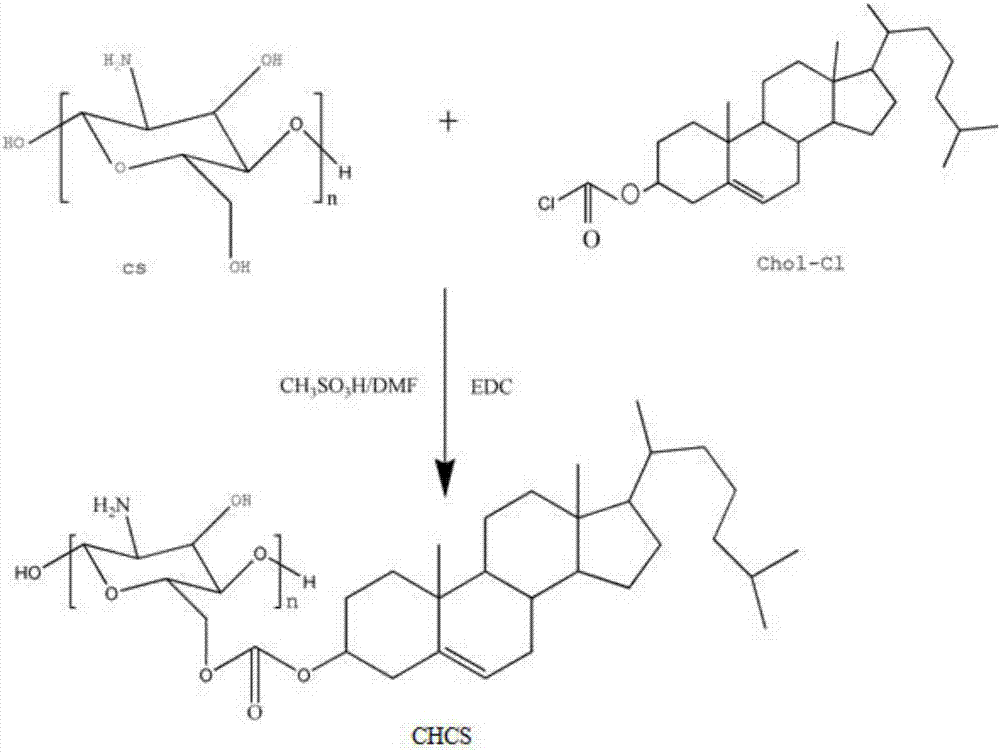
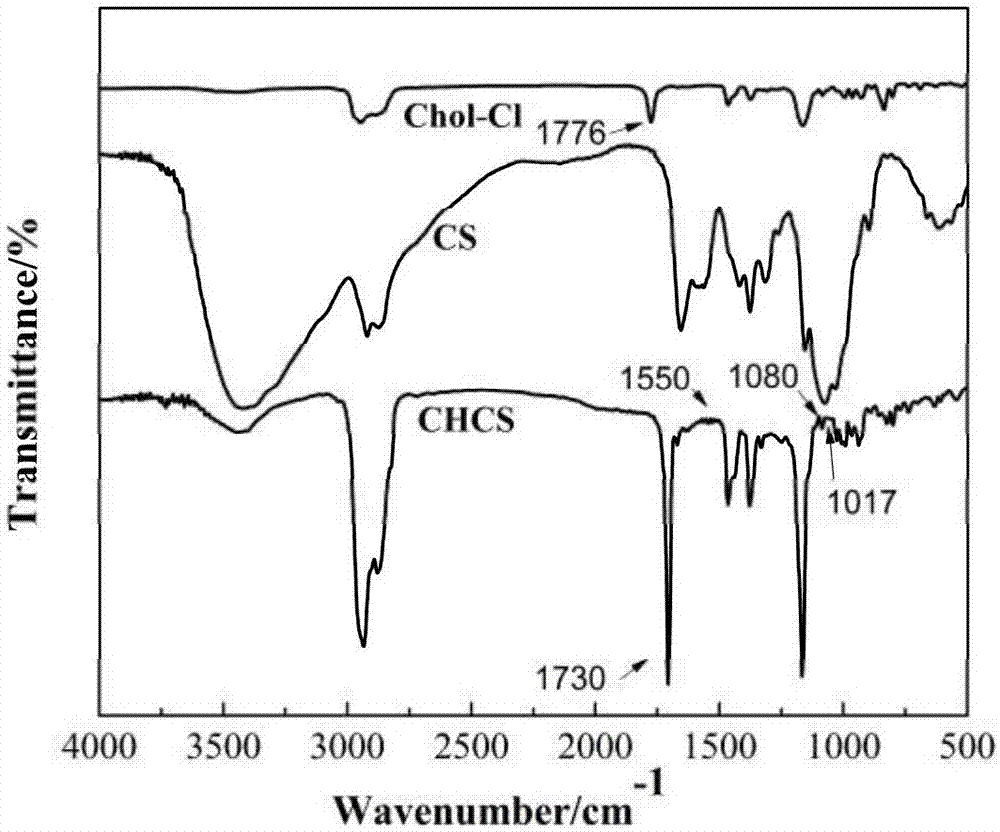
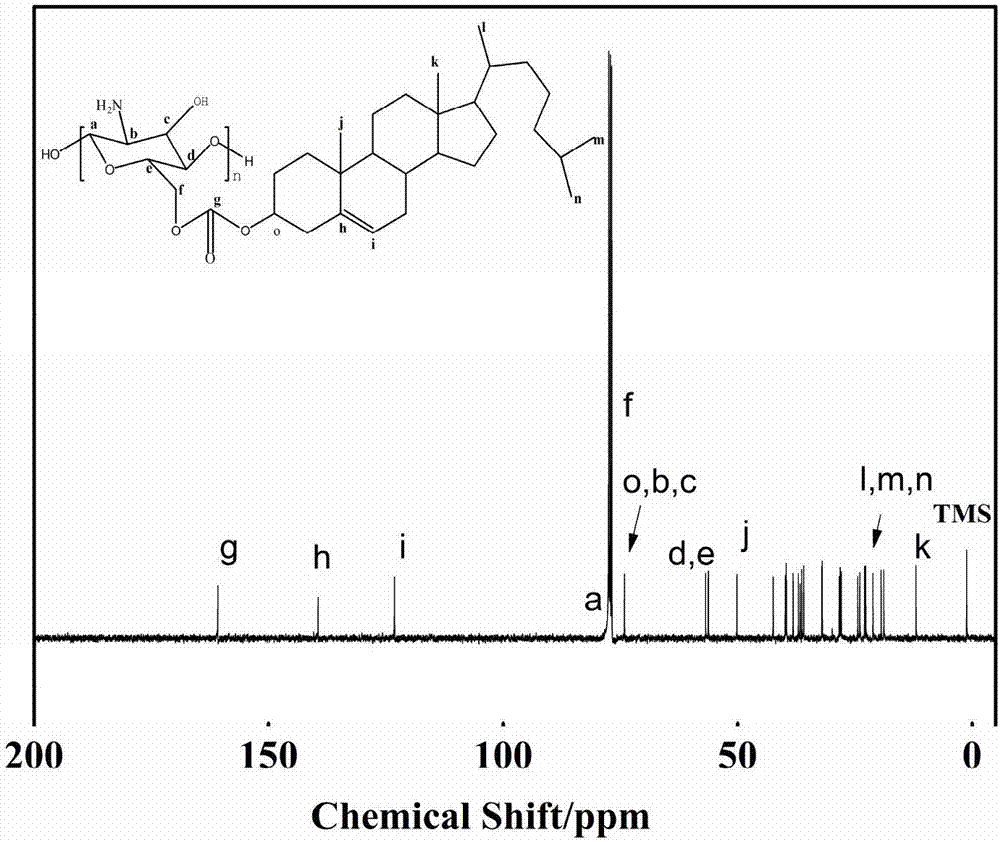
Preparation method and application of amphiphilic chitosan derivative protein adsorption-resistant coating
A technology of chitosan derivatives and proteins, which is applied in the fields of biomedical materials and polymer chemistry, can solve problems such as difficult fixation of solid surfaces, reduced mechanical strength, and difficulty in copolymerization, so as to improve amphiphilic properties, improve membrane properties, The effect of good application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] (1) Activation of cholesterol chloroformate
[0055] In a 250 mL round bottom flask, add 1.38 g cholesterol chloroformate (Chol-Cl), 100 mL sequentially N,N - Dimethylformamide (DMF) and 0.60 g of 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC), the reaction was stirred at 45 °C for 2 h to obtain no Color clear solution A;
[0056] (2) Synthesis of anti-protein amphiphilic cholesterol chitosan ester (CHCS)
[0057]In a 250 mL three-neck flask, add 1.0 g of chitosan, followed by 35 mL of methanesulfonic acid, seal it with nitrogen gas to remove oxygen, and stir until the chitosan is completely dissolved. The solution A in the reaction process continued to precipitate out, and the reaction was stirred at 45°C for 72 h. After the reaction, the above mixture is poured into a large amount of ice water, the product is washed after centrifugation, and then the obtained washed product is purified by chloroform dissolution-methanol precipitation, then suctio...
Embodiment 2
[0059] (1) Activation of cholesterol chloroformate
[0060] In a 250 mL round bottom flask, add 2.76 g cholesterol chloroformate (Chol-Cl), 100 mL N,N -Dimethylformamide (DMF) and 1.20 g 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC), the reaction was stirred at 45 ° C for 2 h to obtain Color clear solution A;
[0061] (2) Synthesis of anti-protein amphiphilic cholesterol chitosan ester (CHCS)
[0062] In a 250 mL three-necked flask, add 1.0 g of chitosan, followed by 35 mL of methanesulfonic acid, seal it with nitrogen gas to remove oxygen, and stir until the chitosan is completely dissolved. The solution A in the reaction process continued to precipitate out, and the reaction was stirred at 45°C for 72 h. After the reaction, the above mixture is poured into a large amount of ice water, the product is washed after centrifugation, and then the obtained washed product is purified by chloroform dissolution-methanol precipitation, then suction filtered, and ...
Embodiment 3
[0064] (1) Activation of cholesterol chloroformate
[0065] In a 250 mL round bottom flask, add 5.49 g cholesterol chloroformate (Chol-Cl), 100 mL N,N -Dimethylformamide (DMF) and 2.40 g 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC), the reaction was stirred at 45 ° C for 2 h to obtain Color clear solution A;
[0066] (2) Synthesis of anti-protein amphiphilic cholesterol chitosan ester (CHCS)
[0067] In a 250 mL three-necked flask, add 1.0 g of chitosan, followed by 35 mL of methanesulfonic acid, seal it with nitrogen gas to remove oxygen, and stir until the chitosan is completely dissolved. The solution A in the reaction process continued to precipitate out, and the reaction was stirred at 45°C for 72 h. After the reaction, the above mixture is poured into a large amount of ice water, the product is washed after centrifugation, and then the obtained washed product is purified by chloroform dissolution-methanol precipitation, then suction filtered, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com