A kind of ortho-phthalaldehyde derivative phosphoramidite monomer, its synthesis method and the method for dna rapid coupling protein
A technology of phosphoramidite and o-phthalaldehyde, applied in the field of o-phthalaldehyde derivative phosphoramidite monomer and its synthesis, can solve the problems of long time required, low coupling efficiency, cumbersome operation and processing, etc. To achieve the effect of cheap synthetic raw materials and simple and feasible steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Embodiment 1 The synthesis of o-phthalaldehyde derivative phosphoramidite monomer, the steps are as follows:
[0040] Step 1: Synthesis of intermediate product 2 (OPA-OH), the synthesis route is shown in the figure below:
[0041]
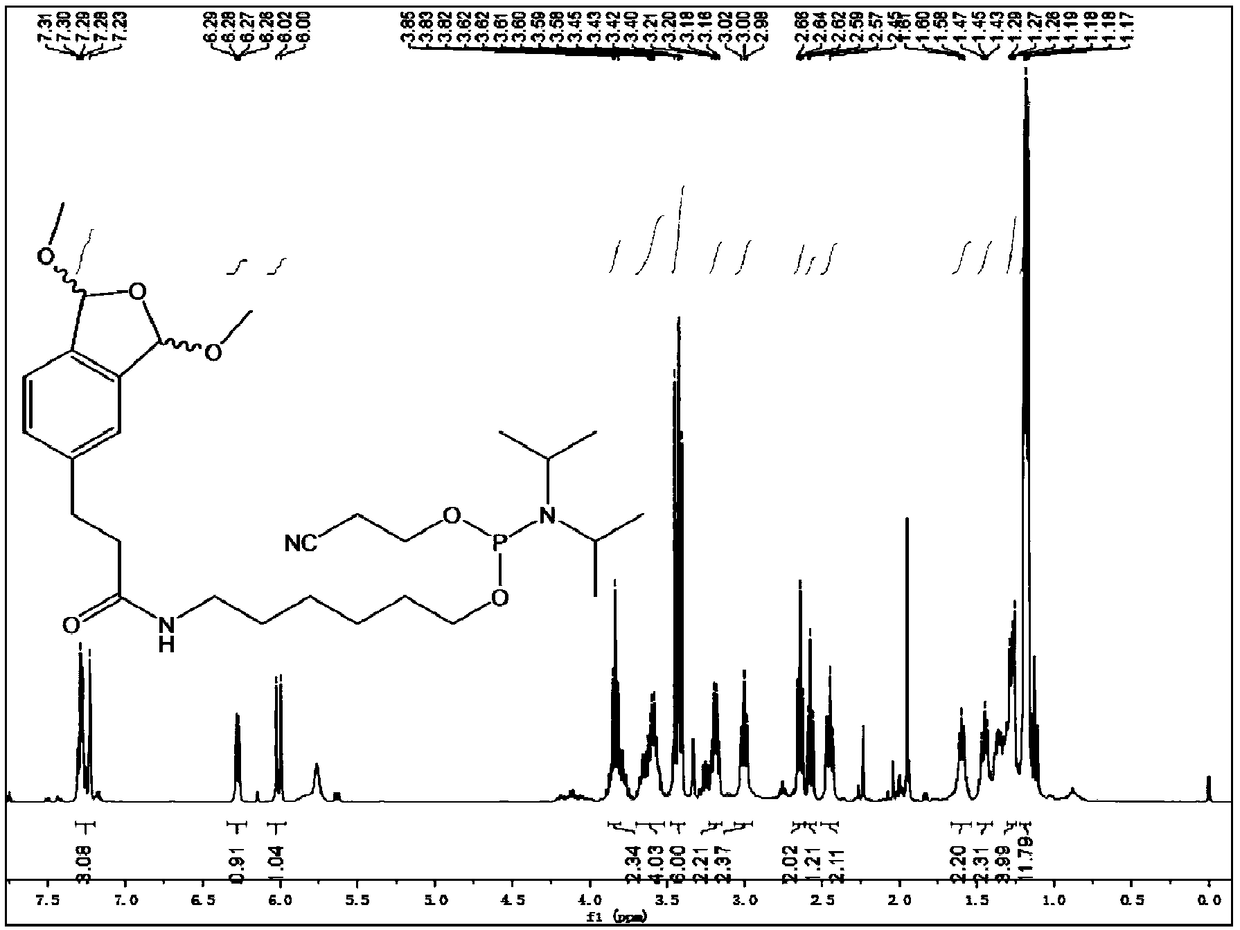
[0042] In a 25 mL round bottom flask, 1 (252 mg, 1 mmol), 6-amino-1-hexanol (234 mg, 2 mmol), DCC (247.2 mg, 1.2 mmol), HOBT (162 mg, 1.2 mmol), 10 mL of solvent were sequentially added Tetrahydrofuran, under the protection of nitrogen, stirred at room temperature for 24h. After the reaction, the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, separated and purified by silica gel column, characterized by NMR and mass spectrometry. 1 H NMR (500MHz, Methanol-D 4 ):δ=7.34-7.28(m,3H),6.29(s,1H),6.03(s,1H),3.56(t,2H),3.44-3.39(m,6H),3.15(m,2H), 3.01(t,2H),2.52(t,2H),1.53(m,2H),1.45(m,2H),1.35(m,2H),1.29(m,2H)ppm. 13 C NMR (500MHz, CDCl 3): δ=174.82,144.31,140.10,137.77,131.20,124.01,123.88,107.85,106.77,62.87,54.72,54.63,40.42,38.81,33.46,32.7...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2 Synthesis and purification of nucleic acid molecules modified by o-phthalaldehyde derivatives.
[0047] Using 6-FAM-labeled CPG as a solid phase carrier, using normal DNA monomer bases as raw materials, synthesize DNA sequences from the 3' end to the 5' end on a DNA synthesizer, and finally modify o-phthalaldehyde at the 5' end Derivative phosphoramidite monomer. The specific synthetic sequence is as follows: 5'-X(T) 10 Y-3', wherein X is the product 3, and Y is 6-FAM. After DNA synthesis, transfer the above CPG to a 1.5mL Eppendorf tube, add 0.4mL methylamine / ammonia water (v / v=1:1), incubate at 65°C for 30min, and cut the DNA from the CPG. Then remove the methylamine / ammonia in a vacuum, dissolve it with 0.5mL 0.1mol / L triethylamine acetate (TEAA), and use C18 reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography to purify, as Figure 4 . The obtained product is vacuum-dried, dissolved in ultra-pure water, desalted and purified with a gel filtration colum...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Example 3 DNA was purified by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography.
[0049] The experiment adopts the gradient elution procedure, using 0.1mol / L TEAA (A phase) and 95% acetonitrile (B phase) as the mobile phase, and using C18 reverse phase chromatographic column to purify DNA. The gradient elution procedure is as follows: 0-3 min, 100% A; 3-35 min, A gradually decreased from 100% to 50%. Since the 3' end of the product DNA was labeled with fluorescein, the product was monitored simultaneously with 260nm and 490nm absorption peaks. From Figure 4 As a result, it can be seen that the product was separated when the retention time was 13 min.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com