Method for extracting chitin nanometer microfiber from marine biomass
A marine organism and nanofiber technology, applied in the field of biopolymers, can solve the problems of destroying the original chemical structure of chitin nanofibers, high equipment cost, low yield, etc. The effect of simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
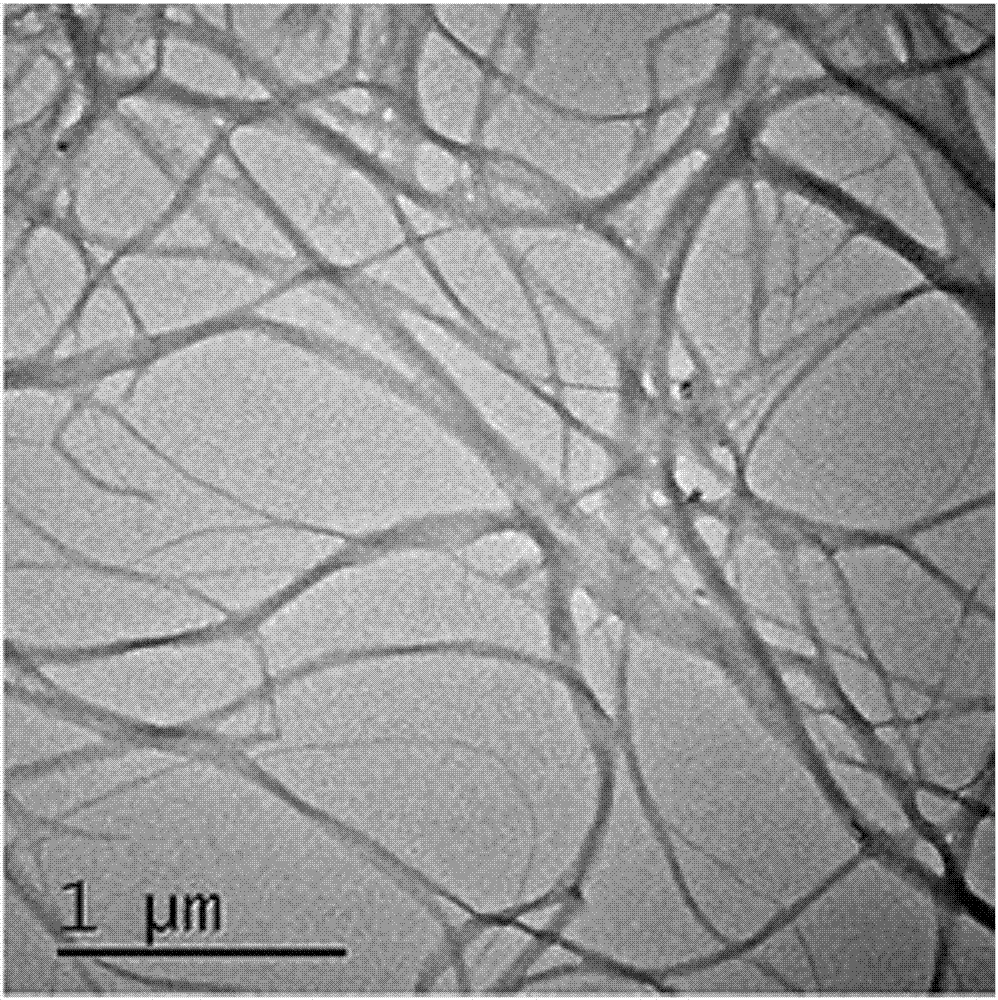
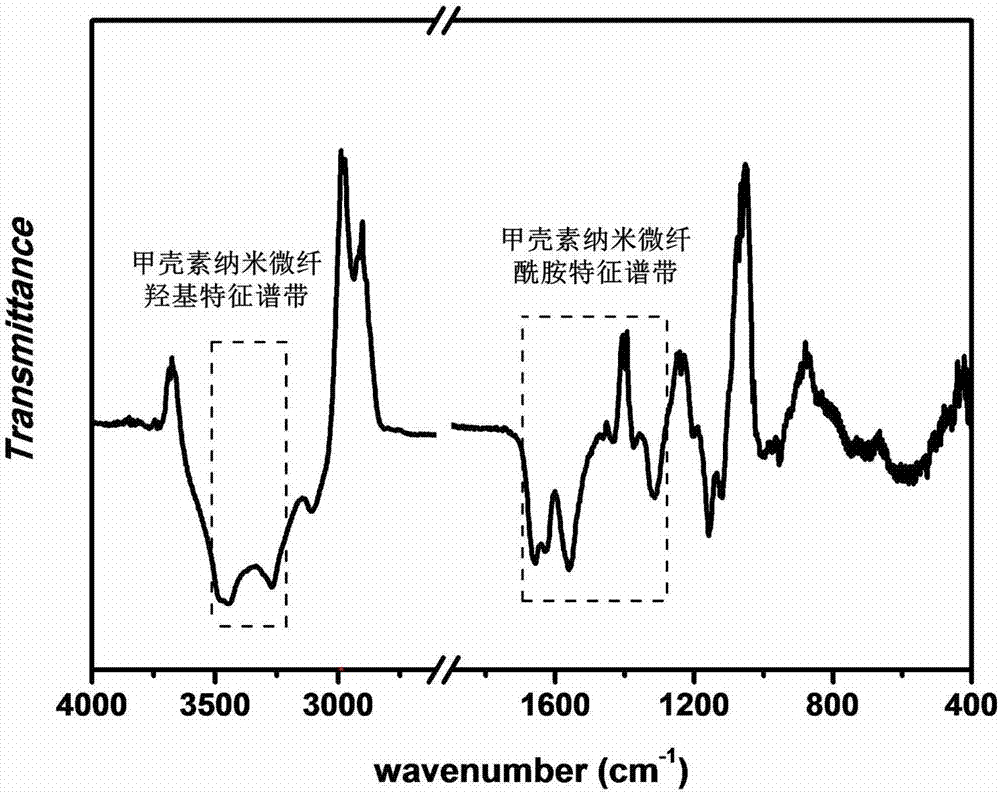
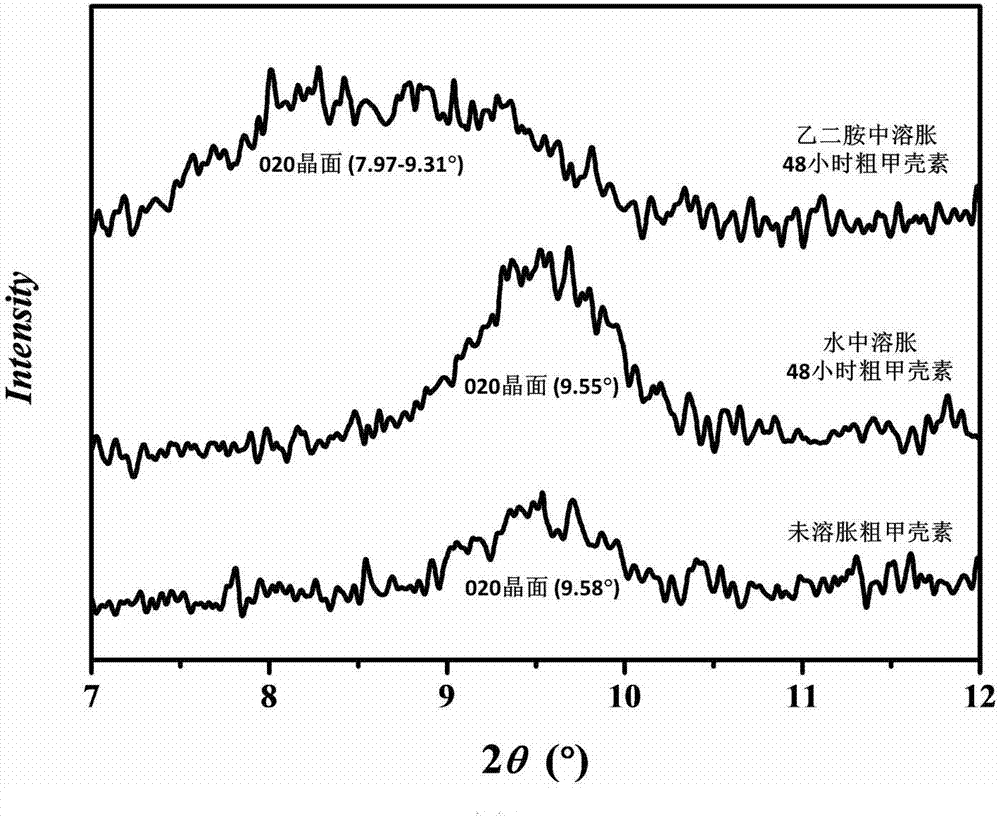
[0026] Shrimp shell powder was obtained by pulverizing the shrimp shell with a pulverizer, weighing 30 g of the shrimp shell powder, slowly adding 300 g of 2 mol / L hydrochloric acid, and stirring at room temperature for 2 days. After the reaction, wash with water 5 times, add 600 g of KOH solution with a mass fraction of 5%, and react at 105° C. for 6 h. After the reaction, wash with water 5 times, dissolve 10.625g of sodium chlorite and 20.4g of sodium acetate trihydrate in 500g of water and add it, and react at 80°C for 2h. After the reaction, wash with water 5 times, add 300 g of KOH solution with a mass fraction of 5%, stir at room temperature for 2 days, wash with water 5 times after the reaction, freeze-dry to obtain crude chitin. Crude chitin with a mass ratio of 1:60 and n-octanol were stirred at room temperature for 2 days, washed with water 5 times after the reaction, and prepared into a water-based suspension with a solid content of 0.5% (mass fraction). The mass r...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Shrimp shells were pulverized by a pulverizer to obtain shrimp shell powder, and 30 g of shrimp shell powder was weighed and slowly added to 300 g of 2 mol / L hydrochloric acid, and stirred at room temperature for 2 days. After the reaction, wash with water 5 times, add 600 g of KOH solution with a mass fraction of 5%, and react at 105° C. for 6 h. After the reaction, wash with water 5 times, dissolve 10.625g of sodium chlorite and 20.4g of sodium acetate trihydrate in 500g of water and add it, and react at 80°C for 2h. After the reaction, wash with water 5 times, add 300 g of KOH solution with a mass fraction of 5%, stir at room temperature for 2 days, wash with water 5 times after the reaction, freeze-dry to obtain crude chitin. Crude chitin with a mass ratio of 1:60 and ethylenediamine were stirred at room temperature for 2 days, washed with water 5 times after the reaction, and prepared into a water-based suspension with a solid content of 0.5 wt%. The mass ratio of c...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Pulverize the crab shells with a pulverizer to obtain crab shell powder, weigh 30 g of the crab shell powder and slowly add 300 g of 2 mol / L hydrochloric acid, and stir at room temperature for 2 days. After the reaction, wash with water 5 times, add 600 g of KOH solution with a mass fraction of 5%, and react at 105° C. for 6 h. After the reaction, wash with water 5 times, dissolve 10.625g of sodium chlorite and 20.4g of sodium acetate trihydrate in 500g of water and add it, and react at 80°C for 2h. After the reaction, wash with water 5 times, add 300 g of KOH solution with a mass fraction of 5%, stir at room temperature for 2 days, wash with water 5 times after the reaction, freeze-dry to obtain crude chitin. Crude chitin with a mass ratio of 1:60 and n-octanol were stirred at room temperature for 2 days, washed with water 5 times after the reaction, and prepared into a water-based suspension with a solid content of 5% by mass. The mass ratio of chitin to ball mill is...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com