Method for producing glyoxylate through oxydehydrogenation of glycollate
A technology of glycolic acid ester and glyoxylic acid ester is applied in the field of oxidative dehydrogenation of glycolic acid ester to produce glyoxylic acid ester, and can solve the problems of low yield of glyoxylic acid ester and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
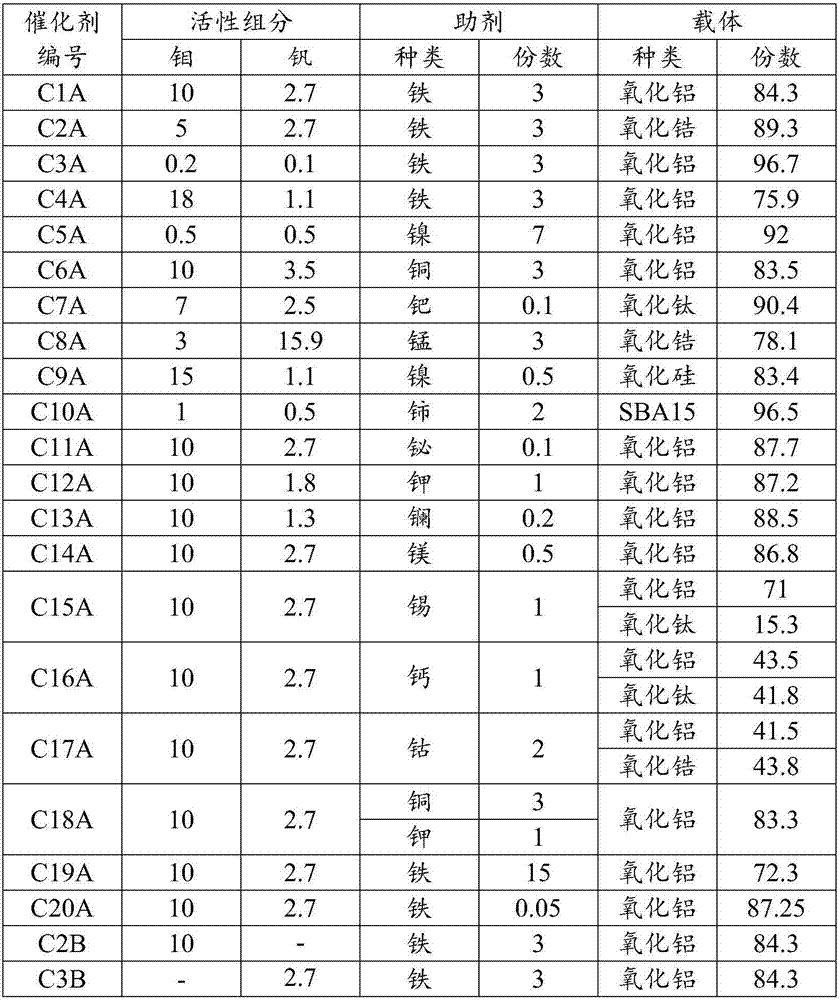
[0030] Prepare 100ml of ammonium molybdate and ammonium metavanadate aqueous solution I containing 12.5% molybdenum and 3.4% vanadium, add 84g of alumina carrier, and stir for 5 hours to obtain slurry II; then mix 100ml of nitric acid containing 4% iron under stirring Slowly add the iron solution to the slurry II, stir for 2 hours, pour the slurry into a 500ml autoclave, and place it at 180°C for 15 hours, then cool and filter, wash with deionized water, dry at 100°C, and dry at 250°C Calcined for 4 hours, and then pressed into tablets to obtain catalyst CA1. The catalyst samples were taken for X-fluorescence (XRF) characterization test to determine the catalyst components as shown in Table 1.
[0031] Take by weighing 6g catalyzer in fixed bed reactor, adopt NO and air and methyl glycolate as raw material, wherein the oxygen molar ratio contained in NO and air is 6, and the oxygen and methyl glycolate molar ratio in air is 0.8, in The reaction temperature is 80°C, the react...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Prepare 100ml of ammonium molybdate and ammonium metavanadate aqueous solution I containing molybdenum 6.3%, vanadium 3.4, add 90g zirconia carrier, stir for 5 hours to obtain slurry II; then mix 100ml iron nitrate containing 4% iron under stirring Slowly add the solution to the slurry II, stir for 2 hours, pour the slurry into a 500ml autoclave, and place it at 180°C for 15 hours, then cool and filter, wash with deionized water, dry at 100°C, and roast at 250°C After 4 hours, the catalyst CA2 was obtained by pressing into tablets, and the catalyst samples were taken for X-fluorescence (XRF) characterization test to determine the catalyst components as shown in Table 1.
[0034] Weigh 6g of catalyst in a fixed-bed reactor and react according to the conditions of [Example 1]. The reaction results are shown in Table 2.
Embodiment 3
[0036] Prepare 100ml of ammonium molybdate and ammonium metavanadate aqueous solution I containing 0.25% molybdenum and 0.2 vanadium, add 97g of alumina carrier, stir for 5 hours to obtain slurry II; then mix 100ml of ferric nitrate containing 4% iron under stirring Slowly add the solution to the slurry II, stir for 2 hours, pour the slurry into a 500ml autoclave, and place it at 180°C for 15 hours, then cool and filter, wash with deionized water, dry at 100°C, and roast at 250°C After 4 hours, the catalyst CA3 was obtained by pressing into tablets, and the catalyst samples were taken for X-fluorescence (XRF) characterization test to determine the catalyst components as shown in Table 1.
[0037] Weigh 6g of catalyst in a fixed-bed reactor and react according to the conditions of [Example 1]. The reaction results are shown in Table 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com