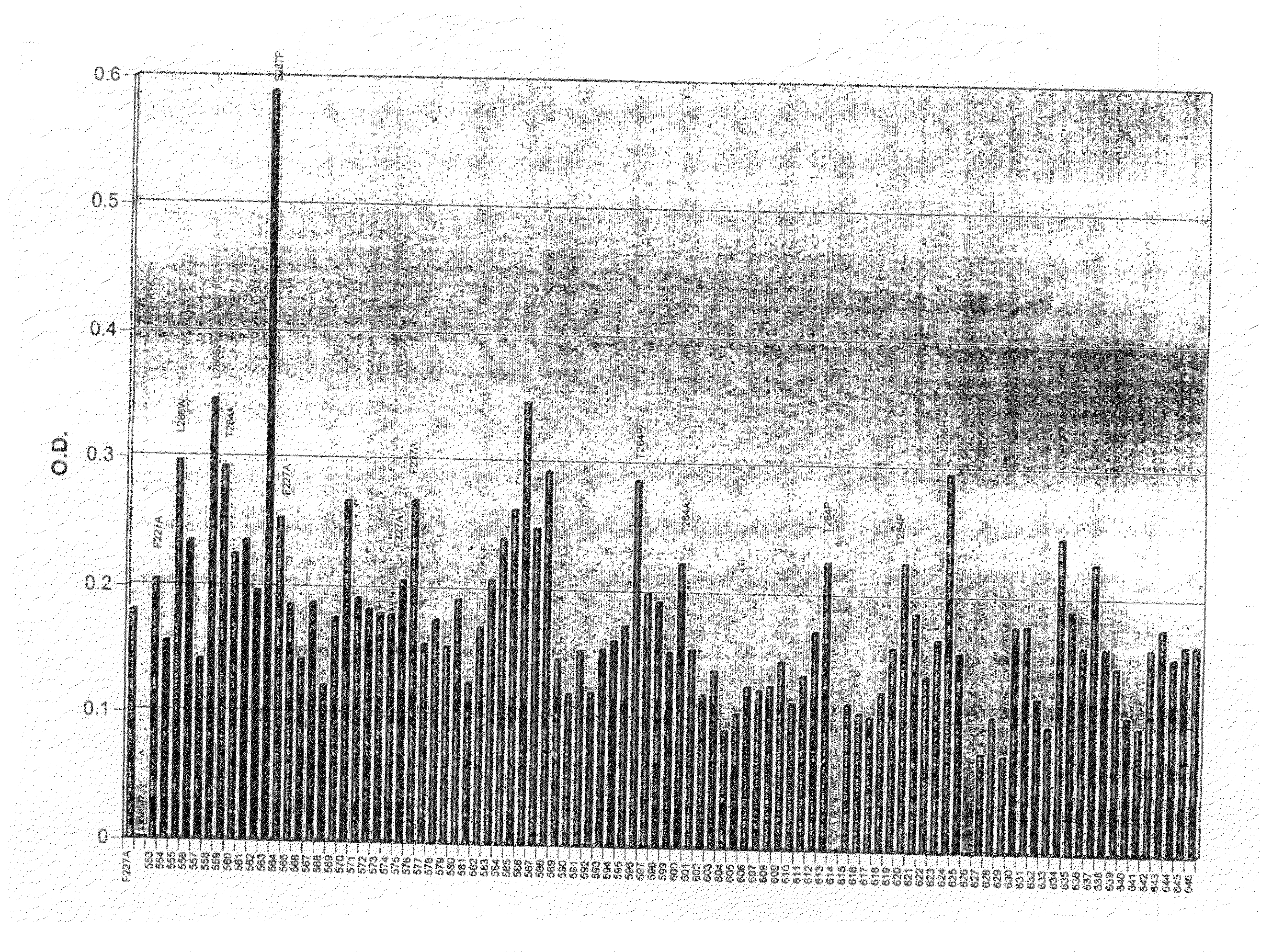
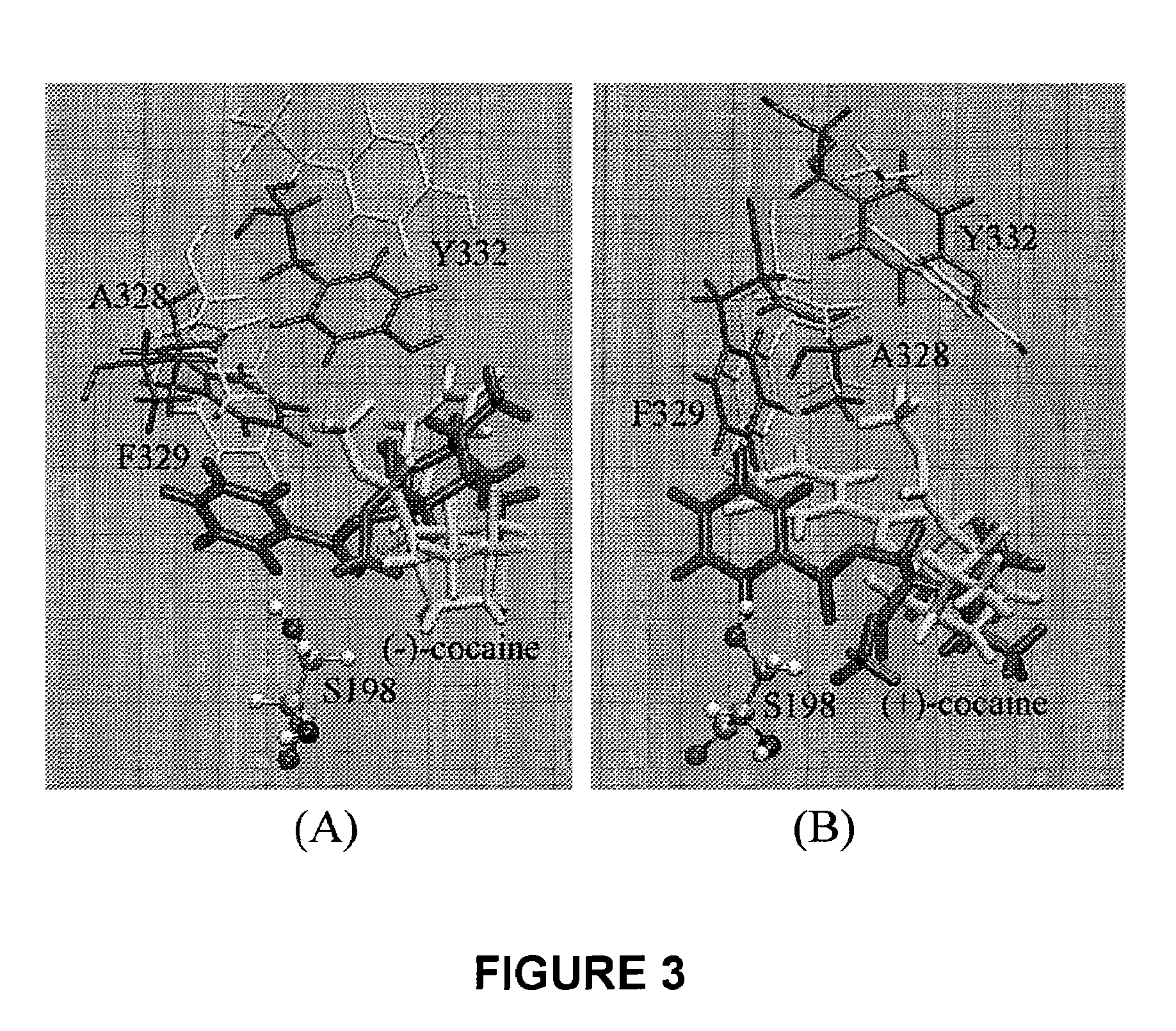
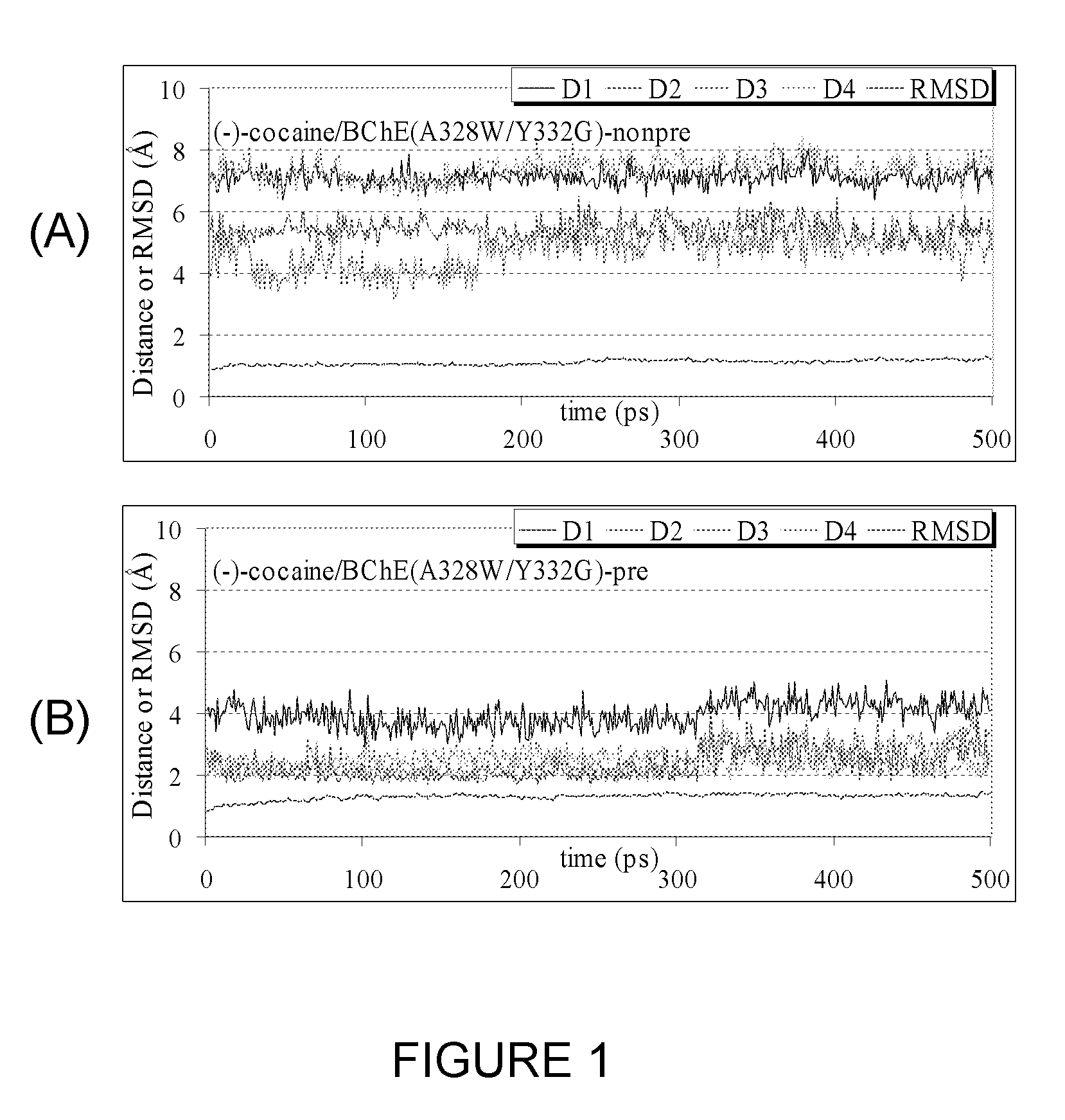
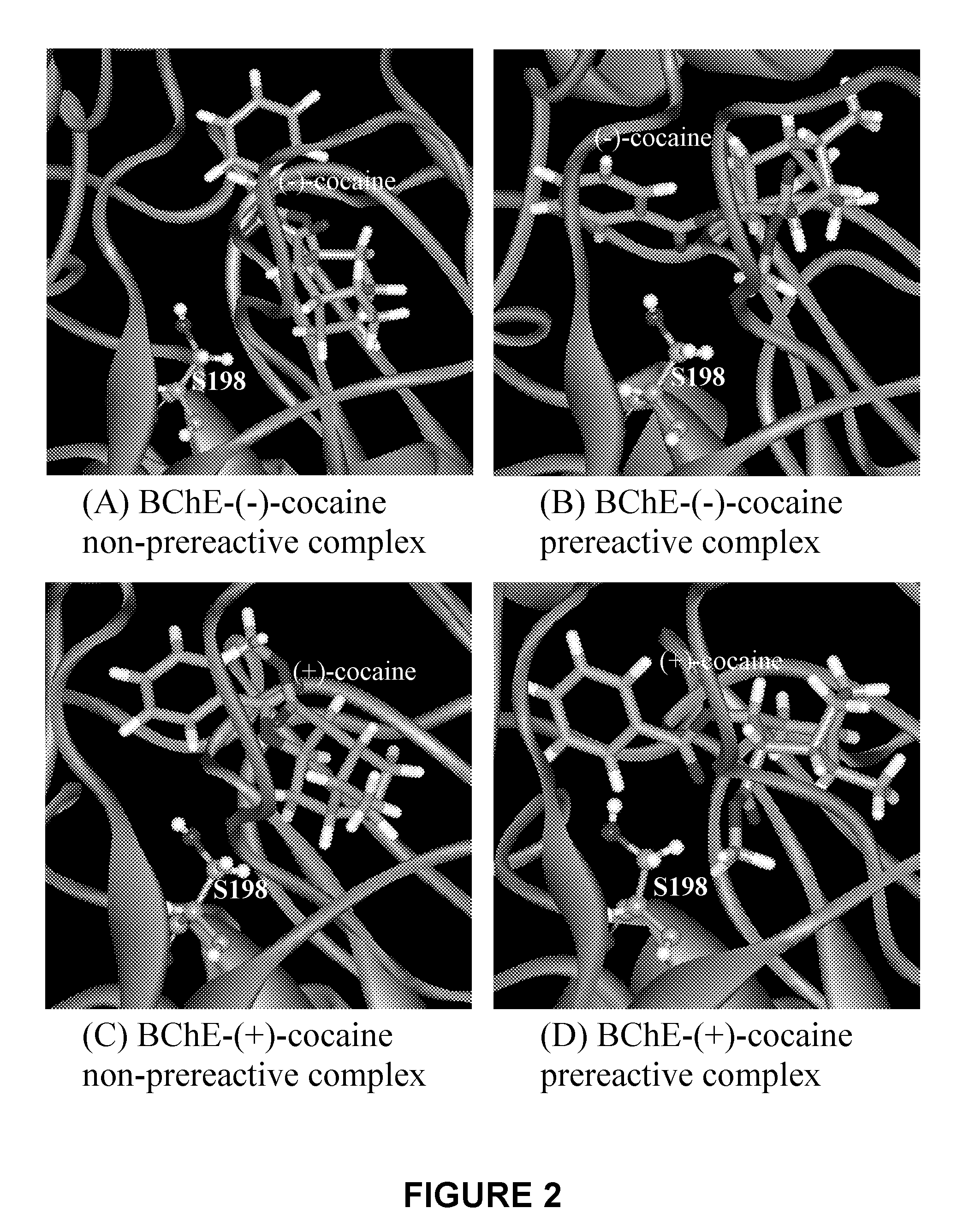
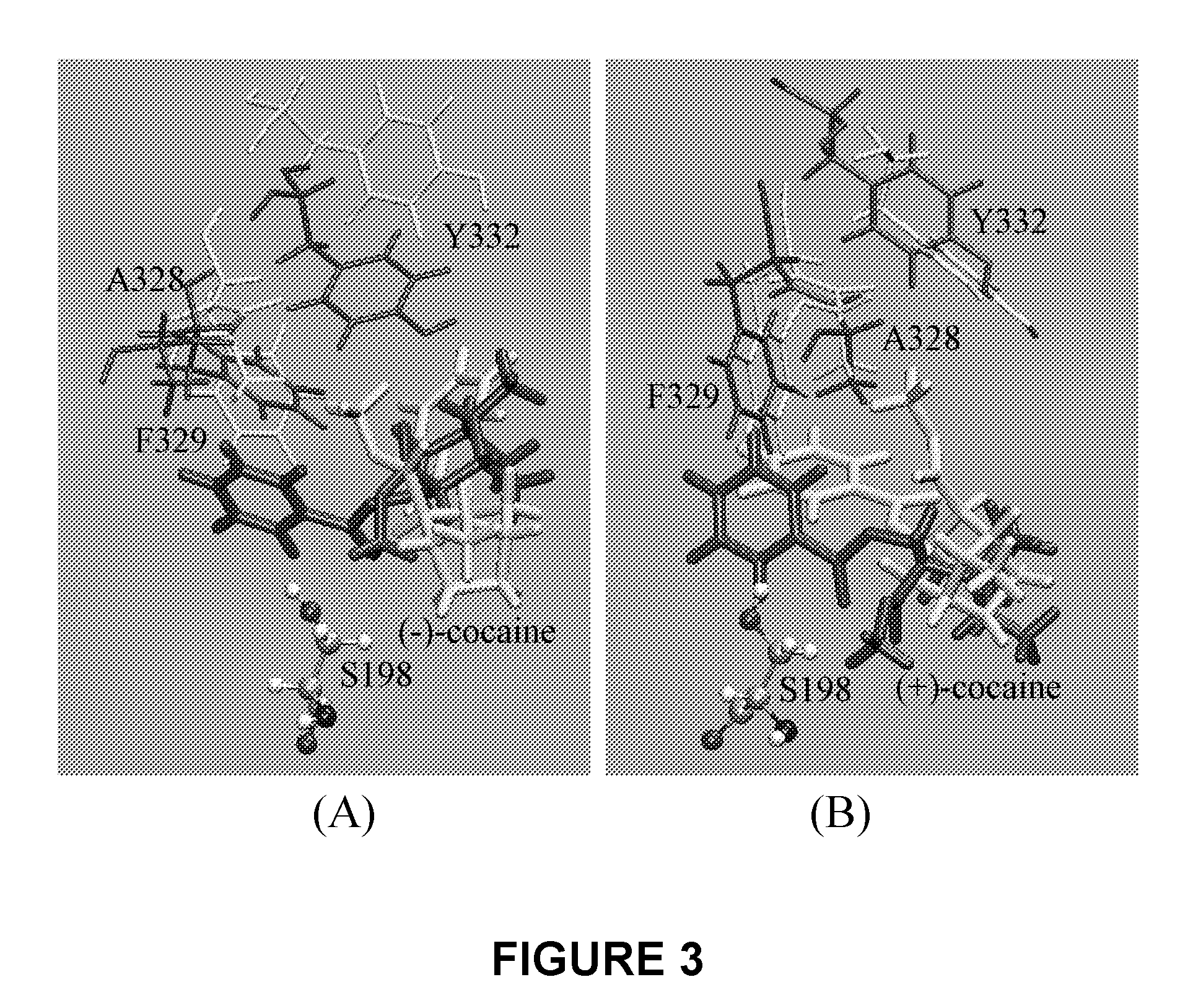
A novel computational method and generation of mutant butyrylcholinesterase for cocaine hydrolysis is provided. The method includes molecular modeling a possible BChE mutant and conducting molecular dynamics simulations and hybrid quantum mechanical / molecular mechanical calculations thereby providing a screening method of possible BChE mutants by predicting which mutant will lead to a more stable transition state for a rate determining step. Site-directed mutagenesis, protein expression, and protein activity is conducted for mutants determined computationally as being good candidates for possible BChE mutants, i.e., ones predicted to have higher catalytic efficiency as compared with wild-type BChE. In addition, mutants A199S / A328W / Y332G, A199S / F227A / A328W / Y332G, A199S / S287G / A328W / Y332G, A199S / F227A / S287G / A328W / Y332G, and A199S / F227A / S287G / A328W / E441D all have enhanced catalytic efficiency for (−)-cocaine compared with wild-type BChE.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Preparation of polyphenol oxidase biosensor and detection of polyphenol oxidase biosensor to pesticide residues
InactiveCN103421878ALow costEasy to makeMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesPesticide residueButyrylcholinesterase
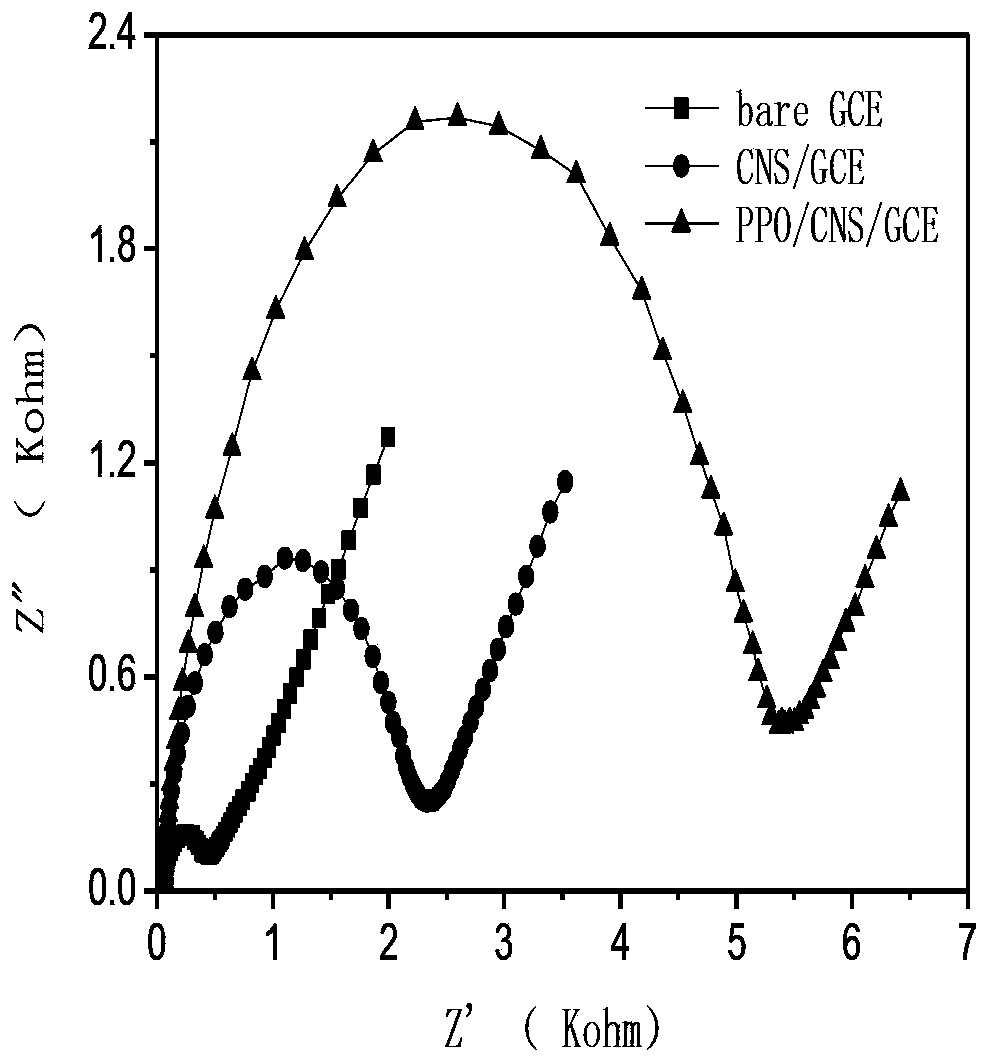
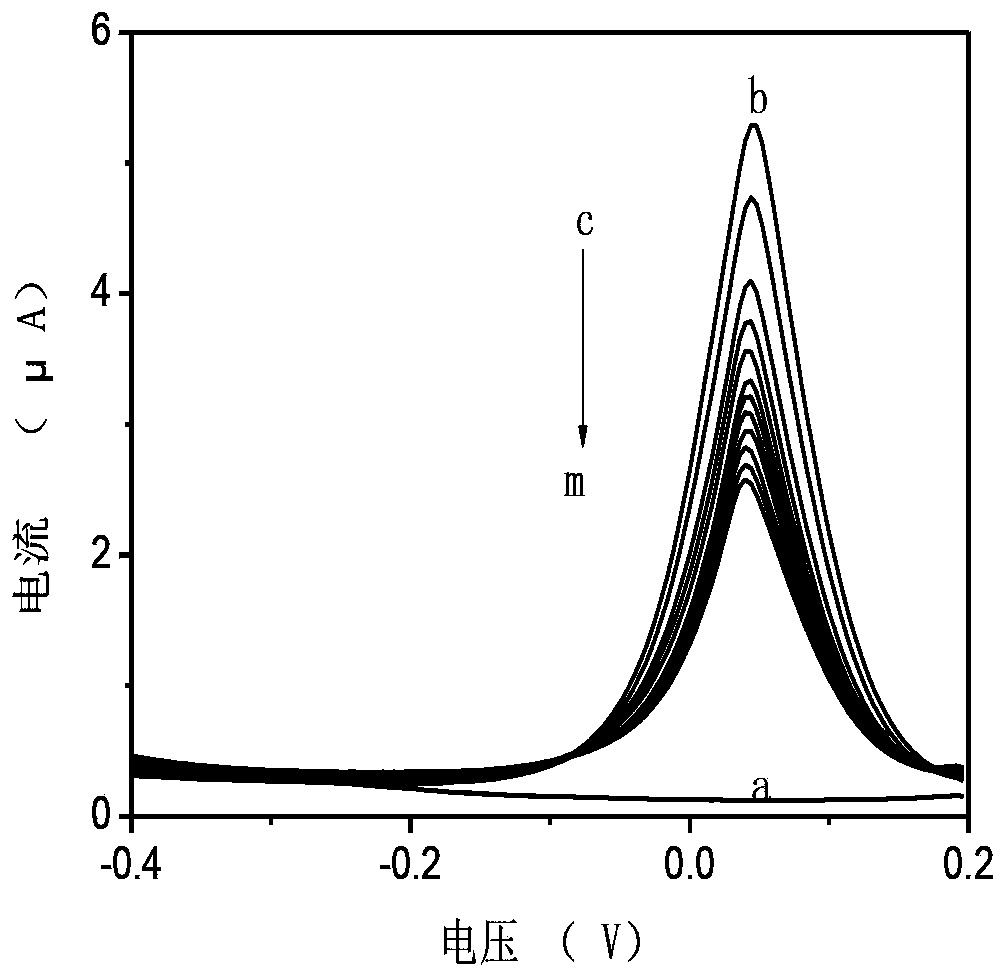
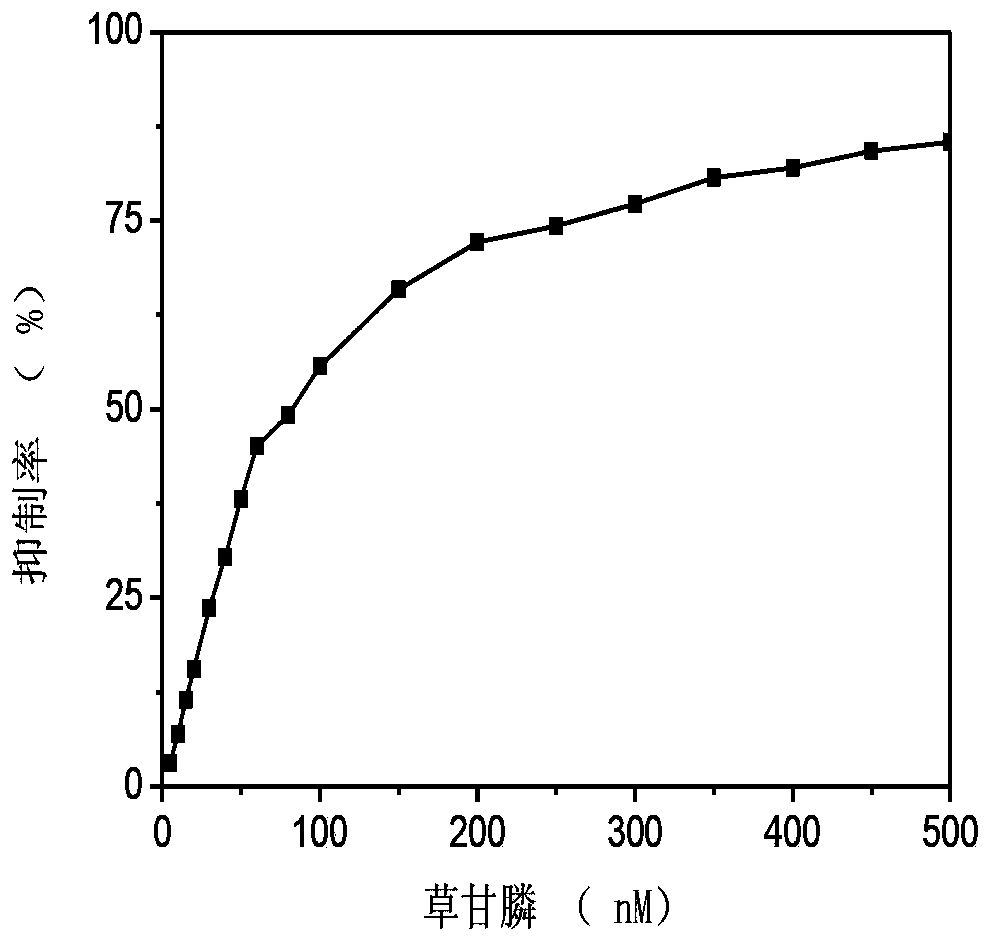
The invention relates to the preparation of a polyphenol oxidase biosensor, which is prepared by adopting carbon nanosphere embedded polyphenol oxidase modified glassy carbon electrode and used for detecting pesticide residues. Polyphenol oxidase is a class of metalloproteinases with wide sources, compared with acetylcholinesterase, butyrylcholinesterase and organophosphorus hydrolase and the like, the polyphenol oxidase has the advantages of wide sources, low price and the like. According to the invention, carbon nanosphere is adopted to embed polyphenol oxidase, and has good biocompatibility, higher mechanical strength and larger specific surface area, so that the fixed quantity of an electrode surface enzyme is improved, and the biological activity of the polyphenol oxidase is maintained to the maximum degree. Therefore, the biological catalytic efficiency of the enzyme, and analysis and detection performance of the biosensor are improved. The polyphenol oxidase biosensor prepared through the method has lower detection limit and an excellent linear range to glyphosate, and has excellent recovery rate to sample detection, meanwhile, has excellent repeatability, reproducibility and stability, and can be used for detecting pesticide residues.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Trifluoromethyl containing quinazoline derivative and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105017259AInhibitory activityPotential to fight dementiaNervous disorderOrganic chemistryButyrylcholinesteraseSolvent
The present invention discloses a trifluoromethyl containing quinazoline derivative and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: under the condition that copper and ligand exist, an N-cyano substituted aryl carboxamides compound reacting with a togni reagent in a solvent, and after completion of the reaction, obtaining the trifluoromethyl containing quinazoline derivative after treatment. The reaction substrate is readily available, the operation is convenient, the obtained quinazolinone derivative is of rich diversity, the required reaction condition is mild, and the reaction time is short. The all-in-one-pot reaction is realized, and not only a structural mother kernel of quinazoline is obtained, but also trifluoromethyl is introduced into the mother kernel structure. And the quinazolinone compound contains the spiropyran compound can be synthesized, which cannot be achieved by the prior art. The obtained product has good activity in inhibiting enzyme acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
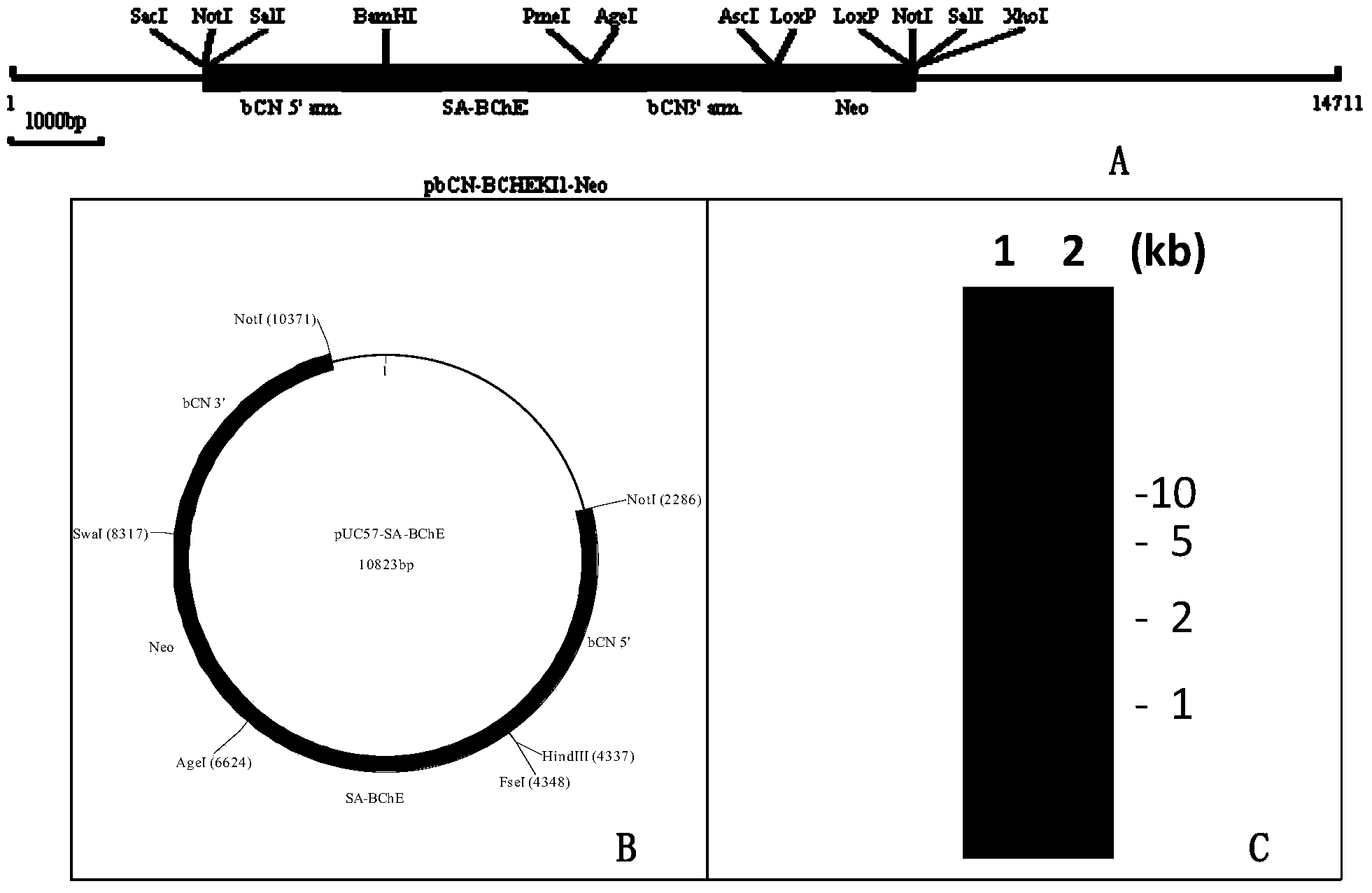
Method for producing recombinant human BChE (butyrylcholinesterase) from transgenic animals by using gene knock-in and nuclear transfer technologies
The invention discloses a method for producing recombinant human BChE (butyrylcholinesterase) from transgenic non-human mammals by using gene knock-in and nuclear transfer technologies, and particularly provides a donor construct used for specific expression of a mammary gland. The construct integrates DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) coding sequences of human BChE to a specific expression protein gene locus of the mammary gland in targeted manner and performs successful transfection on non-human mammal embryo fibroblasts, juvenile and adult somatic cells or embryonic stem cells, clone is performed by using a somatic cell nuclear transfer technology so as to obtain a new individual, and the carried human BChE gene enables the mammary gland of a non-human mammal to express stably and secrete holoenzyme or a monomer of the human BChE. Recombinant protein produced with the method can be used for preventing and treating nerve poison and organic phosphorus compound poisoning as well as apnea caused by cocaine poisoning and succinylcholine, and for detecting and removing residues of organic phosphorus compounds on vegetables, other crops, various article layers and the soil.
Owner:SHANGHAI JENOMED BIOTECH CO LTD
Compound with dual restraining activities to acetyl cholinesterase and butyryl cholinesterase and use thereof
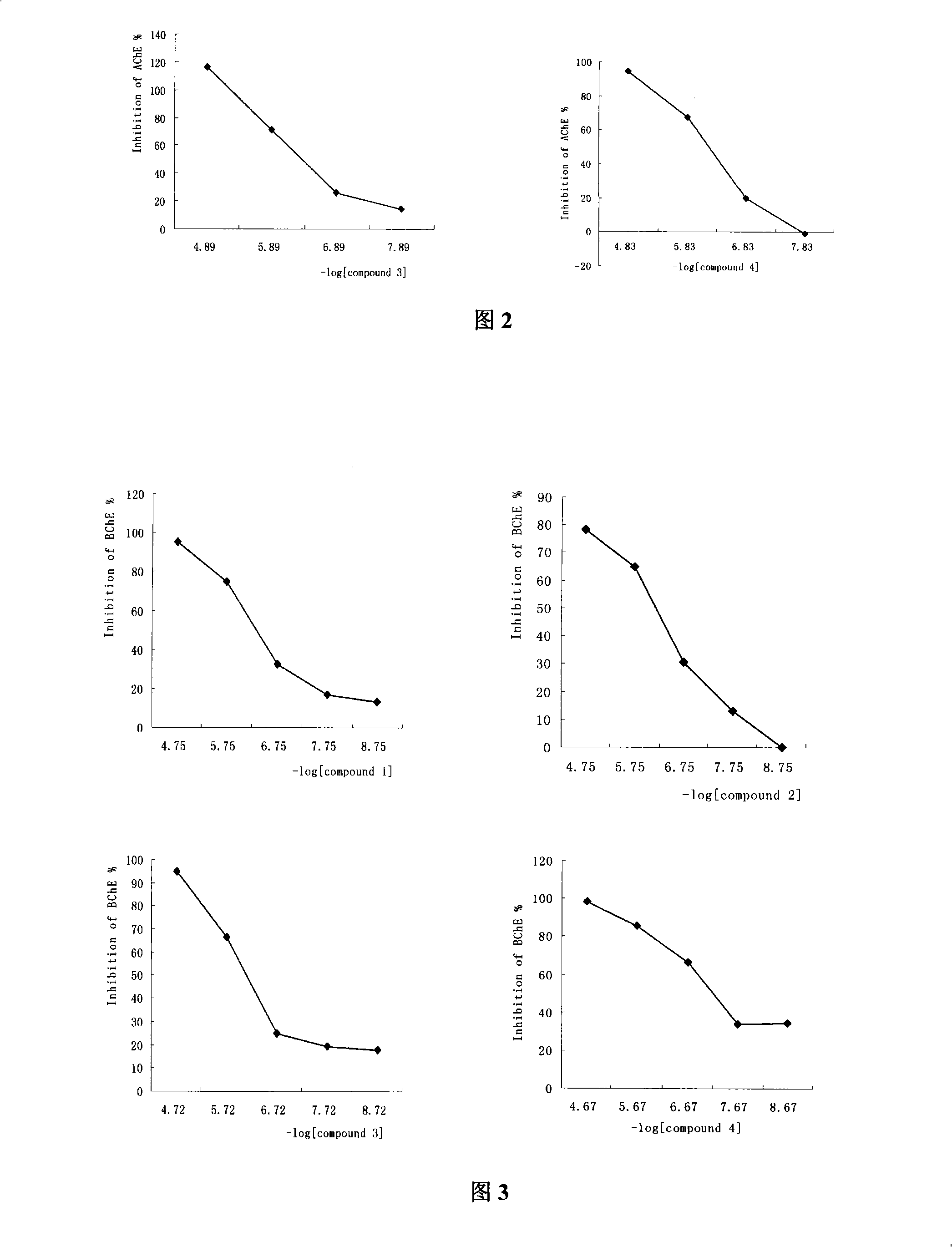
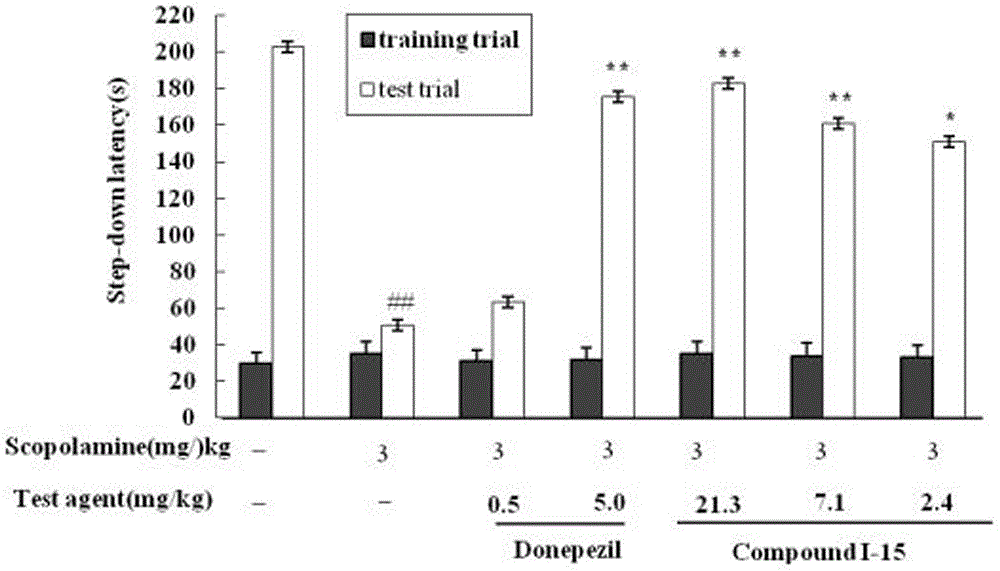
The invention adopts a virtual medicine screening technology and a high-throughput screening technology, assesses the AChE inhibitory activity of more than ten thousand samples in a compound sample library and finds a batch of compounds with higher inhibitory activity by establishing a virtual acetylcholinesterase inhibitor screening method and an AChE activity detection method. Then according to the pathological features of senile dementia, the compounds with higher AChE inhibitory activity are subject to butyryl choline esterase inhibitory activity detection. Research results show that bimolecular 3-piperidyl-ethyl phenyl ketone not only has comparatively high AChE inhibitory activity, but also has very strong BuChE inhibitory activity; the results of animal experiments prove that the bimolecular 3-piperidyl-ethyl phenyl ketone can remarkably improve aphronesia caused by scopolamine and sodium nitrite and can enhance the ability of learning and memory.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Multiple-target effects of isoflavone derivative and its application in improvement of learning and memory
ActiveCN104095849ARegulating neuroinflammationImprove learning and memory functionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDamage repairDisease injury
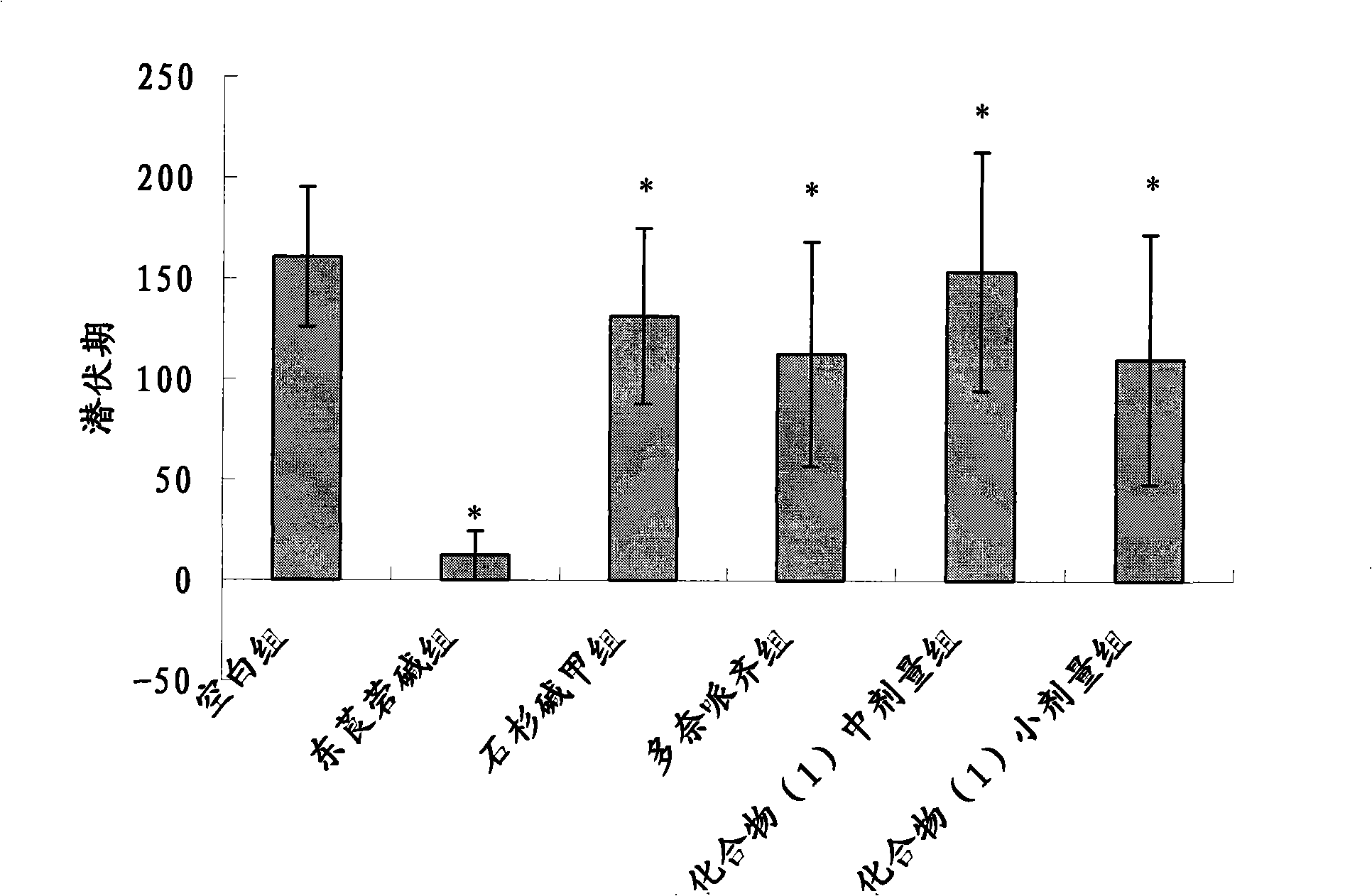
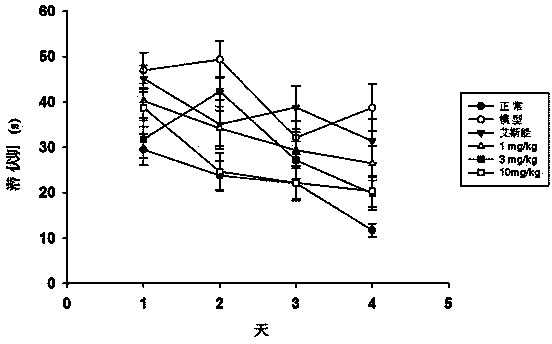
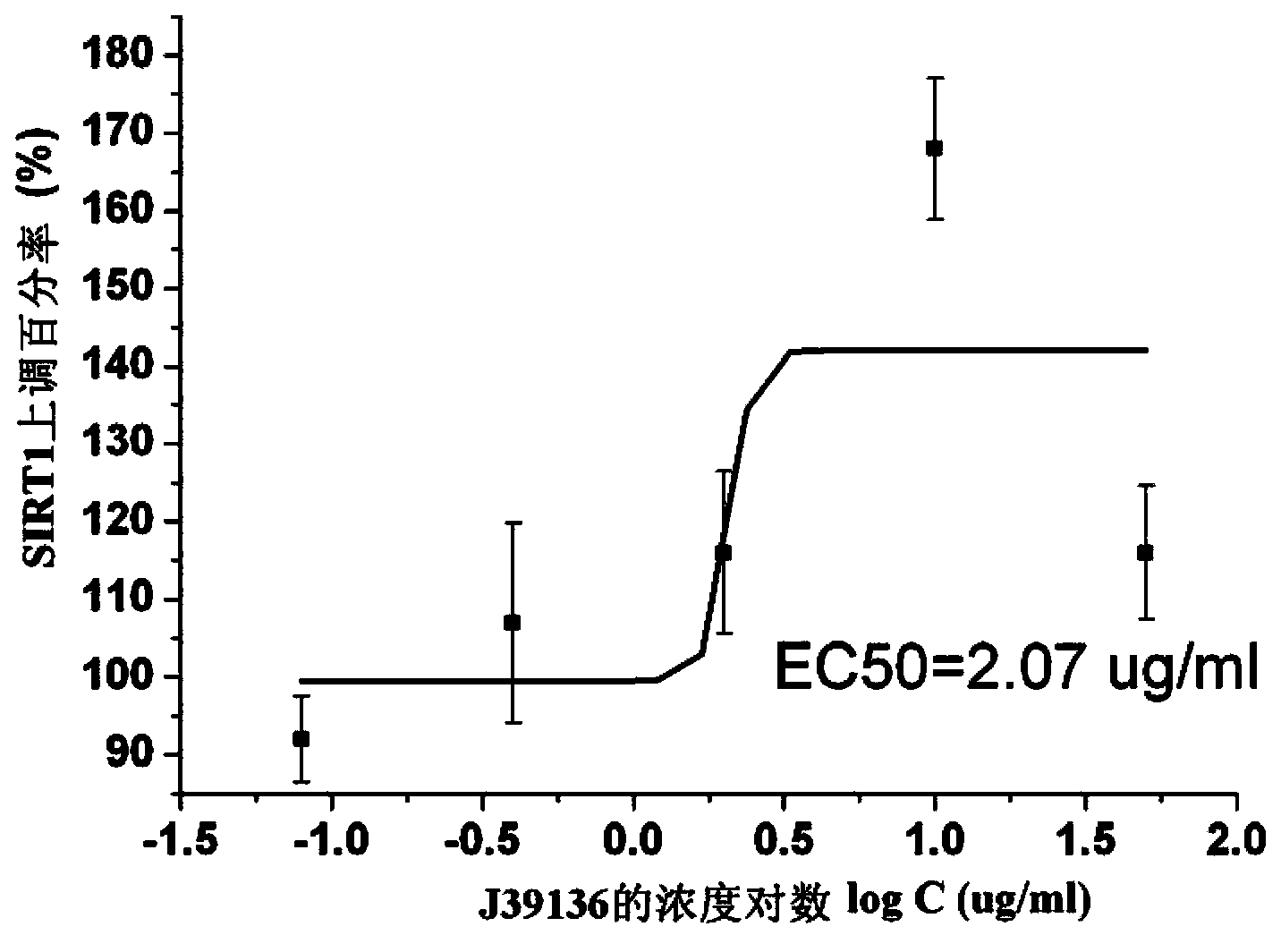
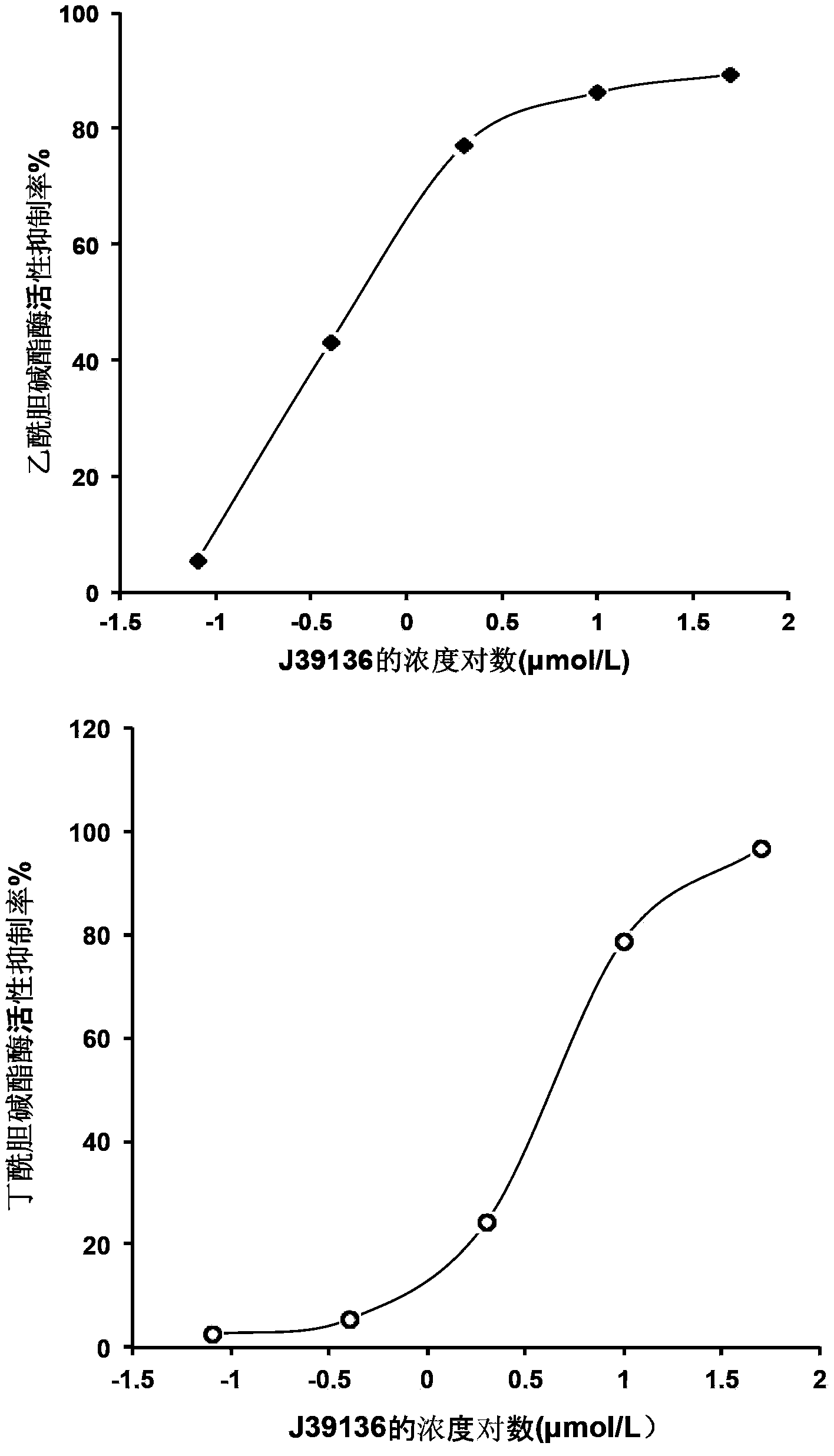
The invention discloses multiple-target effects of an isoflavone derivative and its application in improvement of learning and memory. Specifically, the invention discloses that a compound J39136 has the effects of: upregulating the expression of SIRT1 protein with damage repair and neuroprotective effects; inhibiting the activity of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase, and dose-dependently inhibiting the acetylcholinesterase activity of cells under a safe dose; protecting nerve cells, inhibiting abnormal expression of beta-APP, and reducing Abeta1-42 secretion; and regulating neuroinflammation. Animal experimental results prove that J39136 has low toxicity, can penetrate the blood-brain barrier, and can significantly improve scopolamine caused mouse dementia and strengthen learning and memory functions. Preclinical study results prompt that J39136 is expected to become the drug for prevention and / or treatment of learning and memory disorder and Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Flavonoid compounds existing in millettia pachycarpa and capable of inhibiting AChE (acetylcholinesterase) and BuChE (butyrylcholinesterase) and application of flavonoid compounds
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine and particularly relates to flavonoid compounds separated from millettia pachycarpa as a leguminous plant and having AChE (acetylcholinesterase) and BuChE (butyrylcholinesterase) inhibiting activity, pharmaceutical salts of the flavonoid compounds and pharmaceutical composition containing the compounds. The three flavonoid compounds have a remarkable inhibiting effect on AChE and BuChE and show unique advantages in preventing and treating learning and memory disorder and senile dementia diseases.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
High-activity mutants of butyrylcholinesterase for cocaine hydrolysis and method of generating the same
ActiveUS7731957B1Avoid high concentrationsPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesRate-determining stepButyrylcholinesterase
A novel computational method and generation of mutant butyrylcholinesterase for cocaine hydrolysis is provided. The method includes molecular modeling a possible BChE mutant and conducting molecular dynamics simulations and hybrid quantum mechanical / molecular mechanical calculations thereby providing a screening method of possible BChE mutants by predicting which mutant will lead to a more stable transition state for a rate determining step. Site-directed mutagenesis, protein expression, and protein activity is conducted for mutants determined computationally as being good candidates for possible BChE mutants, i.e., ones predicted to have higher catalytic efficiency as compared with wild-type BChE. In addition, mutants A199S / A328W / Y332G, A199S / F227A / A328W / Y332G, A199S / S287G / A328W / Y332G, A199S / F227A / S287G / A328W / Y332G, and A199S / F227A / S287G / A328W / E441D all have enhanced catalytic efficiency for (−)-cocaine compared with wild-type BChE.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
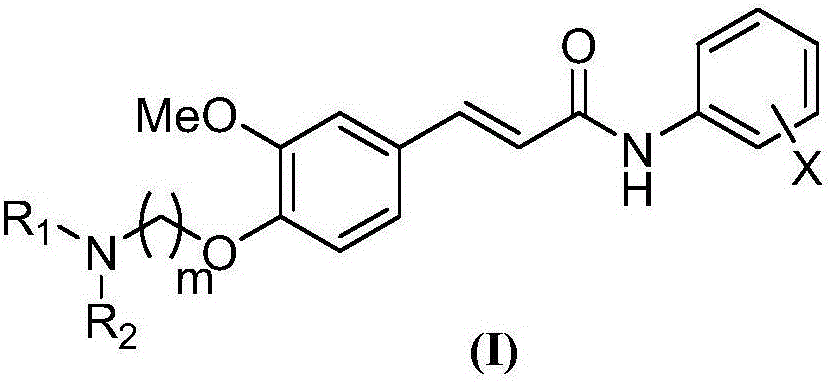
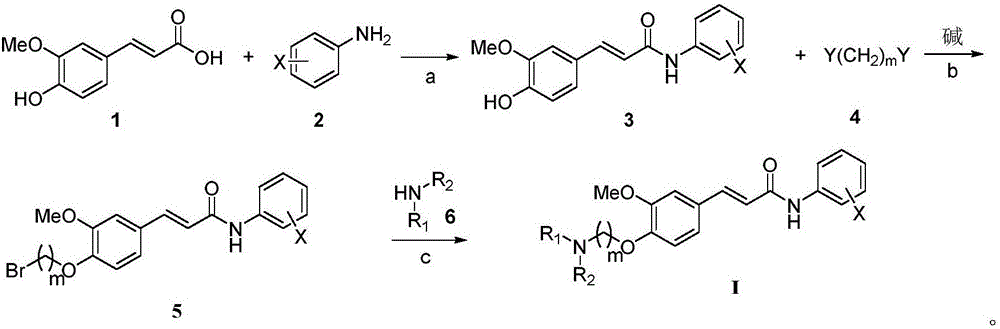
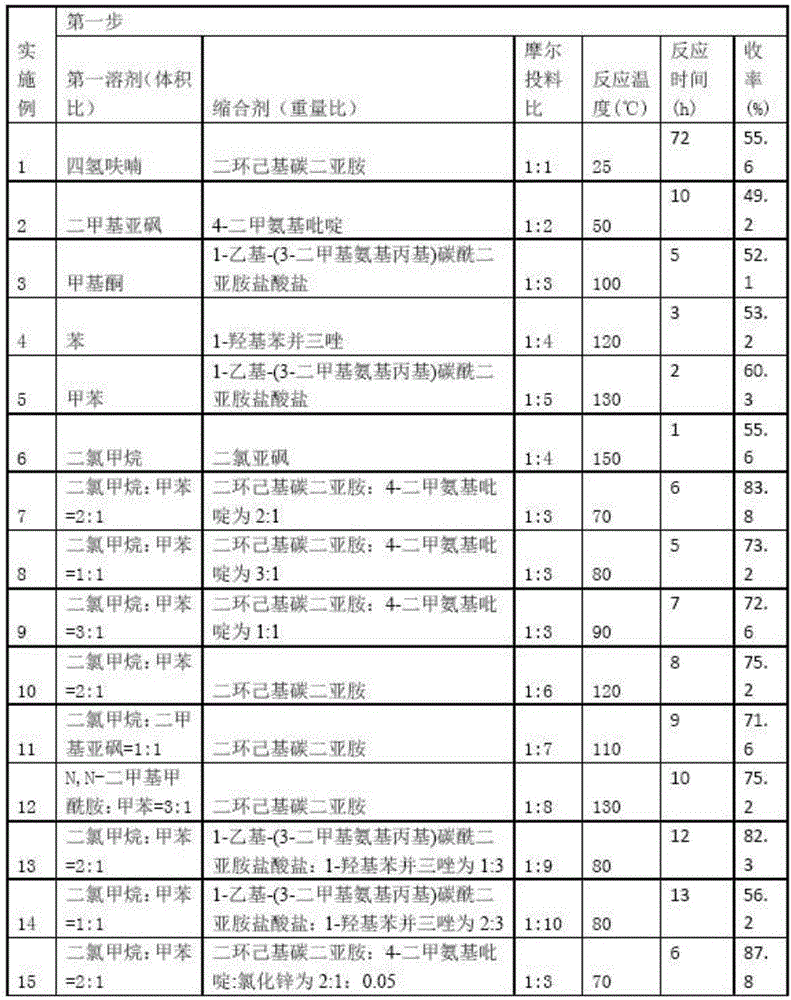
4-amino alkoxy-3-methoxy cinnamic acid benzamide compounds as well as preparation methods and applications thereof
InactiveCN105801448AImprove protectionImproves antioxidant activityNervous disorderOrganic compound preparationButyrylcholinesteraseSolvent
The invention relates to 4-amino alkoxy-3-methoxy cinnamic acid benzamide compounds as well as preparation methods and applications thereof. The preparation methods of the compounds comprise the following steps: step 1, ferulic acid is taken as a starting material and subjected to a reaction with substituted aniline under the conditions of a first solvent and a condensing agent, and corresponding ferulic acid benzamide compounds are obtained; step 2, the ferulic acid benzamide compounds are subjected to a reaction with a dihalogenated alkyl compound under the condition of a second solvent and a first alkaline condition, and a corresponding halogen compounds are obtained; step 3, the halogen compounds are subjected to a reaction with an organic amine compound under the condition of a third solvent, and the 4-amino alkoxy-3-methoxy cinnamic acid benzamide compounds are obtained. The compounds have a remarkable inhibiting effect on acetylcholinesterase, the IC50 is 0.01 mu M-5 mu M, and the inhibitory activity on acetylcholinesterase is greatly higher than that on butyrylcholinesterase, so that the compounds have certain selective inhibiting effect on acetylcholinesterase.
Owner:NANYANG NORMAL UNIV
Butyrylcholinesterase variant polypeptides with increased catalytic efficiency and methods of use
The invention provides a butyrylcholinesterase variant having increased cocaine hydrolysis activity as well as the corresponding encoding nucleic acid. The invention further provides methods of hydrolyzing a cocaine-based butyrylcholinesterase substrate as well as methods of treating a cocaine-induced condition with the invention variant.
Owner:APPLIED MOLECULAR EVOLUTION
Vegetable pesticide residue detection method
InactiveCN109001195AImprove readinessFast measurementMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorCuvettePesticide residue
The invention provides a vegetable pesticide residue detection method, and particularly relates to the technical field of pesticide residue detection. The method comprises the following steps of S1, performing reagent preparation: preparing a buffer solution, a butyrylcholinesterase solution, a substrate and a color developing agent; S2, performing sample preparation: cutting leaves, melon pulp orthe like into small blocks, putting the small blocks into an extraction bottle, adding the buffer solution, shaking to obtain an extracting solution, and standing to obtain a supernate for later use;S3, performing control solution detection: adding the buffer solution and the butyrylcholinesterase solution into a reaction flask, adding the color developing agent, performing placement for a certain time in a constant-temperature incubator, adding the substrate, pouring a mixture into a cuvette, and carrying out detection by using a pesticide residue fast detection instrument; S4, performing to-be-detected sample solution detection: taking the supernate, the butyrylcholinesterase solution and the color developing agent, performing placement in the constant-temperature incubator for a period of time, pouring a mixture into the cuvette, shaking, and carrying out detection by using the pesticide residue fast detection instrument; and S5, calculating a detection result. The method has theadvantages that the preparation rate is increased, the detection speed is high, and the operation is simple.
Owner:常州常检一诺食品检测中心有限公司
Amide group substituted hesperetin derivatives, preparation method thereof and application of derivatives as anti-AD (anti-Alzheimer's disease) drugs
ActiveCN106905280AStrong inhibitory activityHigh selectivityNervous disorderOrganic chemistryAcetylcholinesteraseButyrylcholinesterase
The invention belongs to the fields of pharmaceutical chemistry and pharmacotherapeutics and discloses amide group substituted hesperetin derivatives, a preparation method thereof and an application of the derivatives as AD (Alzheimer's disease) treatment drugs. Study proves that the amide group substituted hesperetin derivatives have strong inhibition property and good inhibition selectivity on acetylcholinesterase, and inhibition capacity of the derivatives on acetylcholinesterase is more than 500 times higher than inhibitory activity on butyrylcholinesterase. The study indicates that the compounds can be developed into the AD treatment drugs.
Owner:ANHUI MEDICAL UNIV
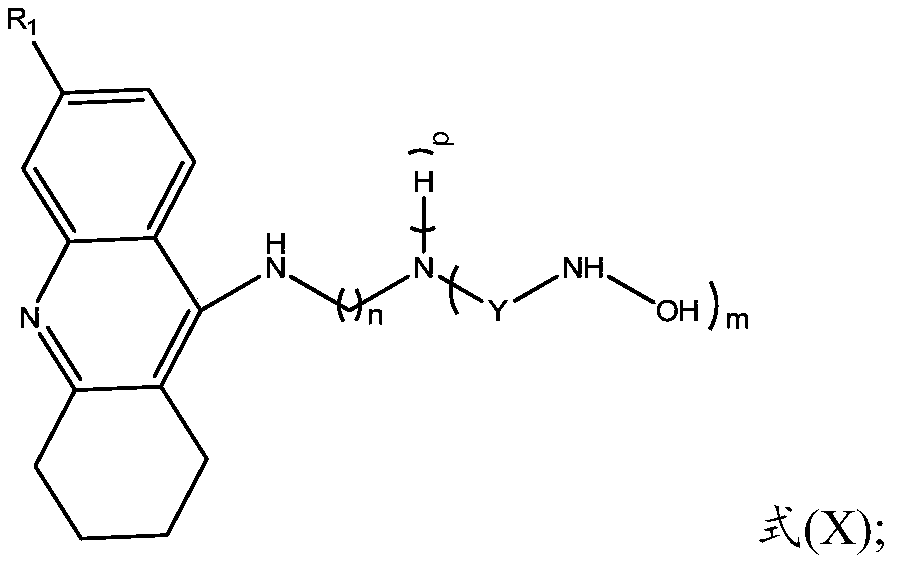
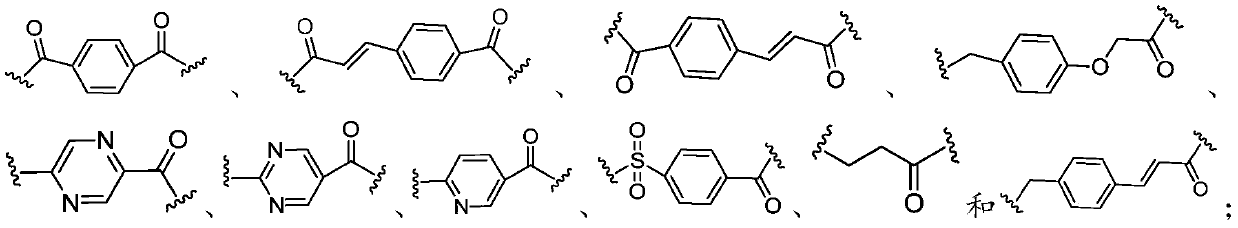
Multi-target tacrine derivative and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110551067AInhibitory activityWide range of securityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderCholinesteraseHalogen
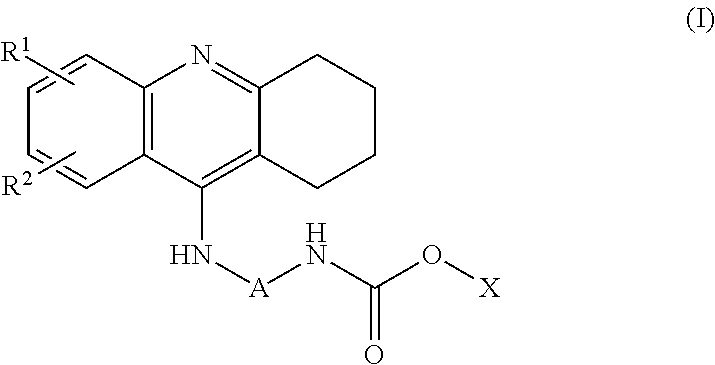
The invention provides a multi-target tacrine derivative and a preparation method and application thereof. The compound has the structure shown in a formula (I) (please see the specification in the formula (I)), wherein n is a natural number greater than 1; m is 1 or 2; p is 0 or 1; R1 is H or halogen; and Y is selected from the following structures (please see the specification for the structures) or, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of a compound in a formula (X). According to the compound, activity of histone deacetylase (HDACs), acetylcholinesterase (AChE) or butyryl cholinesterase (BChE) can be effectively inhibited.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
N-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolinyl)-feruloylagmatine-O-alkylamine compound and application
InactiveCN106831574AImproves antioxidant activitySignificant neuroprotective effectOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseOxidation Activity
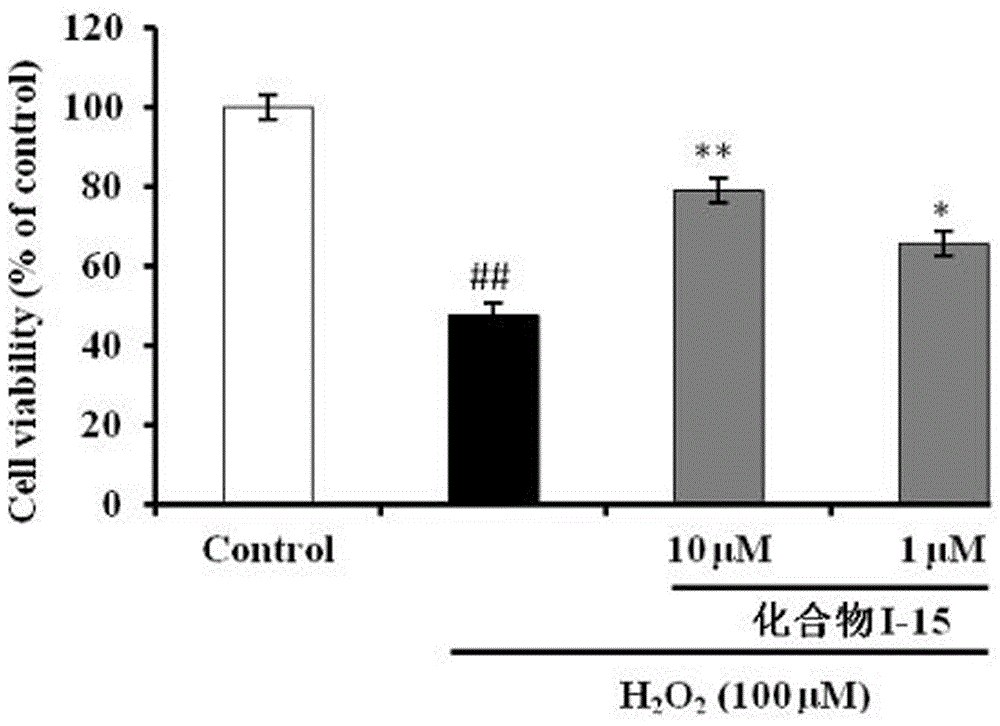
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicinal chemistry and discloses a N-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolinyl)-feruloylagmatine-O-alkylamine compound (I) and pharmaceutically acceptable salt, and a preparation method and application thereof. The structure is as shown in a formula I. The compound (I) provided by the invention has high butyrylcholine esterase inhibiting activity, anti-oxidation activity and Abeta1-42 aggregation inhibiting activity, and has remarkable neuroprotective function on PC12 cell injury induced by hydrogen peroxide, which indicates that the compound is a multi-target-point inhibitor. The compound further shows a good effect of treating alzheimer disease in in-vivo experiments, and has low toxicity and a good clinical application prospect.
Owner:NANYANG NORMAL UNIV
Butyrylcholinesterase zwitterionic polymer conjugates
The present invention provides recombinant butyrylcholinesterase fusion proteins, including Fc fusion proteins and multi-armed high MW polymers containing hydrophilic groups conjugated to the fusion proteins, and methods of preparing such polymers.
Owner:KODIAK SCI
Novel hybrid cholinesterase inhibitors
The invention relates to novel hybrid cholinesterase inhibitors containing the melatonin or its oxidation products unit and tetrahydroacridine unit linked via a carbamate bond. Due to the high selectivity of action, which is expressed with high ratio of IC50 for acetylcholinesterase inhibition to IC50 for butyrylcholinesterase inhibition ([IC50(AChE)] / [IC50(BChE)]), the novel compounds may be used in relief and / or treatment of the neurodegenerative diseases, among them the Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:UNIWERSYTET WARSZAWSKI +1
Butyrylcholinesterase variant polypeptides with increased catalytic efficiency and methods of use
The invention provides a butyrylcholinesterase variant having increased cocaine hydrolysis activity as well as the corresponding encoding nucleic acid. The invention further provides methods of hydrolyzing a cocaine-based butyrylcholinesterase substrate as well as methods of treating a cocaine-induced condition with the invention variant.
Owner:WATKINS JEFFRY +1
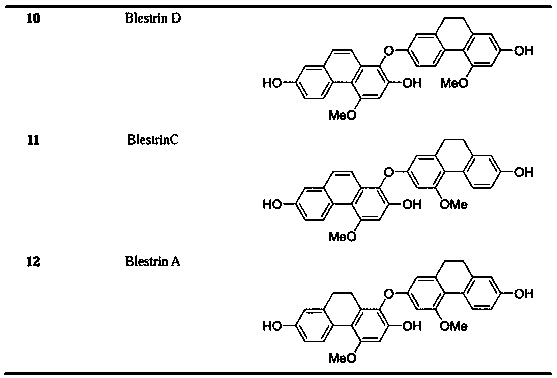
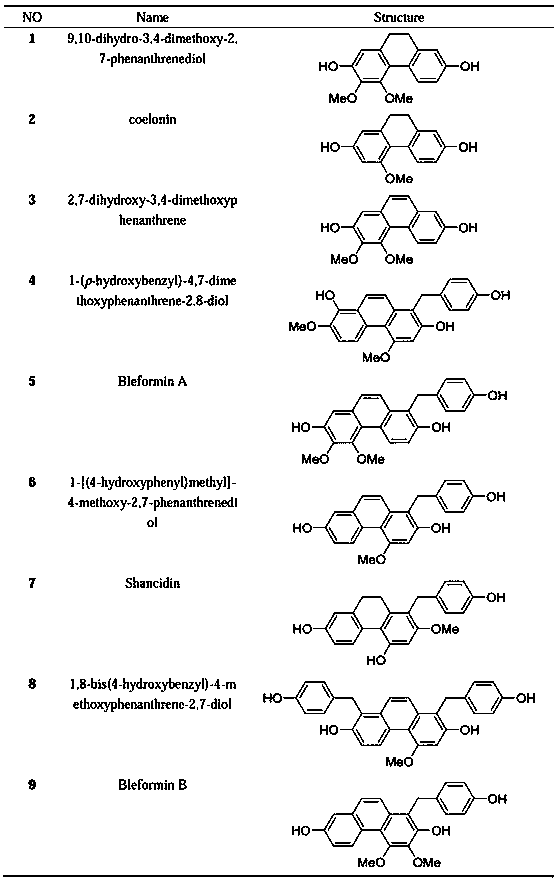
Monomer components having selective butyrylcholinesterase inhibitory effect in Bletilla striata (Thunb)Reichb.f. and application thereof
ActiveCN108191616ATo achieve the purpose of medicationGood treatment effectNervous disorderEther separation/purificationBletilla striataButyrylcholinesterase
The invention belongs to the field of medicine science and technology, and particularly relates to monomer compounds having selective butyrylcholinesterase inhibitory activity obtained by performing separation from orchidaceae Bletilla striata (Thunb)Reichb.f. and medicial salt thereof, and a pharmaceutical composition containing the compounds. The 12 compounds disclosed by the invention have selective inhibitory effects on butyrylcholinesterase to different extents, and IC50 values of five of the 12 compounds are smaller than 10 micrometers, so that a powerful butyrylcholinesterase inhibitoryeffect is shown, and a unique advantage of the compounds in treatment of senile dementia diseases.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Butyrylcholinesterase variants and methods of use
InactiveUS20060063248A1Increased cocaine hydrolysis activitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsCholinesteraseButyrylcholinesterase
The invention provides four butyrylcholinesterase variants having increased cocaine hydrolysis activity as well as the corresponding encoding nucleic acids. The invention also provides libraries comprising butyrylcholinesterase variants having at least one amino acid alteration in one or more regions of butyrylcholinesterase and further having at least one butyrylcholinesterase variant exhibiting enhanced cocaine hydrolysis activity compared to butyrylcholinesterase. The invention further provides methods of hydrolyzing a cocaine-based butyrylcholinesterase substrate as well as methods of treating a cocaine-induced condition.
Owner:LOCKRIDGE OKSANA +1
Fluorescent probe for detecting butyrylcholinesterase activity as well as synthesis method and application of fluorescent probe
ActiveCN111592504AAvoid interferenceAchieving a fluorescent turn-on responseOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesCholinesterase
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe for detecting butyrylcholinesterase activity as well as a synthesis method and application of the fluorescent probe. The invention discloses a novel butyrylcholinesterase sensing strategy established on the basis of background-signal-free detection, and under the action of butyrylcholinesterase, fluorescence signals develop from nothing so that the concentration level of butyrylcholinesterase is detected. According to the fluorescent probe, a targeting site of butyrylcholinesterase is introduced into a non-emission skeleton to generate a probe P1, sothat the inherent fluorescent background of the detection probe is avoided, and the detection sensitivity is greatly improved. After butyrylcholinesterase is added, cyclopropylbutyric acid can be removed, and then spontaneous in-situ cyclization is performed to generate a fluorescent product PF to serve as an indicator for reflecting the activity of BChE. The fluorescent probe has greatly improved detection sensitivity, but also has good selectivity and biocompatibility, and has great potential in the field of clinical diagnosis.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
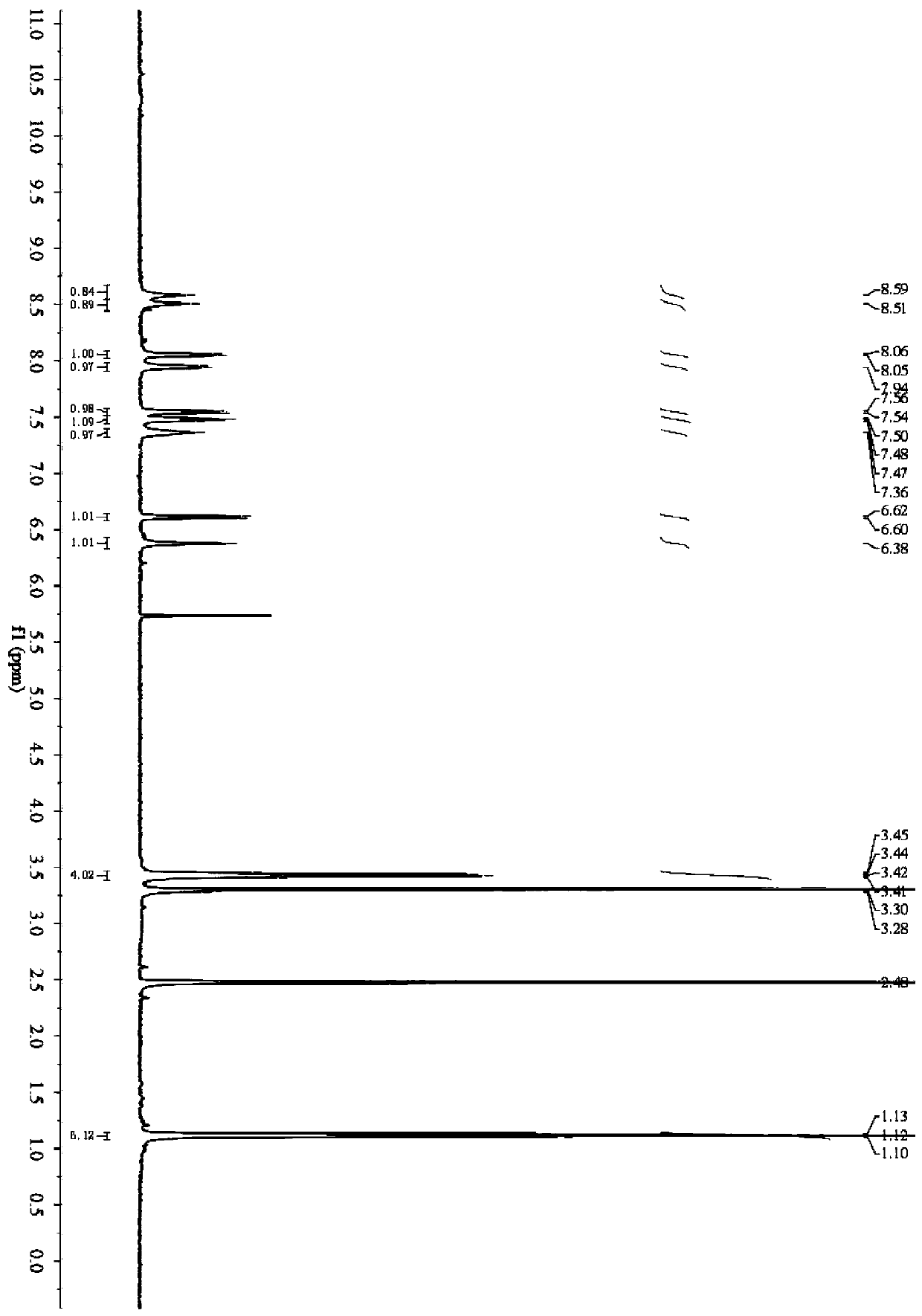
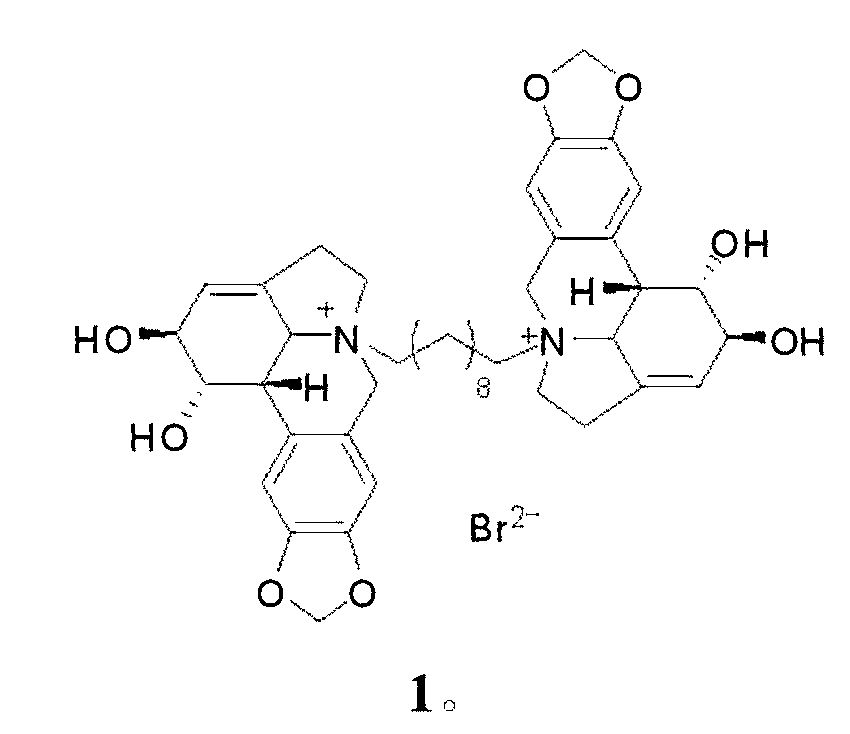
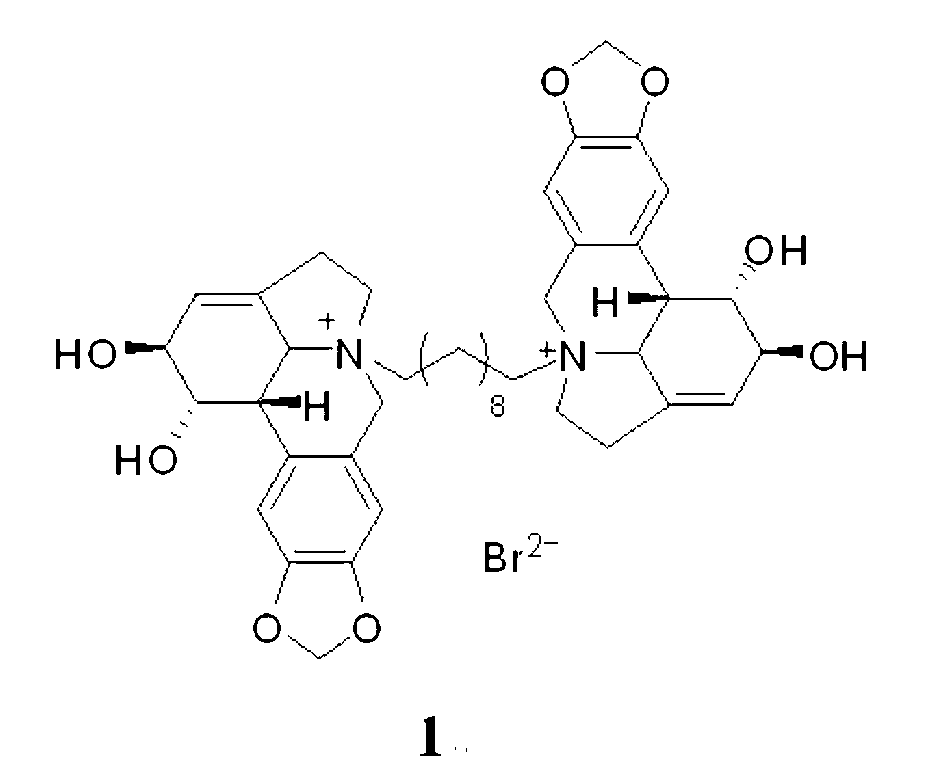
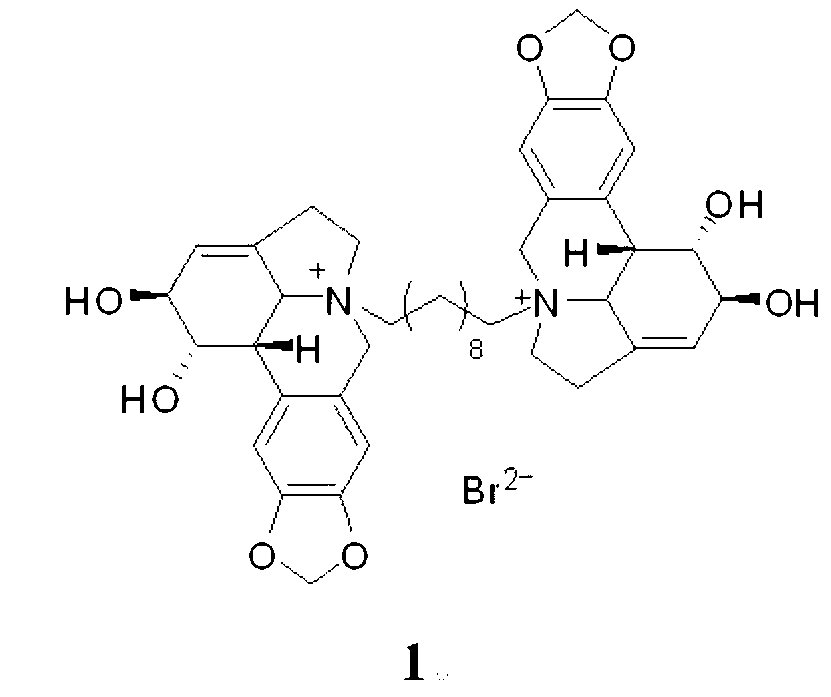
Compound 1,10-N-decylene lycorine dibromo salt, pharmaceutical composition and application thereof in medicine
InactiveCN102746325AOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAcetylcholinesteraseButyrylcholinesterase
The invention relates to a compound 1, 10-N-decylene lycorine dibromo salt showed by the structural formula (1), a pharmaceutical composition of the compound, application of the compound in the preparation of medicines for treatment of Alzheimer's diseases (senile dementia) and in the preparation of a dual inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase, and preparation methods of the compound and the pharmaceutical composition.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Treatment for exposure to nerve agent
ActiveUS20140294926A1Avoid toxicityHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsCholinesteraseButyrylcholinesterase
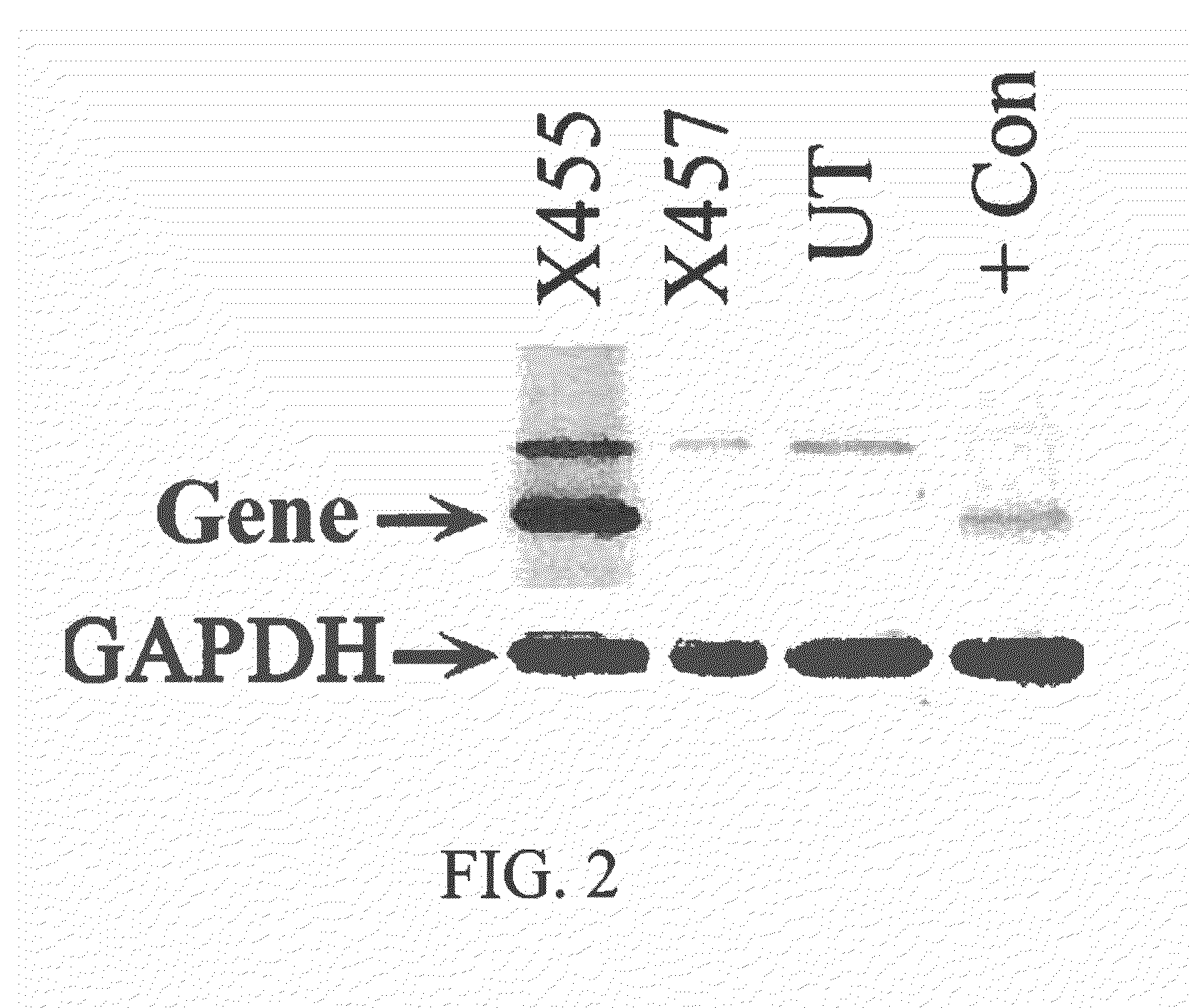
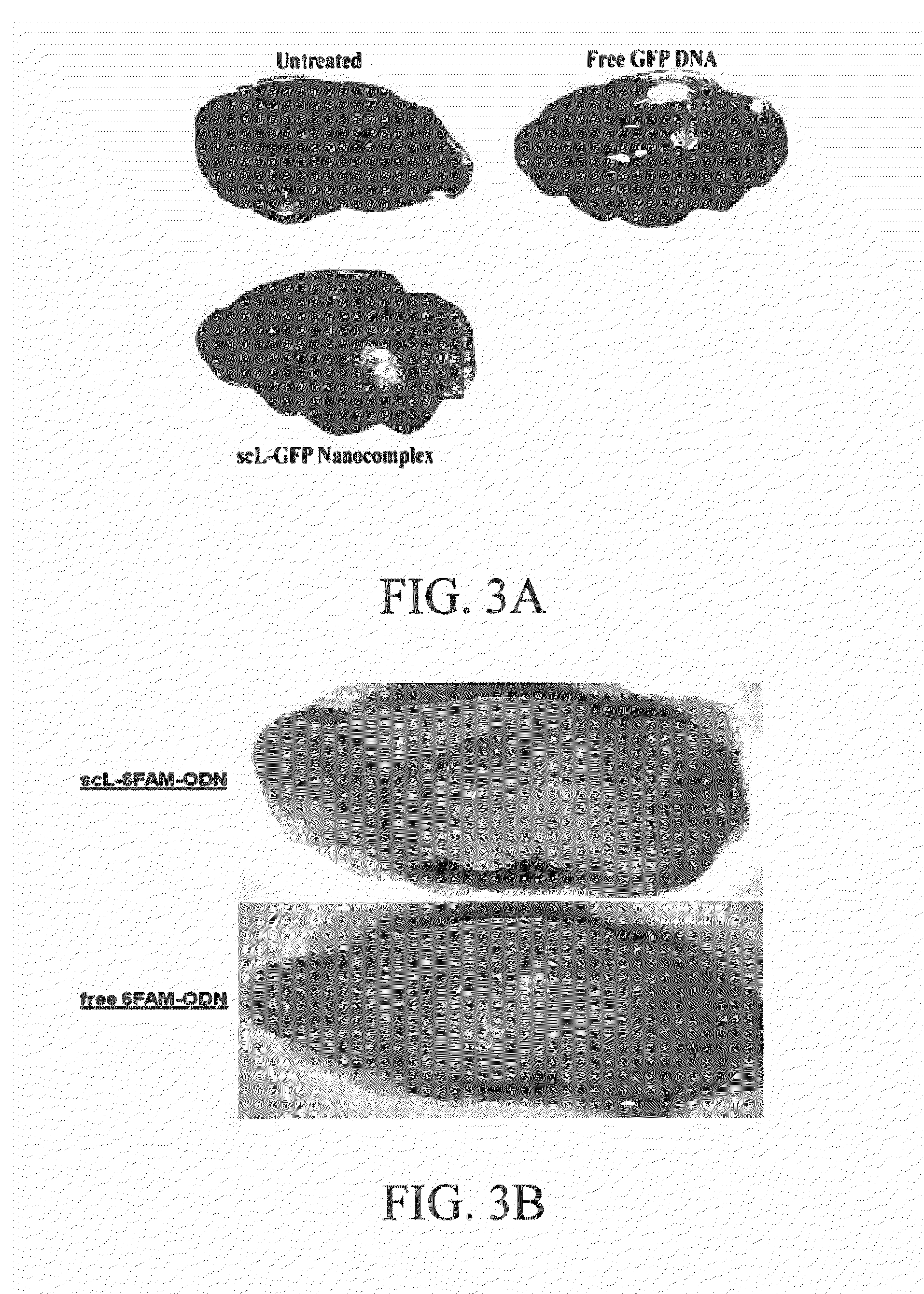
The present application provides methods of preventing and treating the toxic effects of exposure to organophosphate agents. In embodiments, targeted cationic liposome complexes delivering nucleic acid molecules encoding butyrylcholinesterase and a polyproline rich peptide are administered. Suitably, the administration is via inhalation or via aerosol. Also provided are cationic liposome complexes and methods of making the complexes for such administration.
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV
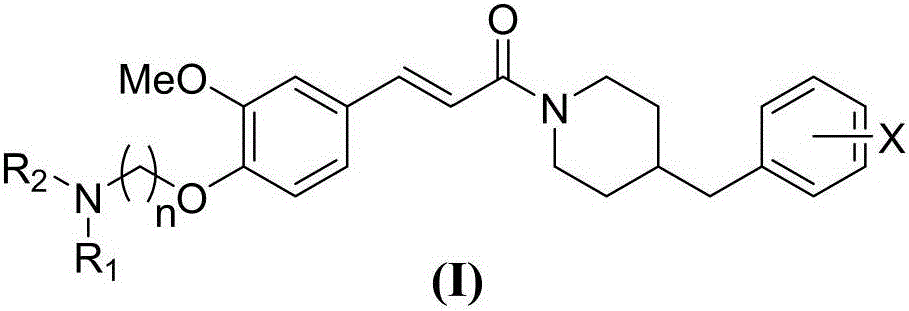
N-(benzylpiperidyl)-feruloylagmatine-O-alkylamine compound, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106749188ALow toxicityImprovement of memory reproduction dysfunctionNervous disorderOrganic chemistrySolventBromine
The invention discloses an N-(benzylpiperidyl)-feruloylagmatine-O-alkylamine compound, a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1, taking ferulic acid and a benzylpiperidine compound as initial raw materials, and condensing in the presence of solvent and condensing agent to obtain an intermediate compound; 2, reacting the intermediate compound and dibromoalkane in the presence of solvent under alkaline conditions to obtain a bromide intermediate compound; and 3, reacting the bromide intermediate compound and secondary amine in the presence of solvent under alkaline conditions to obtain the N-(benzylpiperidyl)-feruloylagmatine-O-alkylamine compound. The compound is a selective butyryl cholinesterase inhibitor, can inhibit Abeta aggregation, and also has an antioxidant effect and a nerve cell protection effect. Further in vivo experiments reflect that the compound has a favorable effect for treating the Alzheimer's disease, is low in toxicity and has good clinical application prospects.
Owner:NANYANG NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com