Method for detecting pathogenic bacteria in foods by isothermal rapid amplification
A pathogenic bacteria and food technology, applied in the field of food safety testing, can solve the problems of limited application range, difficulty in basic level, high testing cost, etc., and achieve the effect of simple sample pretreatment, short time, simple principle and operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
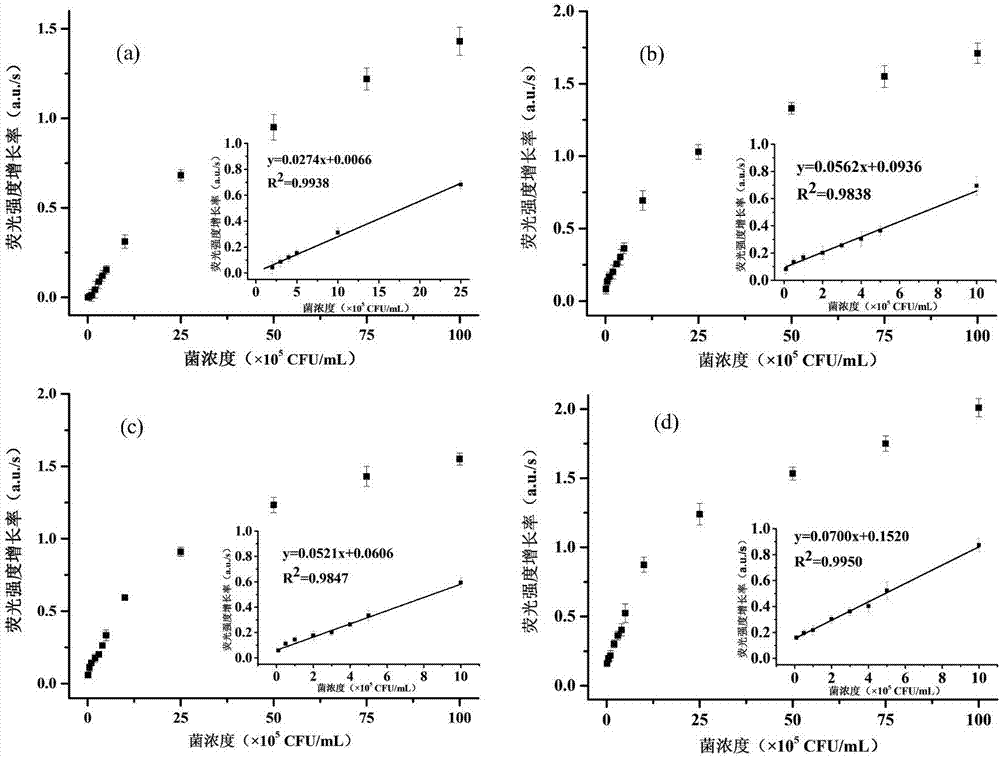
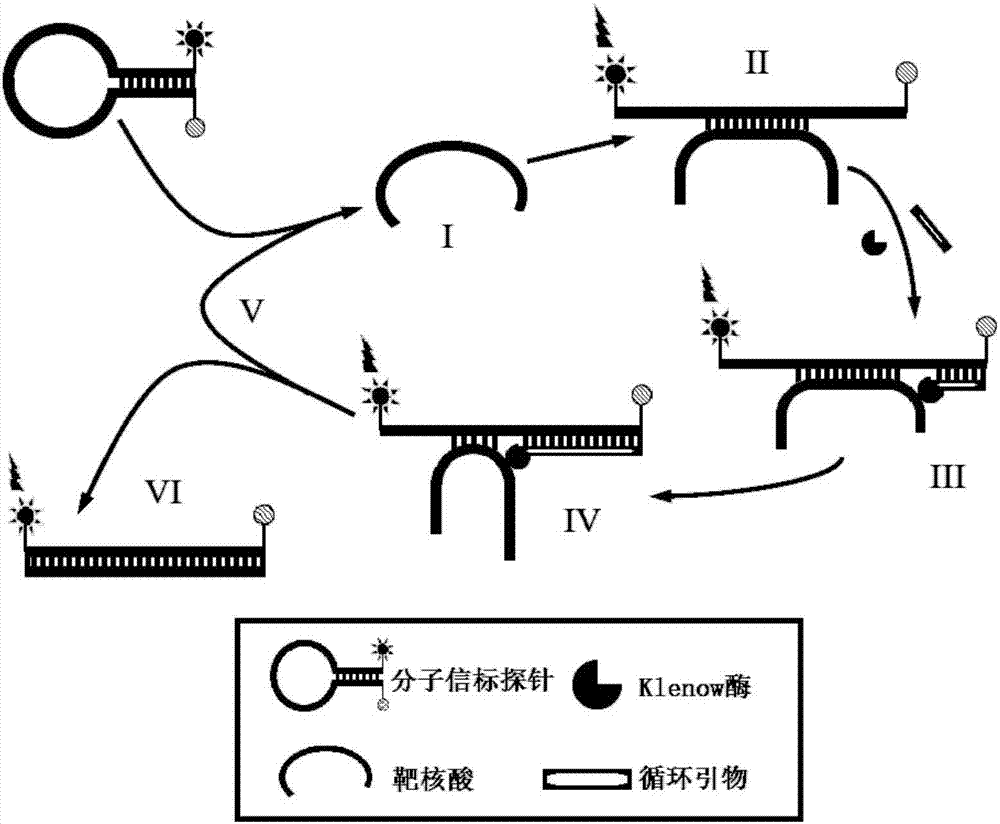
[0042] Embodiment 1: CSDPR amplification principle
[0043] Such as figure 1 Shown is a schematic diagram of the principle of CSDPR amplification.
[0044] The CSDPR reaction opens the stem structure of the molecular beacon probe through the hybridization of the target nucleic acid fragment and the molecular beacon loop sequence, and forms the molecular beacon-cDNA structure under the action of the primer and DNA polymerase, and retains the opened molecular beacon probe. Needle signal, the release of target nucleic acid fragments during cDNA formation triggers the next cycle, and signal amplification is achieved through the amplification of non-target nucleic acids.
Embodiment 2
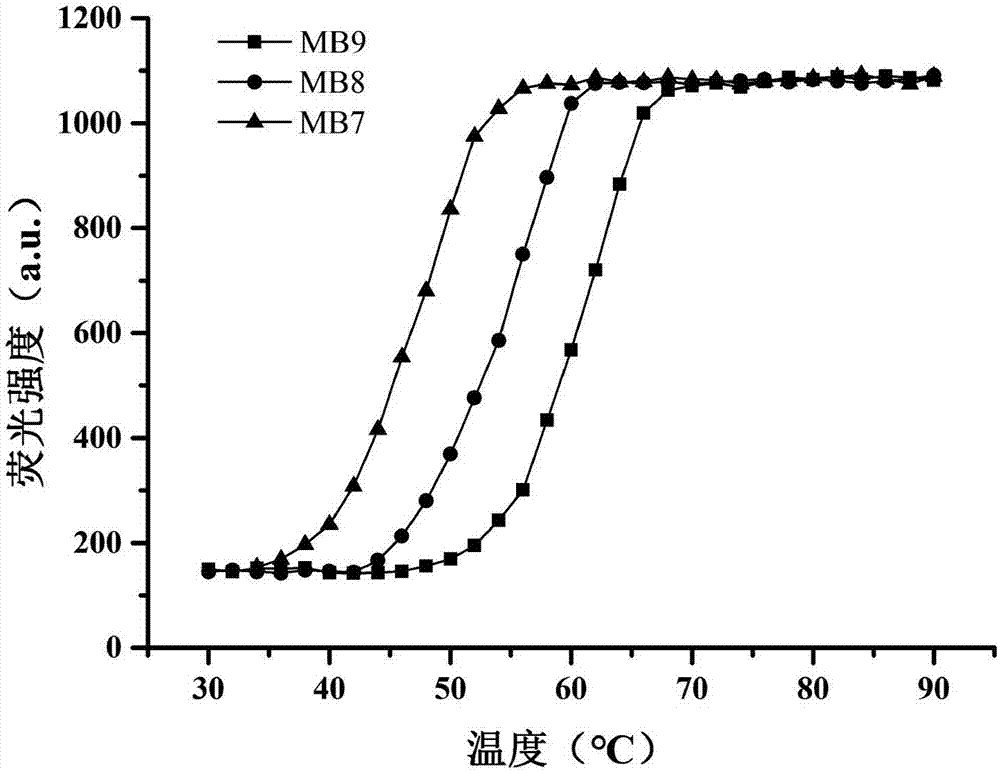
[0045] Embodiment 2: the design of probe and primer
[0046] (1) Design of the pathogenic bacteria probe loop sequence in the molecular beacon probe
[0047] (1) Design of the loop sequence of the molecular beacon probe of Staphylococcus aureus
[0048] Search for Staphylococcus aureus ATCC6538, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus caprae, Staphylococcus capitis, Staphylococcus pasteuri by keywords in NCBI's nucleic acid database The 16S rDNA sequence of the above 5 sequences was compared using DNAMAN, and the fragments in the 16S rDNA sequence of Staphylococcus aureus that differed from the other four sequences by more than 3 nucleotides were selected (5'-GGA CGA GAA GCT TGC TTC -3', ie SEQ ID NO:11) as the target sequence for Staphylococcus aureus detection. Design a Staphylococcus aureus probe loop sequence complementary to the target sequence (5'-GAA GCA AGC TTC TCG TCC-3', namely SEQ ID NO:3).
[0049] (2) Design of Escherichia coli Molecular Beacon Probe Loop Se...
Embodiment 3
[0066]Embodiment 3: the method for detecting Staphylococcus aureus based on real-time fluorescent CSDPR
[0067] (1) Activation and enrichment culture of Staphylococcus aureus
[0068] Prepare nutrient agar (1L) before activating Staphylococcus aureus: 10g of peptone, 3g of beef extract powder, 5g of sodium chloride, 15g of agar, and the final pH is 7.3±0.2. After autoclaving at 121°C for 15 minutes, cool to about 45°C for pouring into a plate or pouring into a sterilized plate for solidification before use. Add 0.3mL of the supporting Staphylococcus aureus resuscitation solution dropwise to the freeze-dried strains, blow and suck repeatedly with a sterile dropper until the freeze-dried strains dissolve into a bacterial suspension; The suspension was inoculated on a nutrient agar plate, and the plate was placed in a 37°C constant temperature incubator and cultured upside down for 12 hours; prepare brain-heart infusion broth (BHI) medium (1L): tryptone 10g, sodium chloride 5g,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com