Patents
Literature
86 results about "Glyoxylates" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
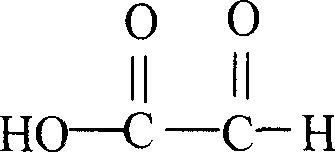
Derivatives of glyoxylic acid (the structural formula C2H2O3), including its salts and esters.
Sheet polarizer and a fabricating method thereof
ActiveCN101813799ANot inferior to polarization performanceHigh degree of polarizationPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsTectorial membraneAlkaline earth metal
This invention provides a sheet polarizer,including polyvinyl alcohols polarizing film, sticking agent layer separated from polyvinyl alcohols polarizing film through at least on face and overlapped with protect film. Said sticking agent layer is comprised of sticking agent components containing followed water solution. Said water solution contains acetyl modified PVA resin and glyoxylate indicated by formula (I) and has a pH valve ranged in 4-10. where, the content of acetyl modified PVA resin is 1-8%( percentage by weight) compared to the 100% water(percentage by weight), the weight ratio of acetyl modified PVA resin with the solid glyoxylate is in the range of 1:0.03-0.25. in formula (I) , M represents alkali metals or alkaline-earth metals, n represents valence mumber correspond to M, indicating 1 or 2. According to said sheet polarizer, sticking property together with warm water resistance between the polarizing film and the protect film are improved.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD +1
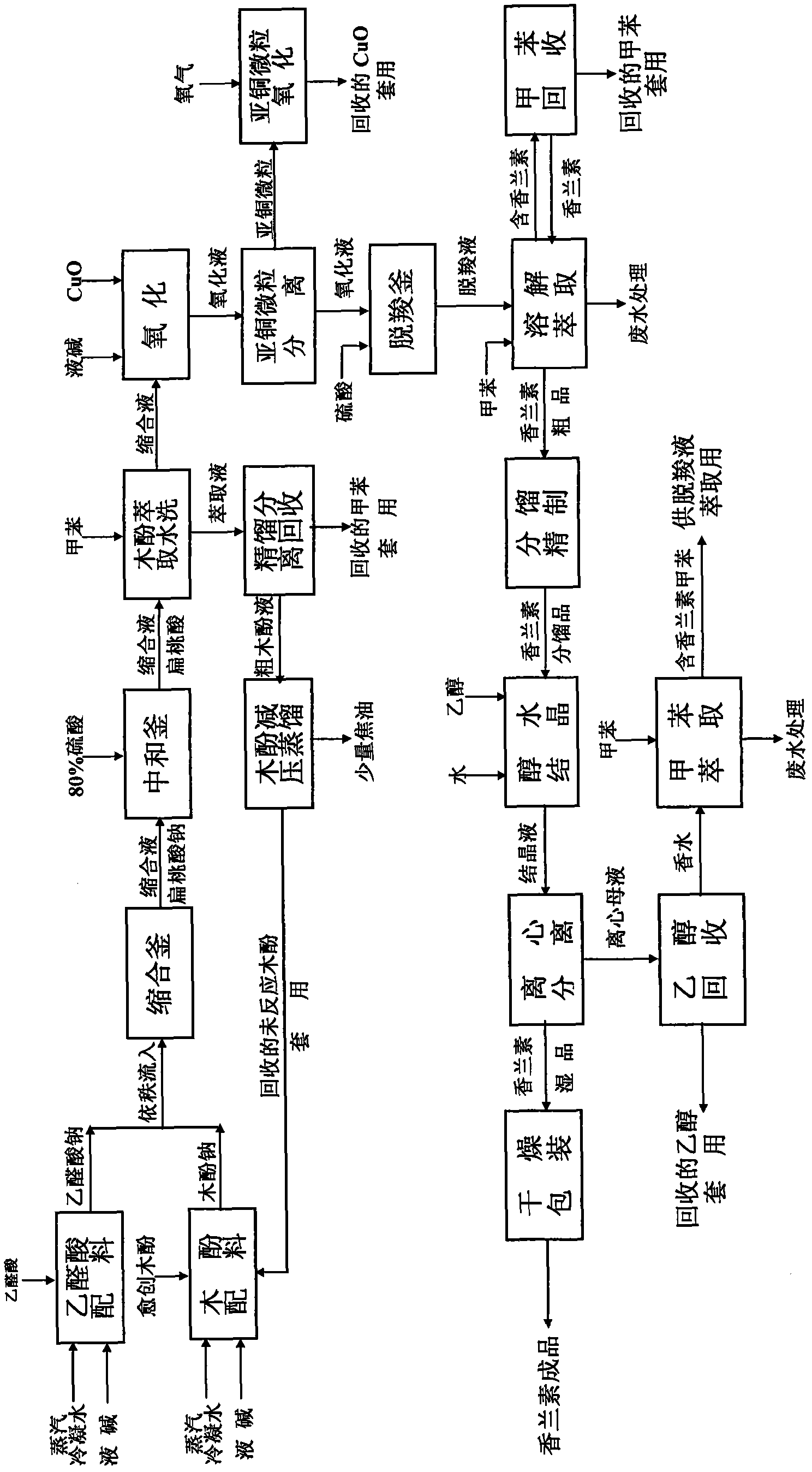
Productive technology of vanlillin by glyoxylic acid method
ActiveCN102010310AReduce organic contentReduce pollution sourcesOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound separation/purificationKetonic acidsFractionation
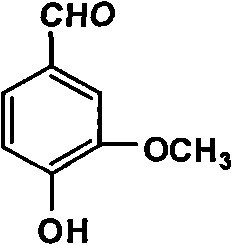
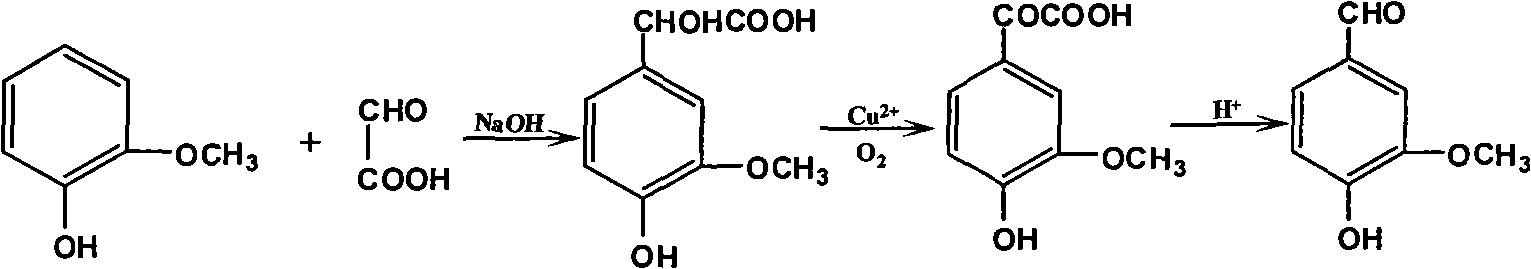
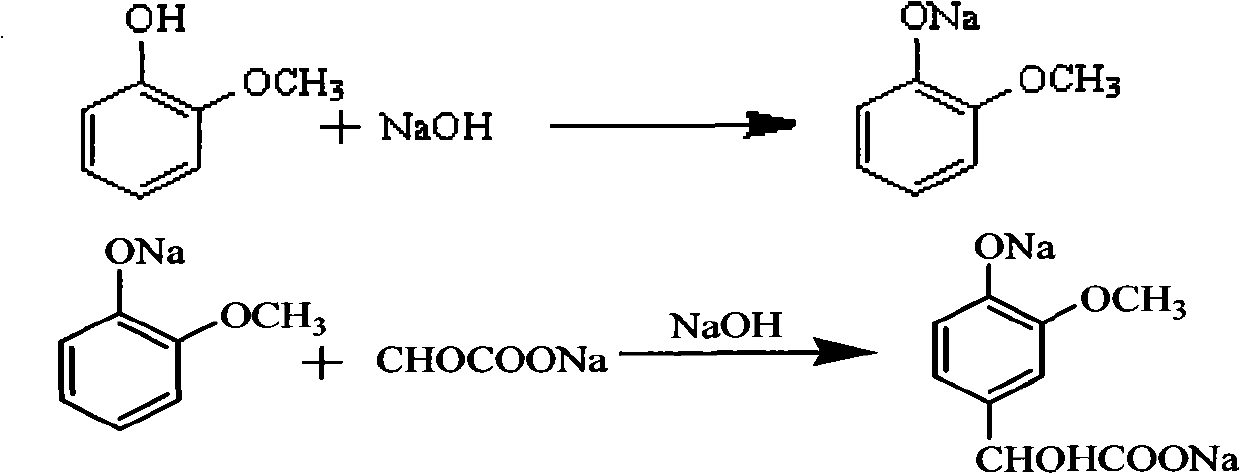
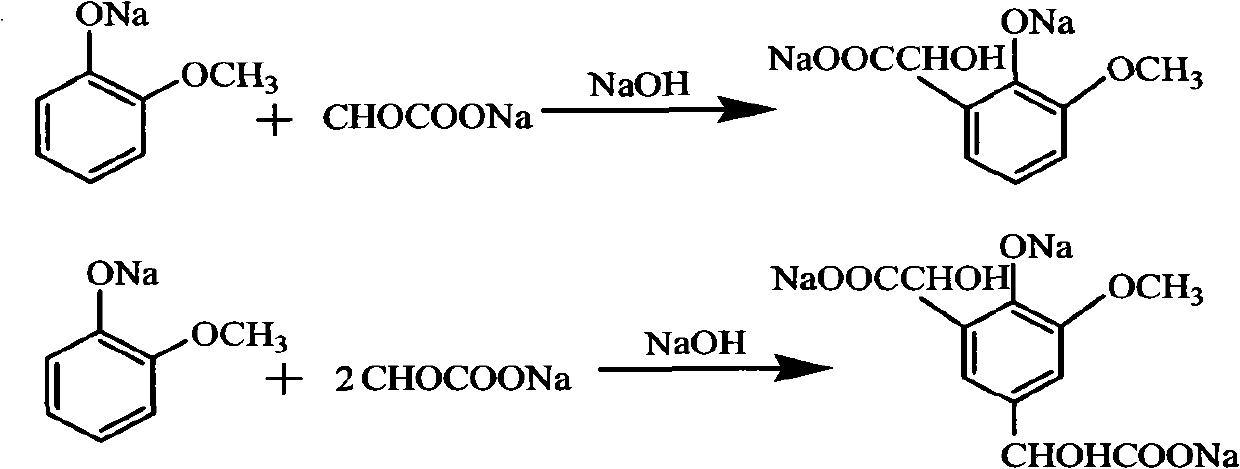
The invention discloses a productive technology of vanlillin by a glyoxylic acid method. The productive technology comprises a synthesis process, a fractionation process and a purification process, wherein the synthesis process comprises condensation treatment, oxidation treatment and decarboxylation treatment of methyl catechol and glyoxylic acid. The productive technology particularly comprisesthe following steps: respectively converting the methyl catechol and the glyoxylic acid into guaiacol sodium and sodium glyoxylate in a sodium hydroxide system; carrying out condensation treatment onthe guaiacol sodium and the sodium glyoxylate; after recovering the unreacted methyl catechol in a condensation liquid, carrying out oxidation treatment, namely carrying out catalytic oxidation on anethanol group in 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzene sodium glycolate by using copper oxide in the sodium hydroxide system to form a ketone group, thereby generating a corresponding ketonic acid compound; after separating red copper oxide particles from an oxidation liquid, carrying out decarboxylation treatment, namely using sulfuric acid to acidize the oxidation liquid, and simultaneously converting an acid group in the ketonic acid compound into carbon dioxide so as to generate 4-hydroxy-3- methoxybenzaldehyde; and carrying out the fractionation process and the purification process to obtain the vanlillin.
Owner:喜孚狮王龙香料(宁波)有限公司
Method for producing glyoxylate through oxydehydrogenation of glycollate
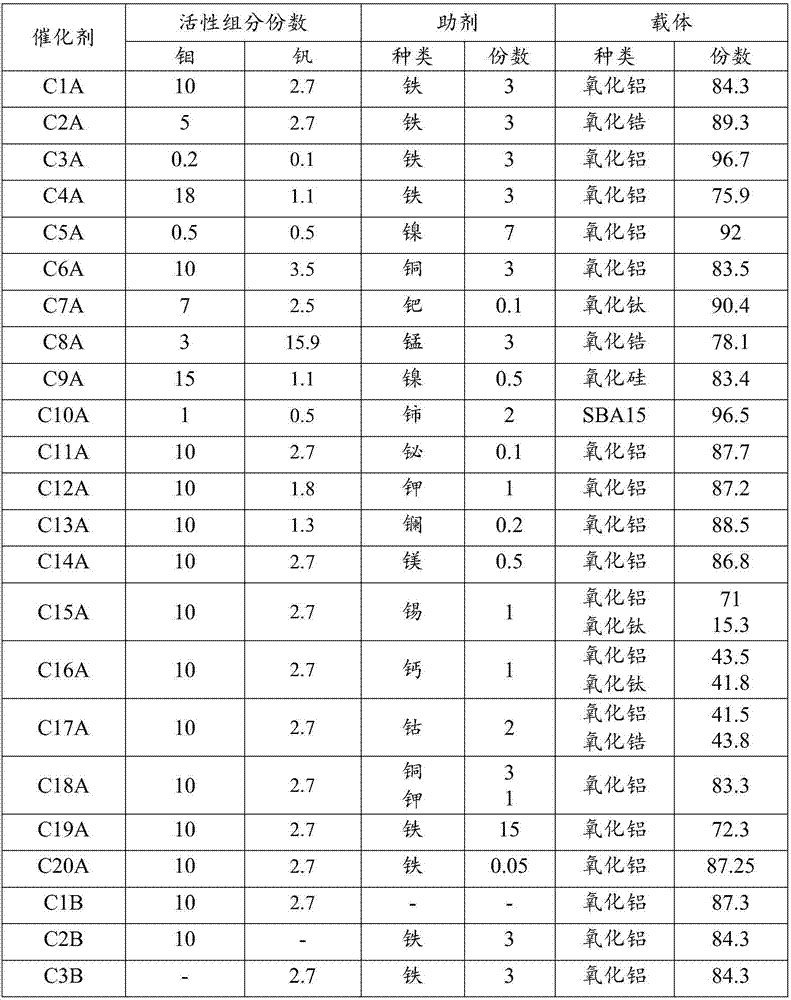
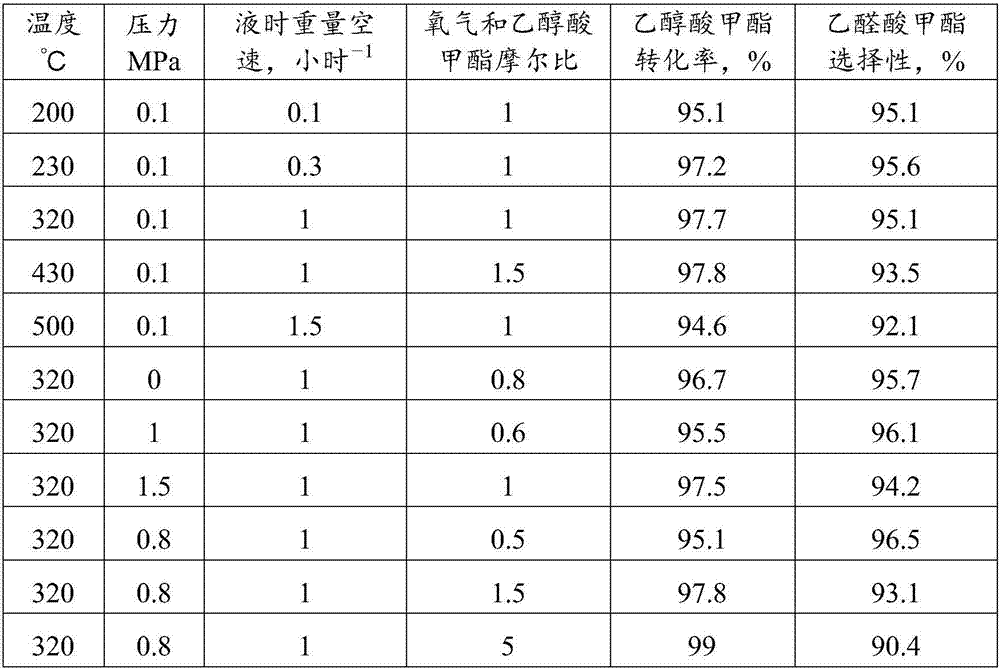
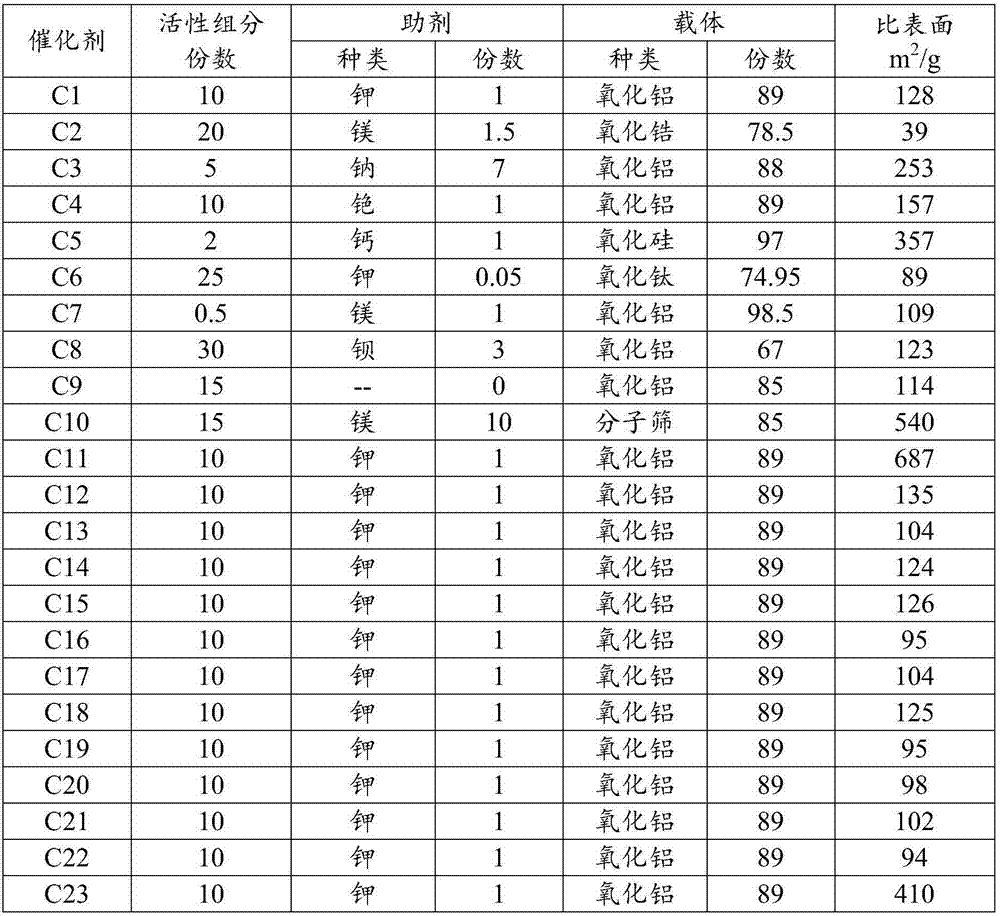
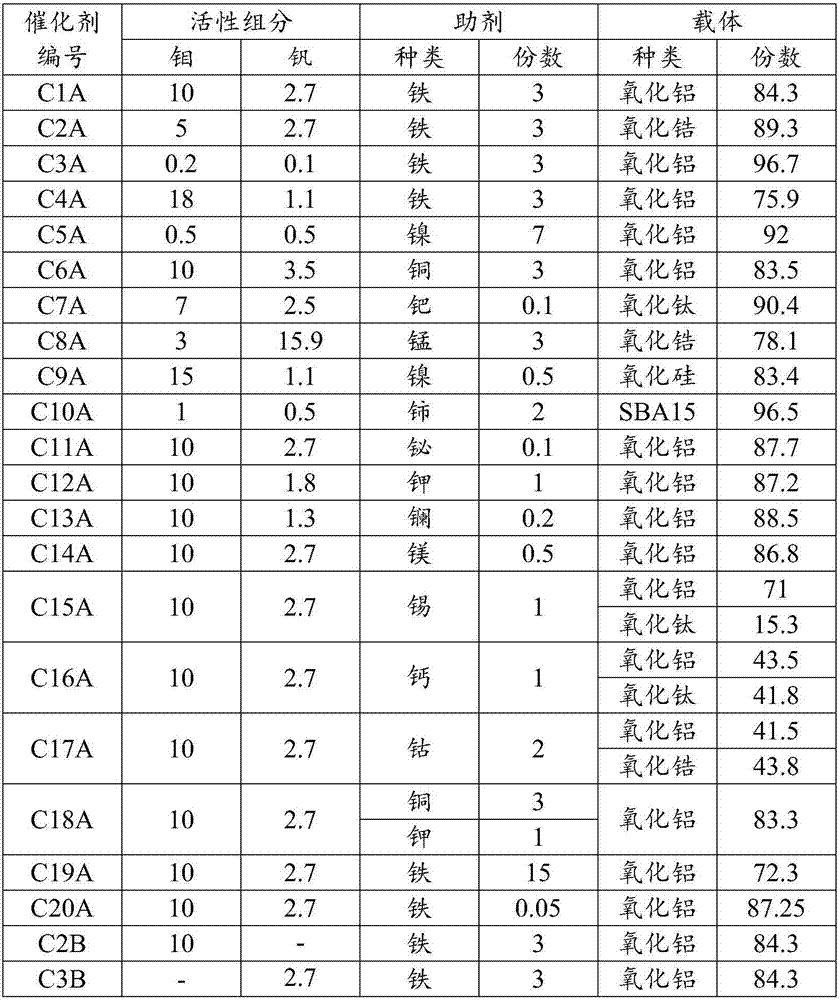
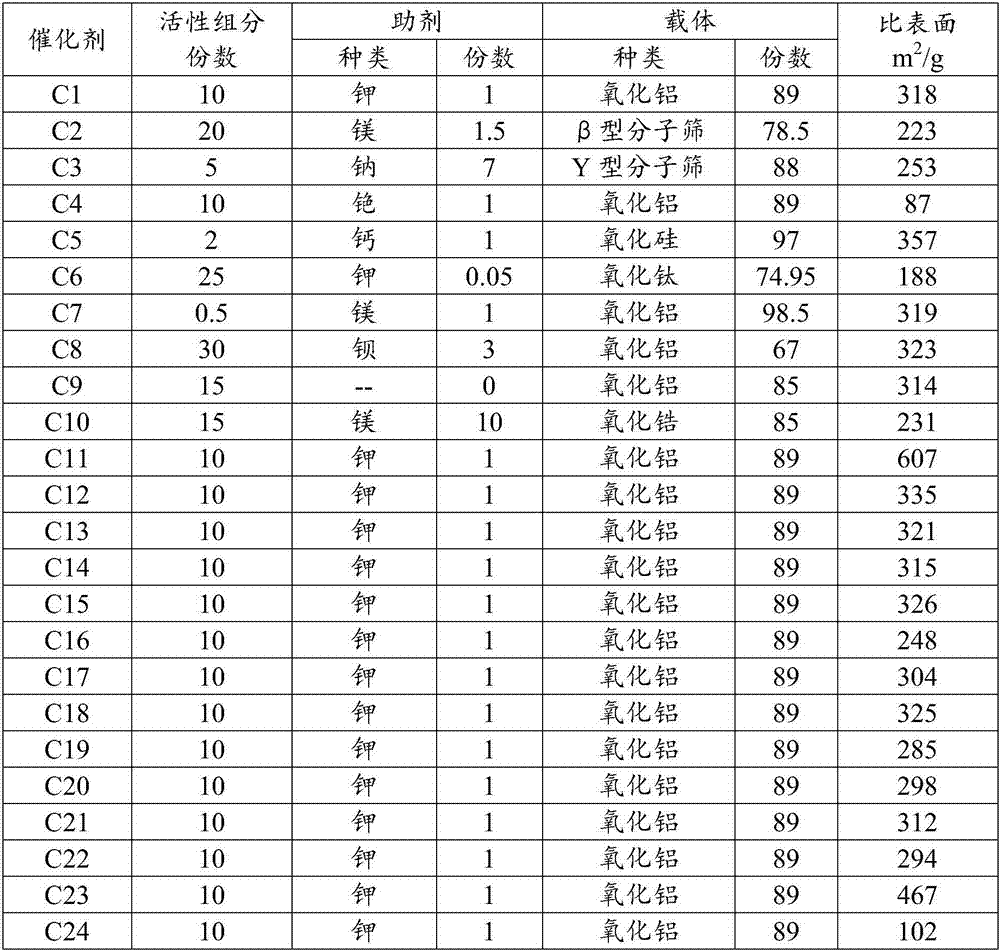
The invention relates to a method for producing glyoxylate through oxydehydrogenation of glycollate. The invention mainly aims to overcome the problem of low selectivity of glyoxylate in the prior art. The method provided by the invention comprises a reaction step of contacting oxygen-containing gas with glycollate in the presence of a catalyst to produce glyoxylate. The catalyst comprises the following components by weight: a) 0.3 to 20 parts of a mixture of molybdenum and vanadium; b) 0.05 to 15 parts of at least one selected from a group consisting of copper, palladium, manganese, nickel, cerium, bismuth, potassium, lanthanum, magnesium, tin, iron, calcium and cobalt; and c) 65 to 99.8 parts of a carrier. With such a technical scheme, the above problem is overcome, and the method is applicable to industrial production of glyoxylate through oxydehydrogenation of glycollate.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Novel red BODIPY fluorescent dye and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102702768ANarrow absorbencyNarrow fluorescence emission spectrumMethine/polymethine dyesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical reaction1,4-Benzoquinone
The invention relates to a novel red BODIPY fluorescent dye with the chemical formula of C10+mH7+nBF2N2+xOy, wherein m, n, x and y are integers from 0 to 100. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving pyrrole with substituent groups R1, R2 and R3 in an organic solution; adding ethyl glyoxylate together with nitrogen to the organic solution for a chemical reaction by using trifluoroacetic acid or toluenesulfonic acid as a catalyst; adding 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone oxidative dehydrogenation; and adding organic amine and a boron trifluoride diethyl ether solution for another reaction. After the reaction solution is concentrated, chromatography is performed with a silicagel column to obtain the fluorescent dye. The fluorescent dye can be used for cell imaging, fluorescent probe or laser dye. The fluorescent dye has the advantages that the ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum and the fluorescence emission spectrum of the fluorescent dye are narrow; fluorescent quanta has high efficiency and good light stability; and the fluorescent dye has simple molecular structure and can be synthesized easily, so as to facilitate popularization and application.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing 3-methoxy-4-hydroxy mandelic acid
ActiveCN102086151APrevent oxidationIncrease profitOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationReaction temperatureGuaiacol
A method for preparing 3-methoxy-4-hydroxy mandelic acid adopts guaiacol and glyoxylic acid as raw materials, and comprises the following steps: slowly adding a 30 wt% sodium hydroxide solution into the glyoxylic acid solution with stirring, allowing the mixed solution to react at a reaction temperature of 0-50 DEG C and a pH value of 1-7 to obtain a sodium glyoxylate solution; adding the guaiacol into water with stirring and under the protection of nitrogen gas, slowly adding the 30 wt% sodium hydroxide solution, allowing the mixed solution to react at a reaction temperature of 0-50 DEG C and a pH value of 11-12 to obtain guaiacol sodium; slowly and dropwisely adding the sodium glyoxylate solution into the guaiacol sodium solution with stirring and under the protection of nitrogen gas, with the mole ratio of the sodium glyoxylate and the guaiacol sodium being 1:1.2-2, allowing the mixed solution to react at a reaction temperature of 0-20 DEG C and a pH value of 11-12, 30-90 min afterthe dropwise addition, stirring the mixed solution for 1-3 hours, stopping the reaction at the reaction temperature for 24-36 hours, then acidifying the reaction solution by a 50 wt% sulfuric acid solution to control the pH value to be 4-5. The yield of the reaction is above 95 wt%.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
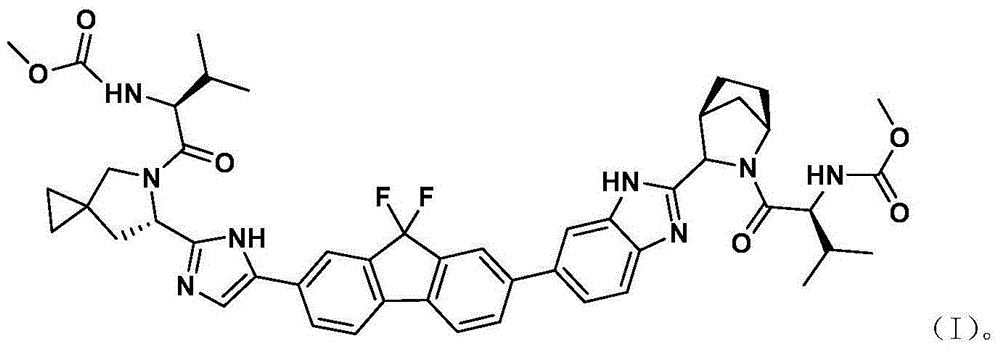
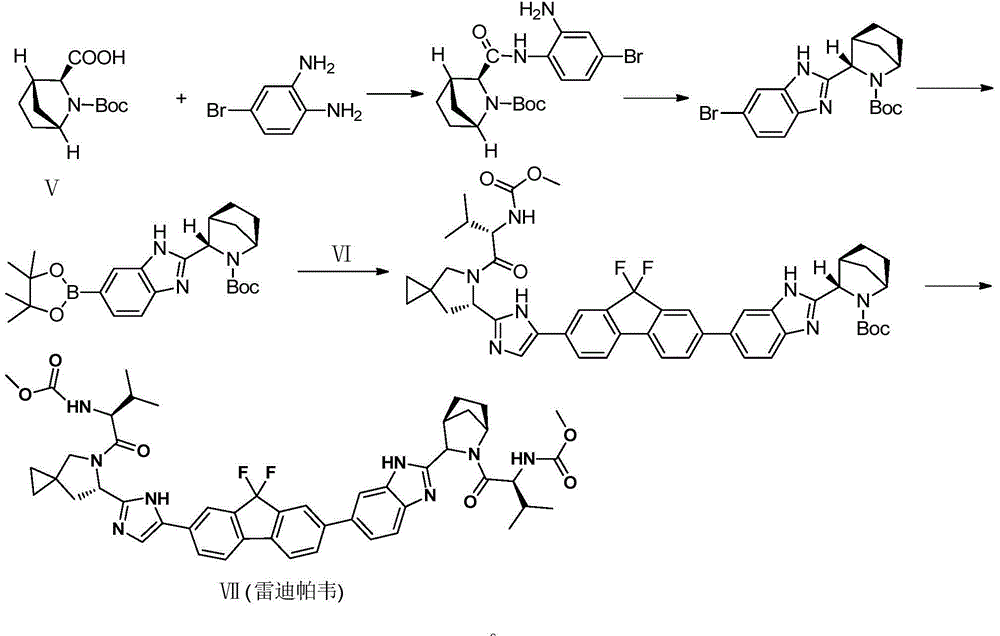
Ledipasvir intermediate preparation method
ActiveCN104478877AEasy to operateEasy to separate and purifyOrganic chemistryTert-Butyloxycarbonyl protecting groupCarboxylic acid
The invention relates to a method for preparing (1R,3S,4S)-N-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-2-azabicyclo[2,2,1]heptane-3-carboxylic acid (formula V), wherein the formula V is defined in the instruction. The method comprises: dissolving glyoxylate in a solvent, cooling to a temperature of -10-0 DEG C, adding a dewatering agent and (R)-phenyl ethylamine, and at unit time intervals, sequentially adding an alcohol solvent, an additive, cyclopentadiene and palladium carbon to carry out catalytic hydrogenation and adding an inorganic alkali aqueous solution and Boc anhydride to carry out a reaction. Compared with the method in the prior art, the method of the present invention has the following significant advantages that: the reaction operation is simple, the multi-step reaction is changed into the one-pot method, the production period is shortened, the separation purification is simple, the single configuration target product can be obtained only requiring the recrystallization, the yield is high, the reaction is efficient, the atom economy is reflected, -78 DEG C and other harsh reaction conditions are abandoned, and the method is expected to be used in mass production.
Owner:SUNSHINE LAKE PHARM CO LTD
Method for synthesizing glyoxylate through oxidation of glycollate
ActiveCN107445833AHigh yieldImprove conversion rateMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic compound preparationActive componentOxygen
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing glyoxylate through oxidation of glycollate. The invention mainly aims to overcome the problem of low selectivity of glyoxylate in the prior art. The method provided by the invention comprises a reaction step of contacting oxygen-containing gas with glycollate in the presence of a catalyst to produce glyoxylate. The catalyst comprises the following components by weight: a) 0.5 to 30 parts of at least one active component selected from a group consisting of iron and iron oxides; b) 0 to 10 parts of an auxiliary agent which is at least one metal selected from a group consisting of group IA or group IIA elements or oxides thereof; and c) 70 to 99 parts of a carrier. With such a technical scheme, the above problem is overcome, and the method is applicable to industrial production of glyoxylate through oxidation of glycollate.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for producing glyoxylate through oxydehydrogenation of glycollate
The invention relates to a method for producing glyoxylate through oxydehydrogenation of glycollate. The invention mainly aims to overcome the problem of low yield of glyoxylate in the prior art. The method provided by the invention comprises a reaction step of contacting a nitrogen oxide and oxygen-containing gas with glycollate in the presence of a catalyst to produce glyoxylate. The catalyst comprises the following components by weight: a) 0.3 to 20 parts of a mixture of molybdenum and vanadium; b) 0.05 to 15 parts of at least one metal selected from a group consisting of copper, palladium, manganese, nickel, cerium, bismuth, potassium, lanthanum, magnesium, tin, iron, calcium and cobalt; and c) 65 to 99.8 parts of a carrier. With such a technical scheme, the above problem is overcome, and the method is applicable to industrial production of glyoxylate through oxydehydrogenation of glycollate.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Diesel lubircant low in sulfur and phosphorus
ActiveUS20060205614A1Improve anti-wear performanceImprove performanceLiquid carbonaceous fuelsAdditivesSulfurSulfate
A low-sulfur, low-phosphorus composition comprising an oil of lubricating viscosity; a substantially nitrogen-free sufurized olefin antiwear agent; a nitrogen-containing dispersant; and an overbased detergent selected from the group consisting of salixarates, saligenins, salicylates, and glyoxylates; containing less than about 0.1 percent by weight phosphorus, less than about 0.5 percent by weight sulfur, and having less than about 1.2% sulfated ash, is useful for lubricating a diesel engine, exhibiting good antiwear performance.
Owner:THE LUBRIZOL CORP
Method for preparing ethanol acid by catalytic oxidation of biformyl
InactiveCN101462946AImprove conversion rateHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMicrosphereNiobium
The invention discloses a method for preparing glyoxylate by catalytic oxidation of oxalic aldehyde; in the method, 20-100 mesh microballoon silochrom are added into aqueous solution which is composed of ammonium metavanadate, niobium ammonium oxalate and ammonium dichromate for being soaked, and activated under the protection of nitrogen, thus preparing a catalyst; the oxalic aldehyde water solution is used as raw material, oxygen is led in in the presence of the catalyst in the invention, and catalytic oxidation reaction is carried out by pressurizing, thus obtaining the target product of glyoxylate in the invention. The yield of the glyoxylate obtained by the method can be more than or equal to 57 percent in a single reaction and the purity is more than 99 percent. Compared with the prior art, the conversion rate of the oxalic aldehyde and the productive rate of the glyoxylate are improved, the product purity is high and the quality is stable, thus being suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAYI GRP CO
Adhesion agent composition used in polarizer and polarizer utilizing the adhesion agent composition
ActiveCN102373024AInhibitionExcellent adhesionNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesLayered productsSolid componentAlkaline earth metal
The invention provides an adhesion agent composition used in a polarizer and a polarizer utilizing the adhesion agent composition having an excellent adhesiveness and a risen warm water resistance, and capable of restraining a knick point to be generated. The adhesion agent composition used in the polarizer comprises a polyvinyl alcohol resin modified from acetoacety, water, an alcohol solvent of which the boiling point is below 100 DEG C, and a glyoxylate represented by the following chemical formula. Relative to 100 parts of water(by weight), the adhesion agent composition used in the polarizer comprises 1-8 parts(by weight) of polyvinyl alcohol resin modified from acetoacety, the weight ratio of the polyvinyl alcohol resin modified from acetoacety and a solid component of the glyoxylate is 1:0.03 to 1:0.25, the weight ratio of the water and the alcohol solvent is 99:1 to 30:70, and the PH value is between 4 to 10; in the formula, M represents an alkali metal or an alkaline-earth metal, n is 1 or 2.
Owner:DONGWOO FINE CHEM CO LTD
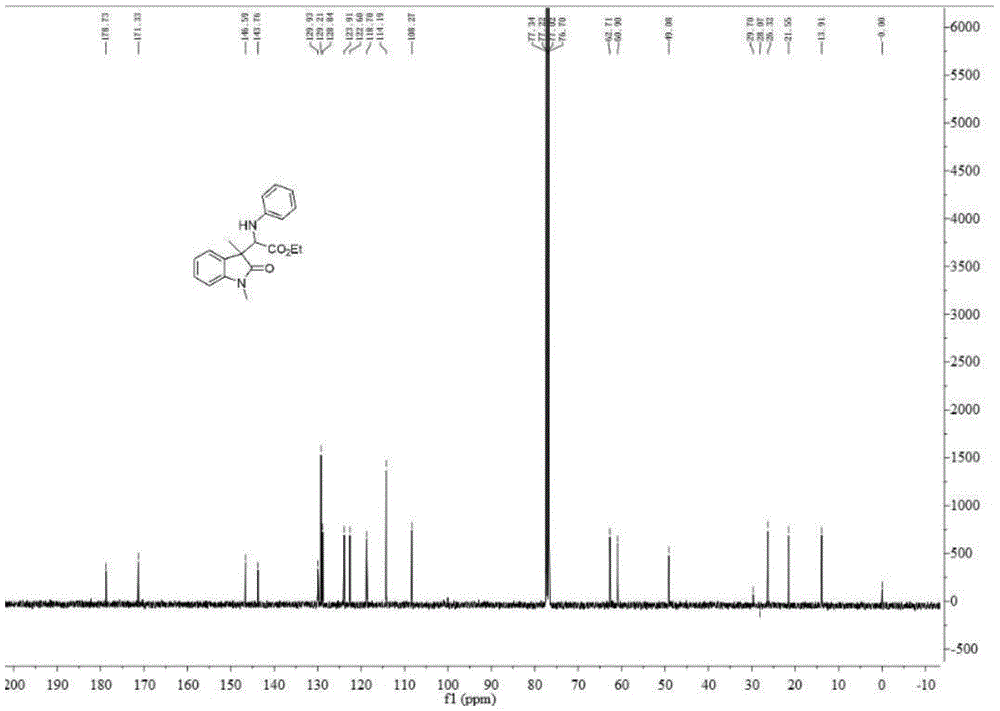
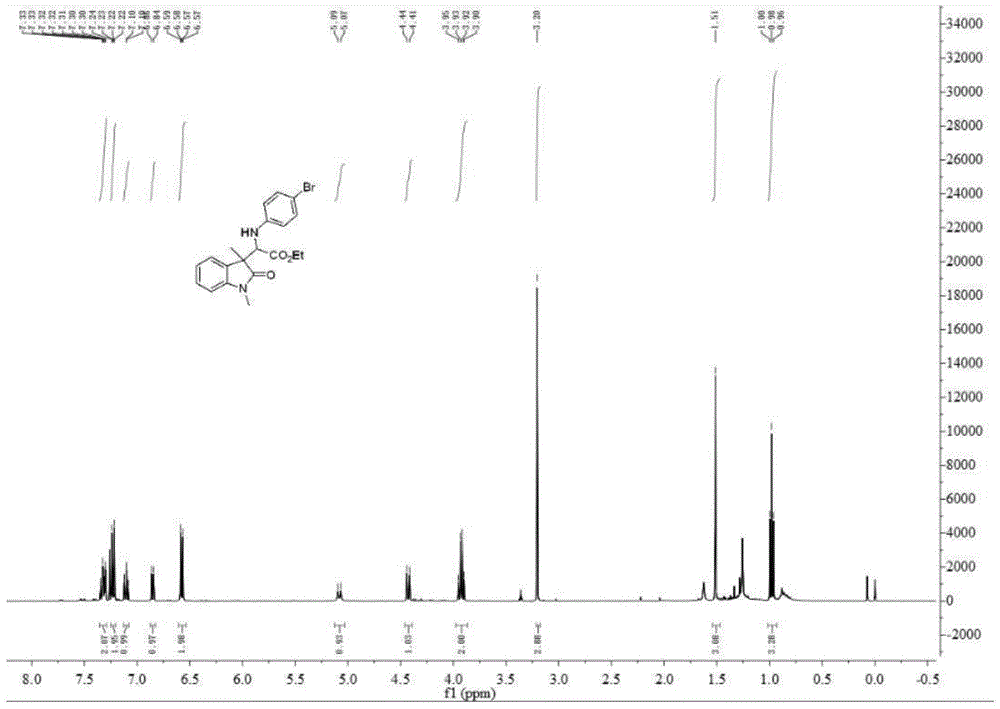
3-substituted oxindole derivatives, and synthetic method and application thereof
InactiveCN104402793AGood inhibitory effectWide range of substratesOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsChemical synthesisSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a kind of 3-substituted oxindole derivatives, and a synthetic method and application thereof. The synthetic method comprises: taking a diazo compound, an aryl amine and a glyoxylate as raw materiasl, taking a 4A molecular sieve as a water adsorber, taking BINOL phosphoric acid and allylpalladium chloride as a co-catalyst, taking an organic solvent as a solvent, and performing one-step reaction, so as to obtain the product. The method has the advantages of high atomic economy, high yield, mild reaction conditions, simple and safe operation, and the like. The 3-substituted oxindole derivatives each with two chiral centers can be taken as important chemical engineering and medicinal intermediates, and have wide application prospect in the field of pharmaceutical chemical engineering.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
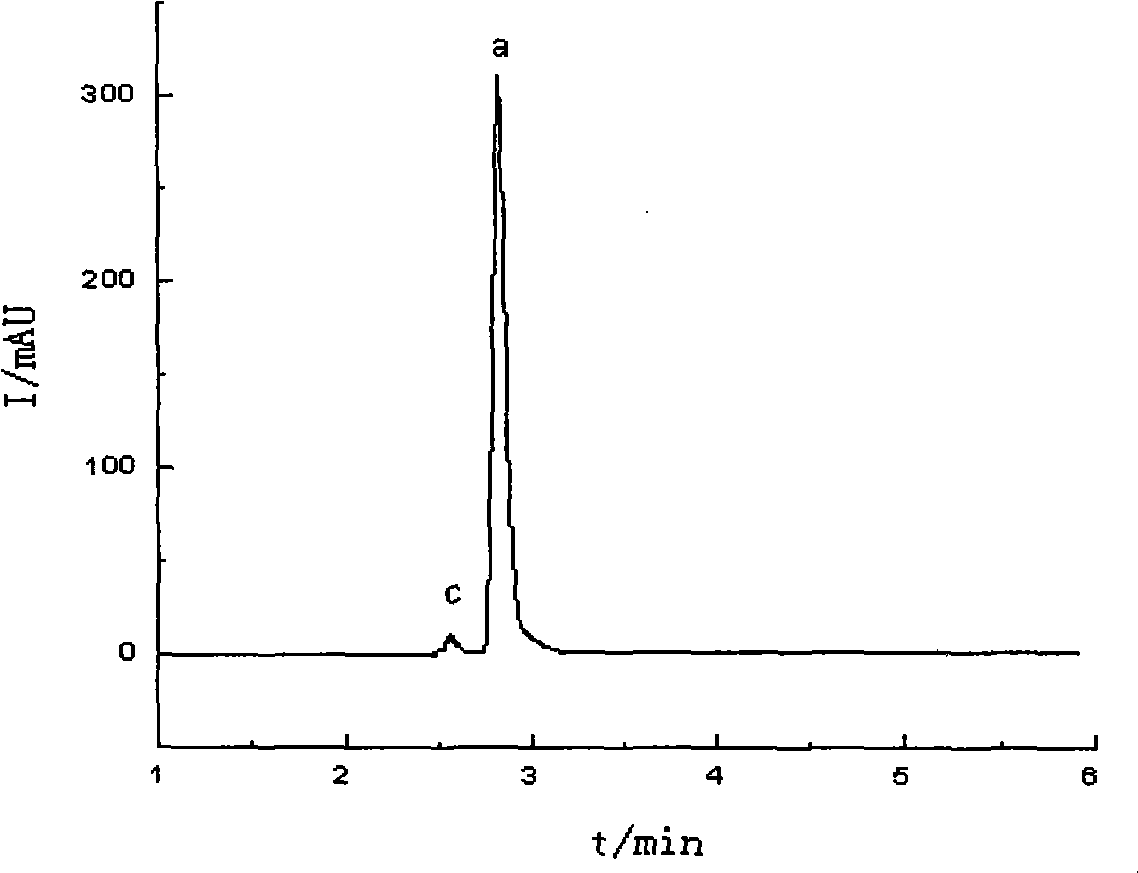
High performance liquid chromatography analysis method for oxalic aldehyde and glyoxalic acid
InactiveCN101509903ASensitive detectionHigh degree of automationComponent separationWater bathsColumn temperature
The invention relates to a high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analytical method of glyoxal and glyoxylate comprising the following specific detection steps of: taking proper amount of samples; adding DNPH, the mole ratio of which to the aldehyde group is 2:1 to 50:1, as a derivative reagent; adjusting the pH to 1.5 to 3 by using weak-acid salt solution; reacting in thermostatic water bath at 30 to 80 DEG C for 60 to 240 minutes; and analyzing the obtained derivative by using HPLC with the ultraviolet detection wavelength of 400-500 nm. The HPLC analysis conditions are as follows: the mobile phase is acetonitrile and aqueous solution, with the volume ratio of 95 / 5 to 50 / 50; the flow rate is 0.6 to 2ml / min; the column temperature is 20 to 50 DEG C; and the sample size is 1 to 20 Mu L. The HPLC analytical method of glyoxal and glyoxylate has the advantages of high degree of automation, high selectivity, sensitive detection, high efficiency and accuracy and the like. Experimental results show that the acetaldehyde, acetic acid and oxalic acid can not generate mutual interference to the detection of the glyoxal and glyoxylate.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for producing glyoxylate through oxidation of glycollate
The invention relates to a method for producing glyoxylate through oxidation of glycollate. The invention mainly aims to overcome the problem of low yield of glyoxylate in the prior art. The method provided by the invention comprises a reaction step of contacting a nitrogen oxide and oxygen-containing gas with glycollate to produce glyoxylate. A catalyst used in the invention comprises the following components by weight: a) 0.5 to 30 parts of at least one active component selected from a group consisting of iron and iron oxides; b) 0 to 10 parts of an auxiliary agent which is at least one metal selected from a group consisting of group IA or group IIA elements or oxides thereof; and c) 70 to 99 parts of a carrier. With such a technical scheme, the above problem is overcome, and the method is applicable to industrial production of glyoxylate through oxidation of glycollate.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Recombinant microorganism having ability to produce [lactate-co-glycolate] copolymer from glucose, and method for preparing [lactate-co-glycolate] copolymer using same
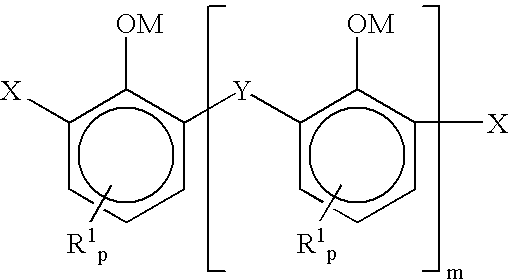
There is provided a recombinant microorganism having producibility of poly(lactate-co-glycolate) from glucose, and more particularly, a recombinant microorganism having producibility of poly(lactate-co-glycolate) without adding an exogenous glycolate precursor, and a method of preparing [poly(preparing lactate-co-glycolate)] using the same. According to the present invention, the poly(lactate-co-glycolate) in which the concentration of the glycolate fraction is high may be prepared at a high concentration without supplying exogenous glyoxylate. Therefore, the present invention may be effectively used for treatment.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +1
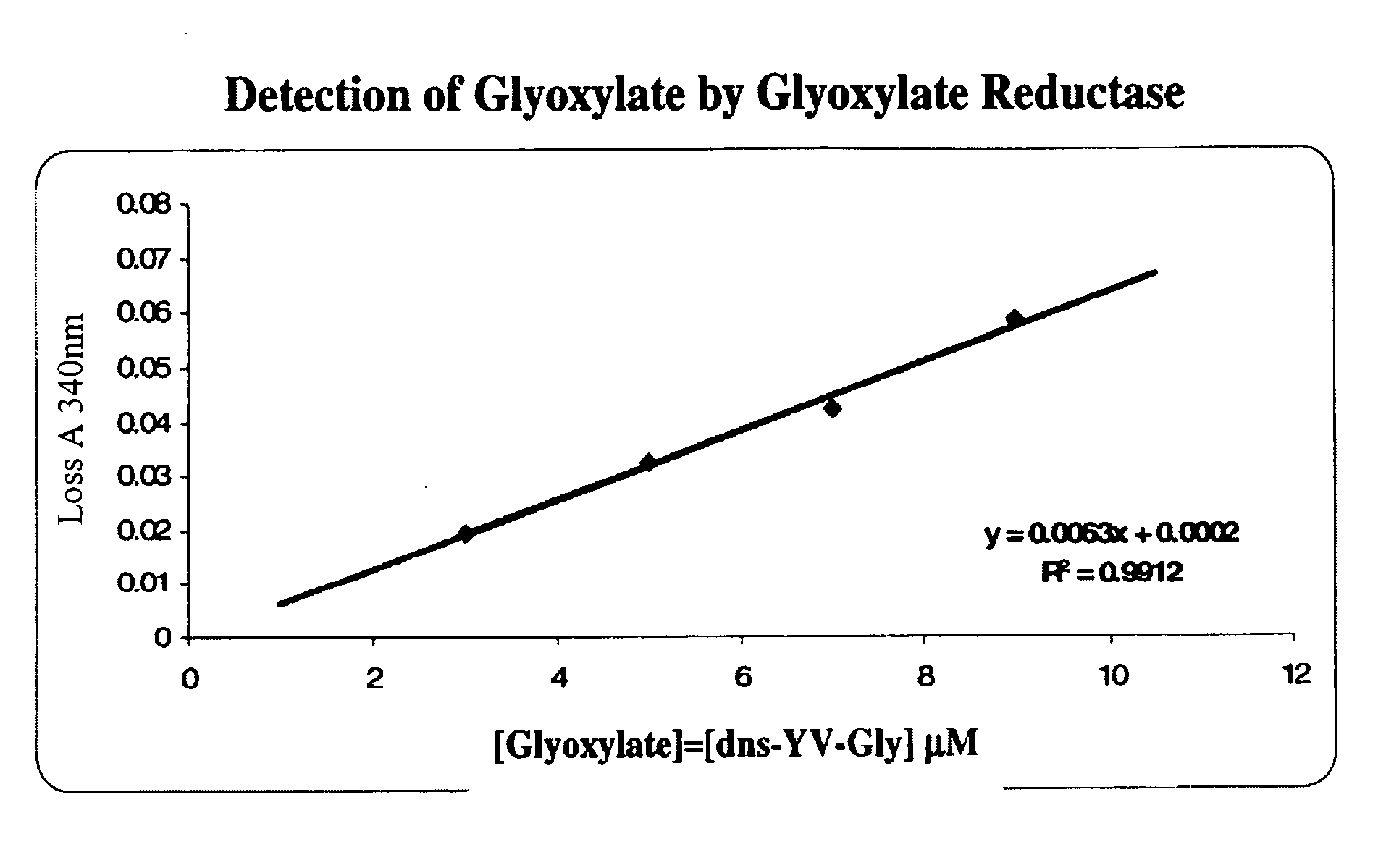
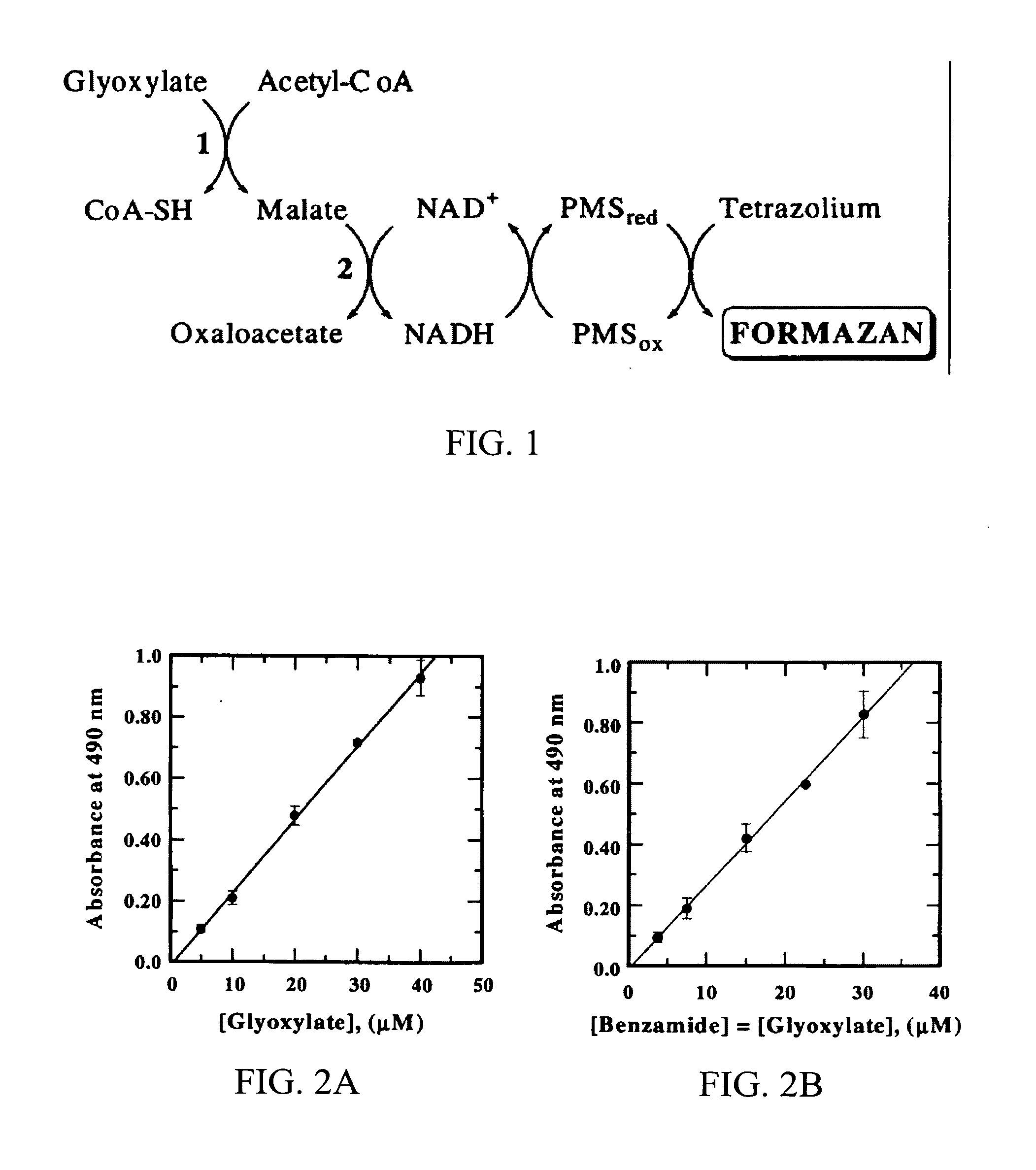
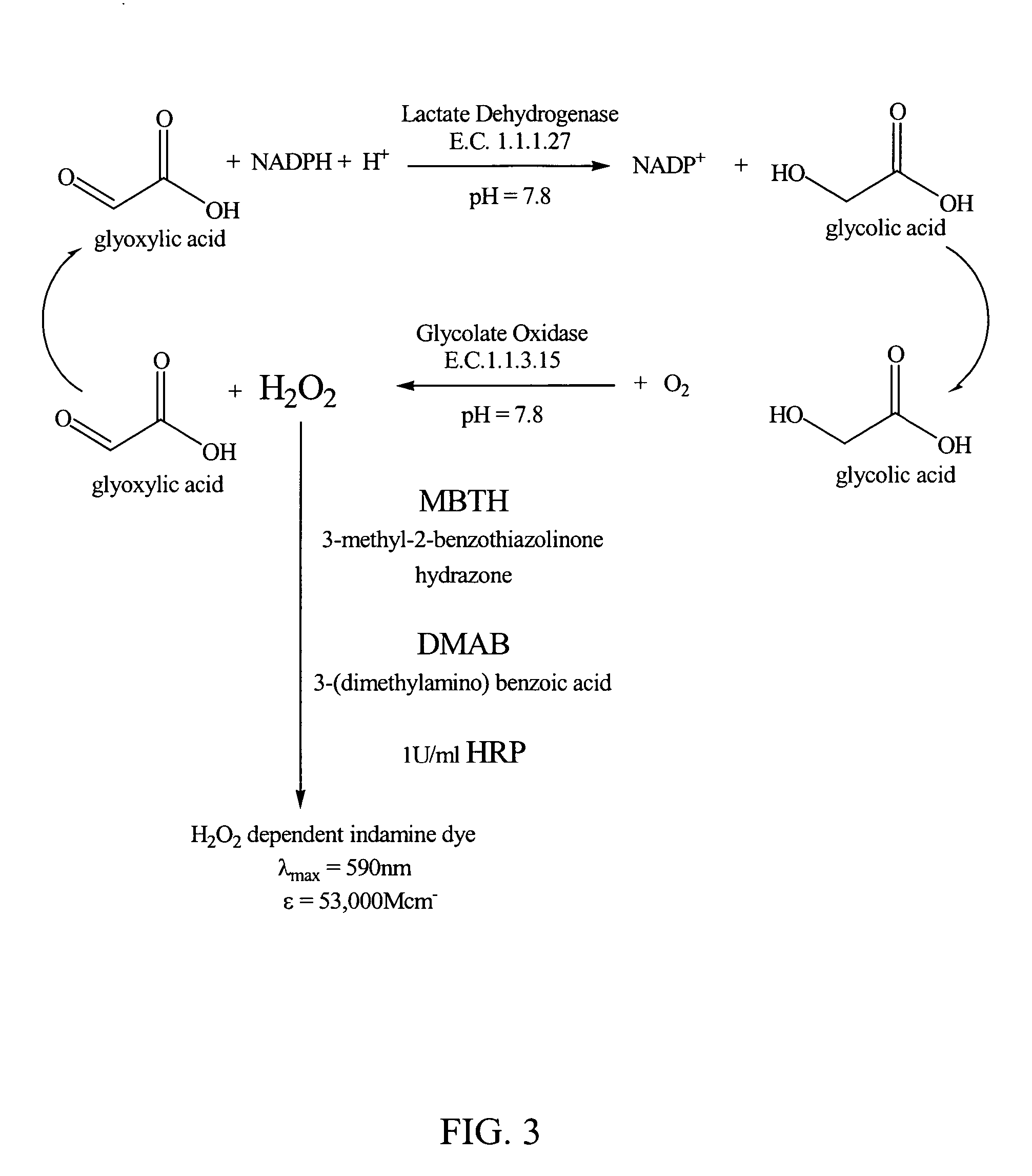
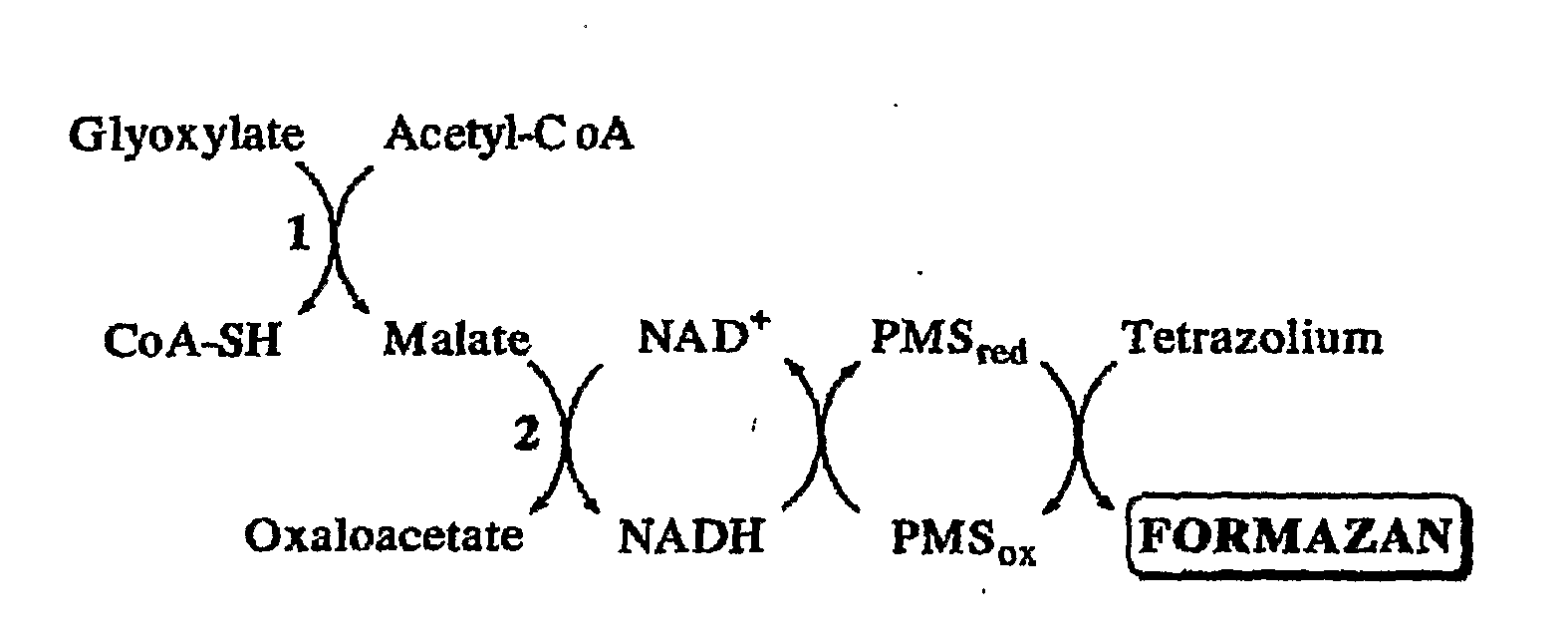
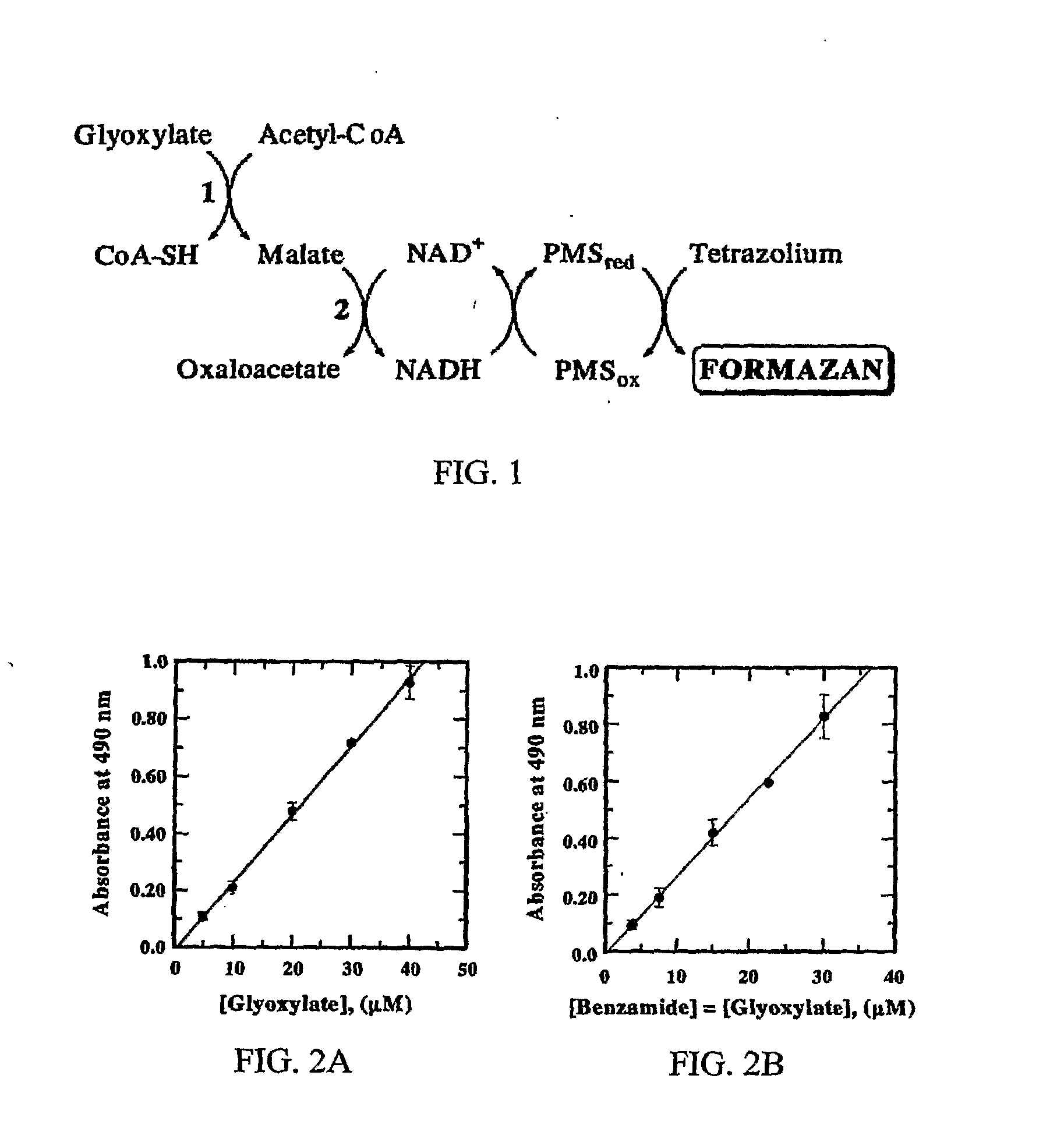
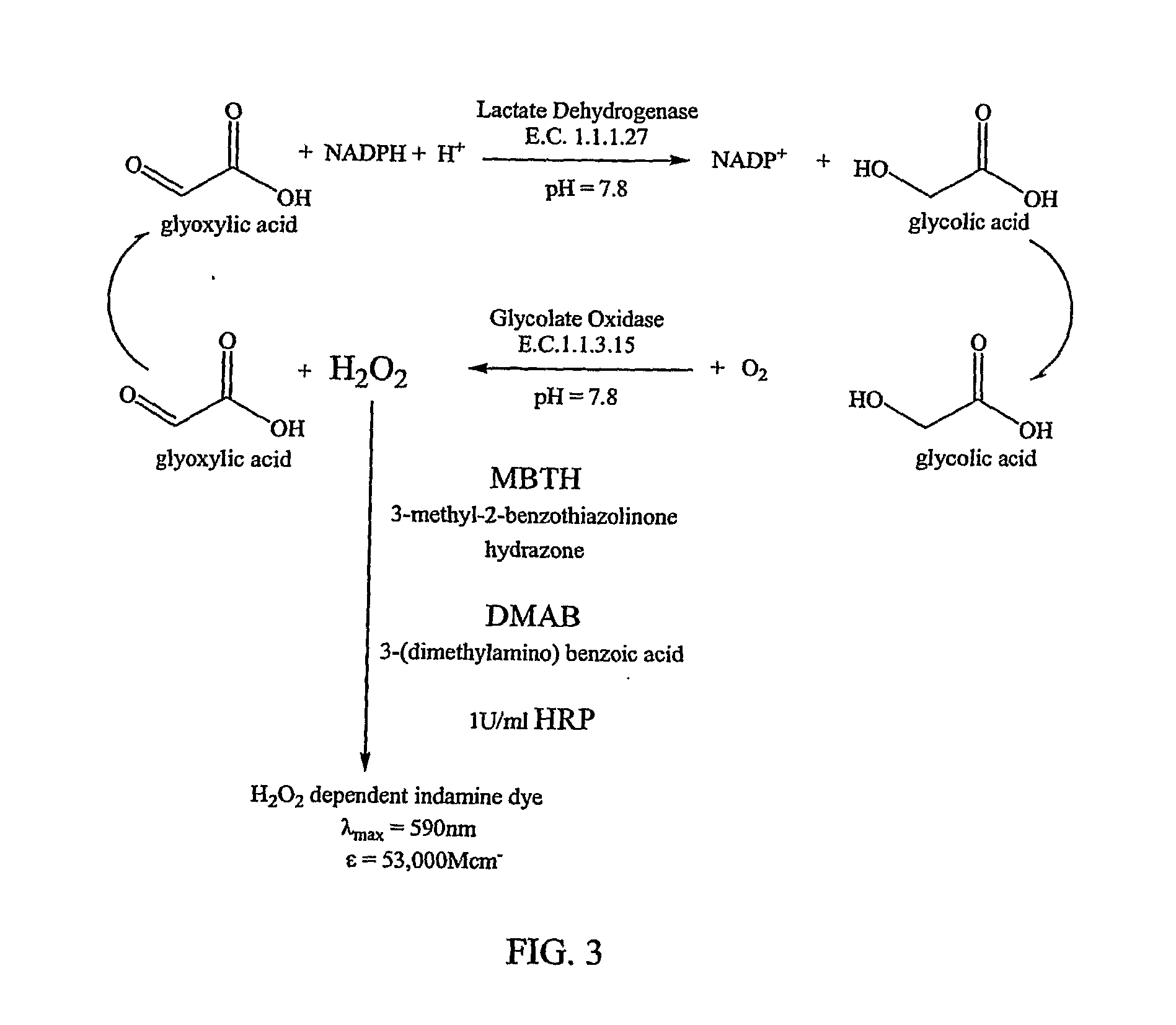
Glyoxylate assays and their use of inden tifying natural amidated compounds
Methods for detecting and assaying for glyoxylate, include enzyme-based assays and / or assays for hydrogen peroxide following liberation of hydrogen peroxide from glyoxylate, are disclosed. In some embodiments, the invention is directed to methods for assaying for glyoxylate produced by the reaction of peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase (PAM). The subject invention also concerns methods for assaying for the enzyme peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase and / or its substrates. The detection of glyoxylate is indicative of the presence of PAM and / or its substrates. The subject invention also concerns methods for screening for peptide hormones, amidated fatty acids, any N-acyl-glycine or N-aryl-glycine conjugated molecule, and generally compounds having a glycine reside in free acid form and attached to a carbonyl group.
Owner:UNIGENE LABORATORIES
Tetrahydro chinolines derivates and synthetic method
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing 2 position functionalized tetrahydroquinoline derivatives of 4-(mono or poly) aryl-substitution-3, 1'-cyclopropyl substitution by hetero Diels-Alder reaction of imine of ethyl glyoxylate and methylene cyclopropane. For various functionalizing substitutions in the reaction, which means that the reaction can be carried out smoothly whether the imine of the ethyl glyoxylate and the methylene cyclopropane is an electron donating group or an electron withdraw group, and corresponding tetrahydroquinoline derivative can be obtained with yield from medium to excellent. In the reaction process, high-strength tetrahydroquinoline derivatives with triatomic ring substitution and 2 position ethyl ester group are generated. The compounds have excellent modification property, can connect a tetrahydroquinoline module with other 2 position functional molecules, and have potential high biological activity.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Production method for glyoxalate
ActiveCN107445831ALow yieldHigh yieldMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic compound preparationGas phaseDiluent
The invention relates to a production method for glyoxylate. The invention mainly aims to overcome the problem of low yield of glyoxylate in the prior art. The method comprises a step of contacting oxygen-containing gas, glycollate, a diluent and carrying gas with a catalyst in a reactor under gas-phase oxidation conditions. With the technical scheme that the oxygen-containing gas is allowed to pass through a ceramic membrane distributor and then enter a reactor, the above problem is overcome, and the production method is applicable to industrial production of glyoxalate from glycollate through oxidation.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for detecting glyoxylate and glyoxal by high performance liquid chromatography
InactiveCN101539543AGood linear relationshipConducive to accurate quantificationComponent separationGlyoxylic acidAcetaldehyde
The invention discloses a method for detecting glyoxylate and glyoxal by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), particularly a method for detecting the content of glyoxylate and glyoxal by HPLC in glyoxylate sample solution which is prepared from reaction solution for the oxidation preparation of glyoxylate from glyoxal by adding sodium hydroxide solution to the reaction solution, so as to carry out the disproportionation reaction between incompletely reacted glyoxal and the sodium hydroxide solution in the reaction solution. By adopting the method of the invention, the content of glyoxal as the raw material and glyoxylate as the product can be detected rapidly and accurately; and the invention has the advantages of simple detection method and good repeatability, therefore, the invention is applicable to the quality control over glyoxylate during the industrialized oxidation preparation process of glyoxylate from glyoxal.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAYI GRP CO
Improved process for the reductive amination and selective hydrogenation of substrates containing a selected halogen
ActiveUS20160207874A1Low costPromote recoveryOrganic compound preparationPreparation by reductive alkylationChemical reactionHalogen
Disclosed is a process for performing a chemical reaction selected from reductive amination and hydrogenation of a first functional group in an organic feed substrate, which feed substrate comprises at least one further functional group containing a halogen atom, wherein the halogen atom is selected from the list consisting of chlorine, bromine, iodine, and combinations thereof, in the presence of hydrogen and a heterogeneous catalyst comprising at least one metal from the list of Pd, Rh, and Ru, together with at least a second metal from the list consisting of Ag, Ni, Co, Sn, Cu and Au. The process is preferably applied for the reductive amination of 2-chloro-benzaldehyde to form 2-chloro-benzyldimethylamine, as an intermediate in the production of agrochemically active compounds and microbiocides of the methoximinophenylglyoxylic ester series. Further disclosed is a composition rich in 2-chloro-benzyldimethylamine, further comprising an amount of 2-chloro-benzyl alcohol and being low in chlorotoluene isomers.
Owner:TAMINCO NV
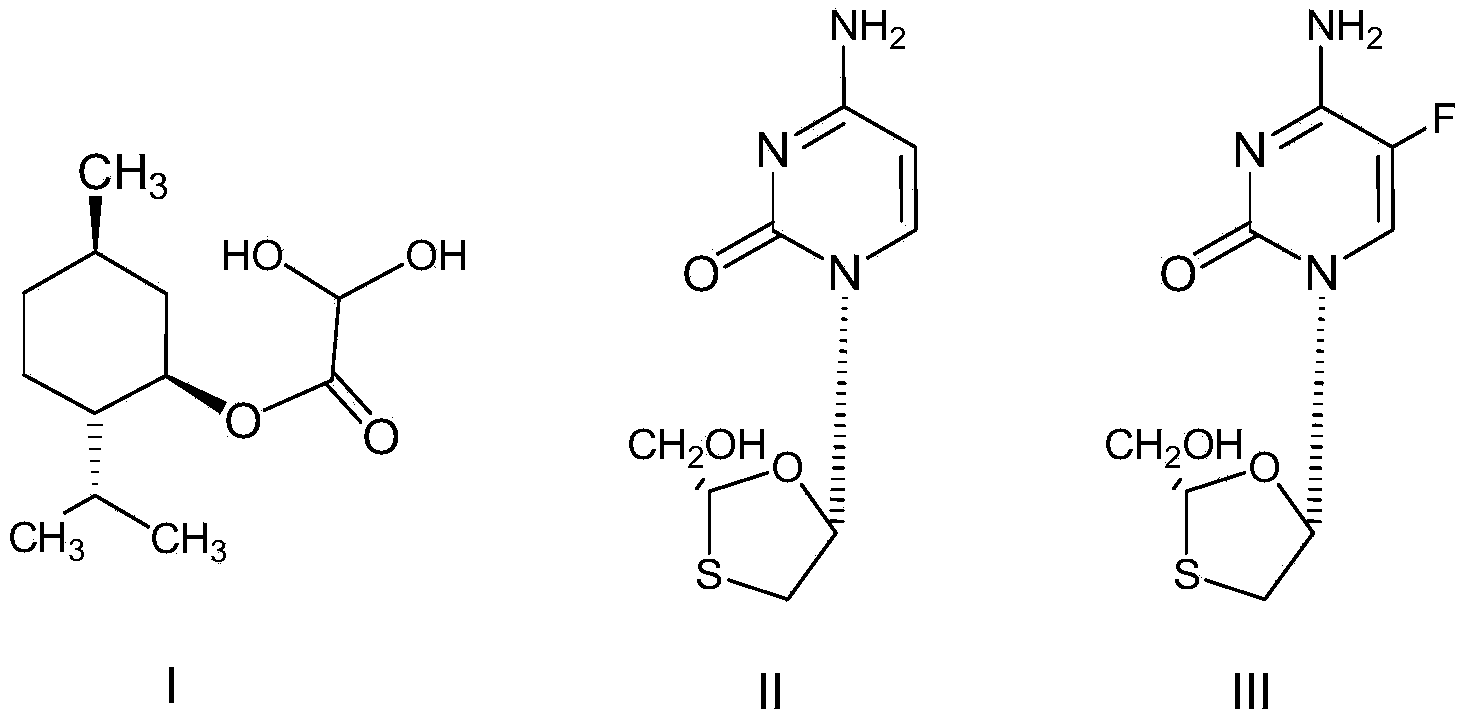
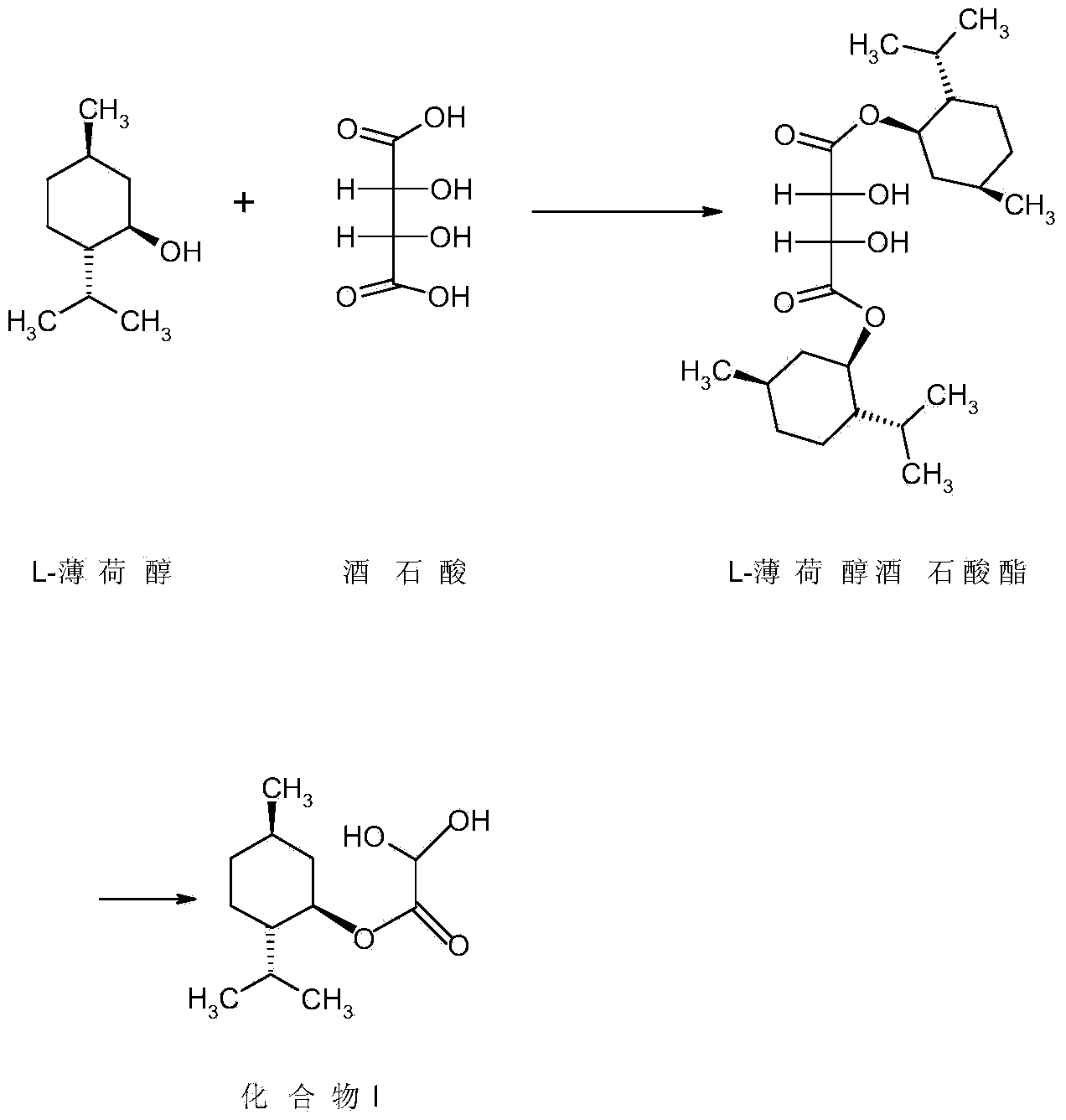
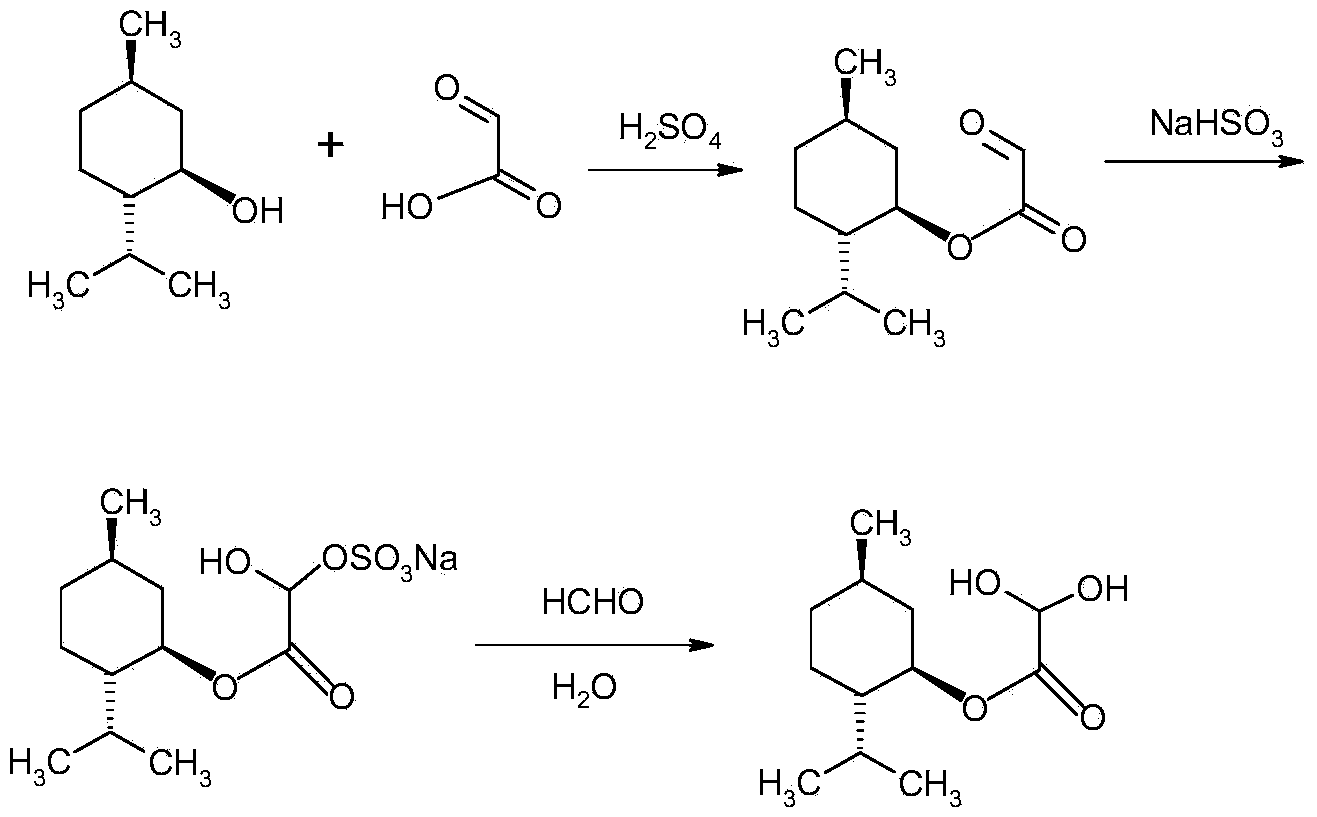
Method for preparing L-menthyl glyoxylate-hydrate through catalysis of heteropoly acid
ActiveCN103951561AEmission reductionControl formationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationHeteropoly acidSulfite salt
The invention discloses a method for preparing L-menthyl glyoxylate-hydrate through catalysis of heteropoly acid. The method comprises the following steps: by taking cyclohexane as a water-carrying agent, and heating and backflowing and dehydrating L-menthol and glyoxylic acid water solution under the catalysis of heteropoly acid, to obtain a reaction liquid A; separating the reaction liquid A so as to remove heteropoly acid, and separating to obtain an organic layer; directly adding the organic layer into a sodium sulfite water solution and a sodium hydrogen sulfite water solution, and fully reacting to obtain a reaction liquid B; separating the reaction liquid B to obtain a water layer, regulating the pH value of the water layer to be 6.8-7.5 through base, then adding formaldehyde water solution, and hydrolyzing to obtain the L-menthyl glyoxylate-hydrate. The method is convenient to operate, and the catalysis of the heteropoly acid has both advantages of liquid acid catalysis and solid acid catalysis; the organic layer obtained by filtering the reaction liquid A to remove heteropolyacid, and filtering is not required for the regulation of pH value, so that the emission of waste acid and salt in the production process can be reduced.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for producing glyoxylate
InactiveCN109574843AAvoid excessive oxidationAvoid decompositionOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationActive componentDehydrogenation
The invention relates to a method for producing glyoxylate. The method comprises the step of enabling oxygen-containing gas to pass through a reactor with a catalyst under the condition of oxidative dehydrogenation. The reactor comprises n sections of catalyst bed layers; the contents of catalyst active components in the n catalyst bed layers from an inlet to an outlet of the reactor are graduallyincreased; and n is an integer between 2 and 10. The method can be used for industrial production of the glyoxylate.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
A kind of manufacture method of d-l-p-hydroxyphenylglycine
InactiveCN102285894AEasy to operateNo heating requiredOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationPotassiumHeating effect
The invention relates to the fields of chemical industry and pharmaceutical production, in particular to a method for producing D-L-p-hydroxyphenylglycine. The technical scheme of the present invention is achieved like this: (1) by weight water: urea: potassium chlorate=100: 3-5: 3-5 configuration solution is standby as reaction solution; (2) drop into in above-mentioned reaction solution according to weight ratio Reaction solution: phenol: sulfamic acid: glyoxylic acid = 20:5-6:9-10:4-5, react at 20-30°C for 1-2 hours and filter to obtain D-L-p-hydroxyphenylglycine crystals. Such a method for producing D-L-p-hydroxyphenylglycine is easy to operate and does not require the effect of heating.
Owner:HENAN NEWLAND PHARMA
Method for preparing glyoxylate
ActiveCN101003474AHigh yieldAvoid the disadvantages of easy pollution and easy corrosion of equipmentOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationSulfateAmmonium hydroxide
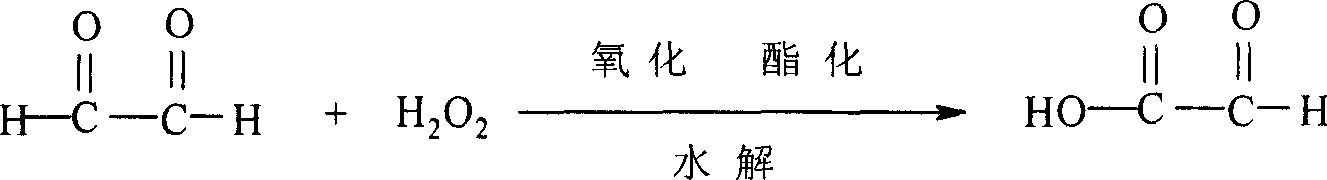
This invention discloses a method for preparing glyoxalic acid. The method comprises: oxidizing glyoxal solution by hydrogen peroxide in the presence of ferrous sulfate catalyst and cocatalyst, esterifying for separation, and hydrolyzing to obtain the target product. The purity, yield and melting point of glyoxalic acid are higher than 98%, 85%-90% and 96.2-97.9 deg.C, respectively. Compared with the present techniques, the method can increase glyoxalic acid yield by adding cocatalyst (ammonia solution). Besides, the method has improved operation condition, thus avoiding environmental pollution and apparatus corrosion. The product has stable quality.
Owner:SHANGHAI SHISI CHEM PROD
Materials and Methods for Assaying for Glyoxylate
The subject invention concerns enzyme-based methods for detecting and assaying for glyoxylate. In particular, the invention is directed to methods for assaying for glyoxylate produced by the reaction of peptidylglycine α-amidating monooxygenase (PAM). The subject invention also concerns methods for assaying for the enzyme peptidylglycine α-amidating monooxygenase. The detection of glyoxylate using the present invention is indicative of the presence of PAM. The subject invention also concerns methods for screening for peptide hormones and any N-acyl-glycine or N-aryl-glycine conjugated molecule.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Production method of glyoxylate
InactiveCN109574834AAvoid excessive oxidationAvoid decompositionOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationDehydrogenationOxygen
The invention relates to a production method of glyoxylate. The method includes the steps of passing, by glycolate and an oxygen-containing gas through a reactor having at least one section of a catalyst bed layer under an oxidative dehydrogenation condition, wherein the catalyst bed layer has a mixture of an inert filler and a catalyst, in the mixture, the weight ratio of the inert filler to thecatalyst is (0.01-2): 1. The method can be used in industrial production of the glyoxylate.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method of ozone oxidation synthesis glyoxylate monohydrate
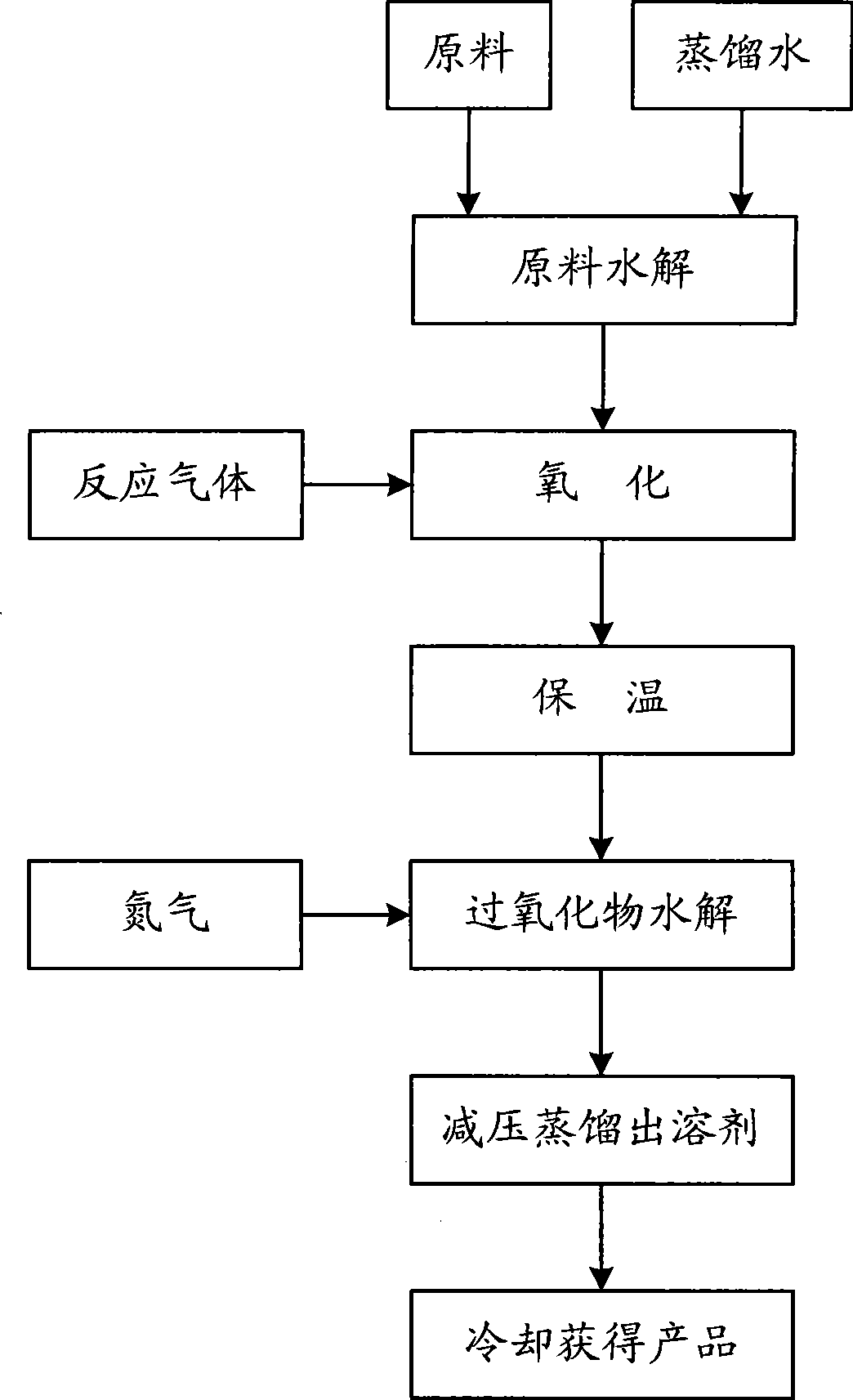
InactiveCN101445450ASimple processPurity effectOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationCis-Butenedioic AcidSolvent
The invention discloses a method of ozone oxidation synthesis glyoxylate monohydrate. The method comprises the following steps: raw material maleic anhydride is dissolved with water to obtain maleic anhydride solution with concentration of 20-40%; the oxygen with ozone is injected into the maleic anhydride solution as a reaction gas, the oxygen with the ozone carries out oxidation reaction with the maleic anhydride solution in a reaction kettle, and a product of glyoxylate and peroxide are obtained after the oxidation reaction; the solution after the reaction is obtained after hydrolysis of the peroxide, the solvent in the solution after the reaction is distilled by reduced pressure, the residual glyoxylate product is cooled to obtain the glyoxylate monohydrate. The glyoxylate monohydrate is synthesized in direct oxidation method, therefore the operation is simple, the processing steps is simple and both productive rate and purity of the product are over 98%.
Owner:QINGDAO GUOLIN ENVIRONMENTAL TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
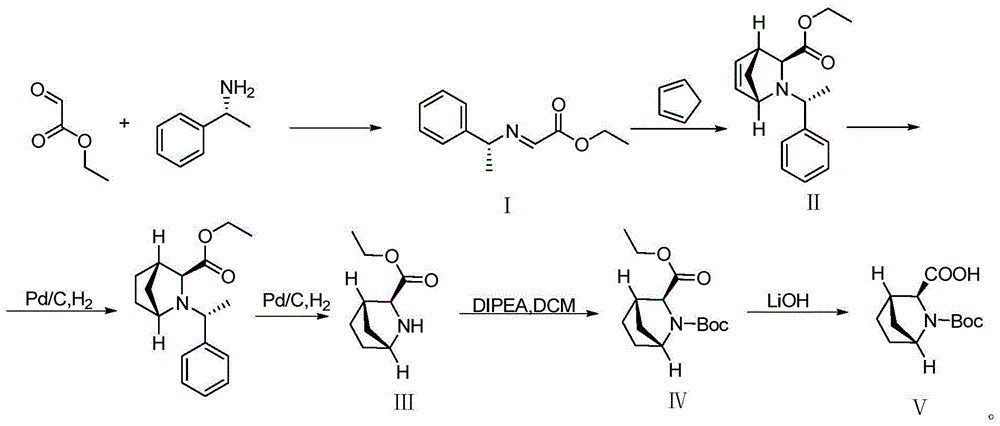
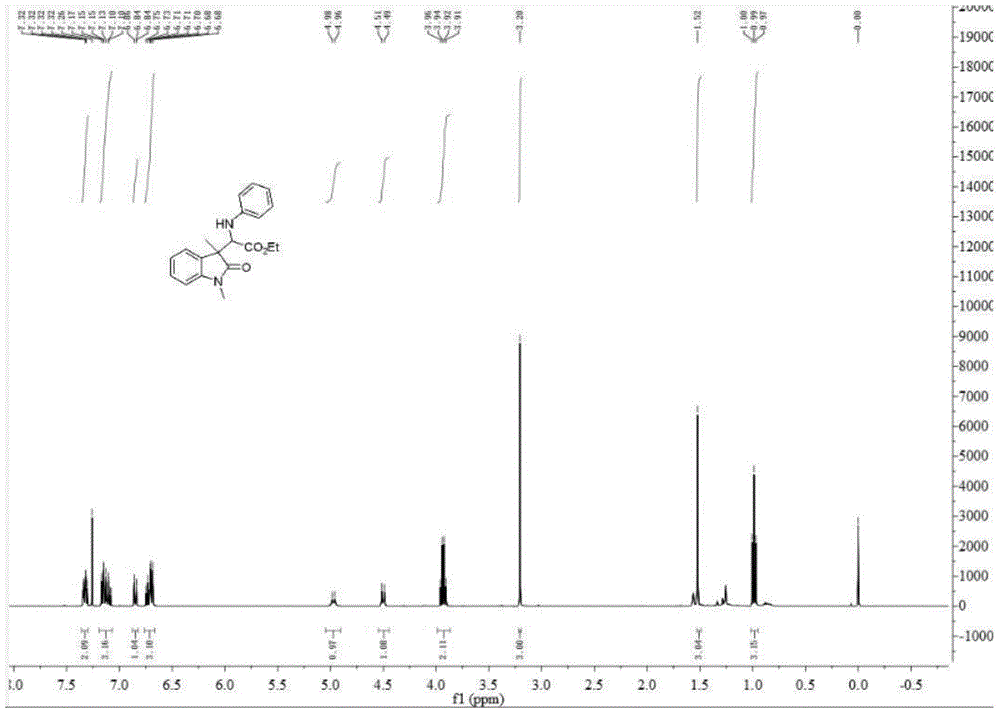
Method for synthesizing (2S,3S)-3-amino-bicyclo[2.2.2]octane-2-carboxylate
ActiveCN109678738ANovel process routeMild reaction conditionsOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsFormateCarboxylic salt
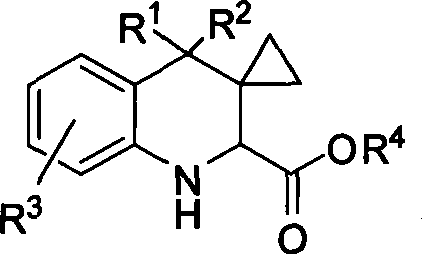
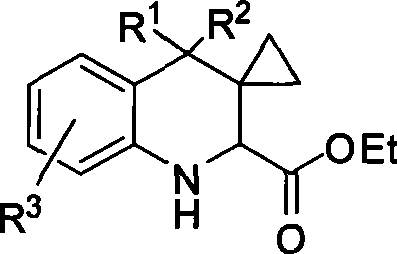
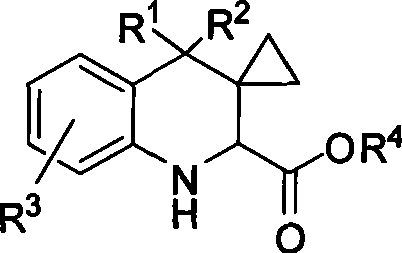
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing (2S,3S)-3-amino-bicyclo[2.2.2]octane-2-carboxylate, belongs to the field of synthesis of medical intermediates and aims to solve the problems that preparation of (2S,3S)-3-amino-bicyclo[2.2.2]octane-2-carboxylate has higher cost, low material safety, difficulty in enlarged production and the like. According to the method, glyoxylate is taken as a starting material and subjected to Henry reaction, elimination, ring closure and reduction reaction sequentially, and an intermediate is obtained. Through the adoption of the method for synthesizing (2S,3S)-3-amino-bicyclo[2.2.2]octane-2-carboxylate, a novel process route is adopted, the yield is higher than 45%, and the method has the characteristics of novel route, relatively mild reaction conditions, low cost and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUAXIAN PHARMA TECH CO LTD
Self-cleaning coating for aluminum alloy doors and windows
InactiveCN106543897AImprove material stabilityStrong adhesionAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesCyclopentanolSilicone oil
The invention relates to self-cleaning coating, in particular to self-cleaning coating for aluminum alloy doors and windows. The self-cleaning coating for the aluminum alloy doors and windows is prepared from the following raw materials including, by weight, 20-30 parts of phenyltrimethoxysilane, 25-40 parts of methyl-ethyloxy silicone oil, 10-15 parts of fluorosilicone, 15-20 parts of methyl glyoxylate, 1-5 parts of oxalic acid, 0.1-0.5 part of cyclopentanol and 0.3-0.7 part of catalysts. According to the self-cleaning coating for the aluminum alloy doors and windows, material stability is good, adhesive force is strong, and the service life is long.
Owner:GUANGXI DEJUN DOOR & WINDOW CURTAIN WALL
Production method for preparing glyoxylate from glycollate
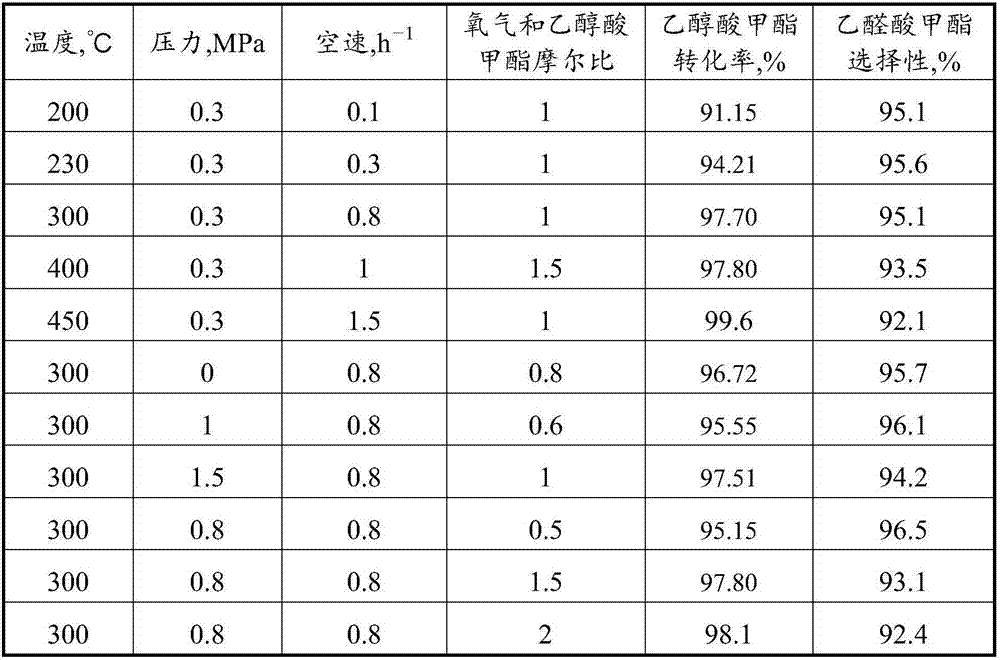
ActiveCN110627645AAvoid separationReduce manufacturing costOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationActive componentSpace velocity
The invention relates to a production method for preparing glyoxylate from glycollate. A purpose of the invention is mainly to solve the problems of excessive oxidation of glycollate, difficulty in product separation and high cost in the prior art. According to the invention, glyoxylate is prepared by directly dehydrogenating glycollate; the catalyst comprises the following components that cu andZn are used as active components, ZrO2 and SiO2 are used as carriers, and a ratio of Cu to Zn to Zr to Si is 1:0-2:1-4:1-7; the reaction conditions comprise that the temperature is 160-240 DEG C, andthe feeding volume space velocity of glycollate is 0.4-1.0 h<-1>; with the method, the conversion rate of glycollate reaches 99%, and the selectivity of glyoxylate reaches 96%; and the method can wellsolve the problems in the prior art, and can be used for industrial production of glyoxylate from glycollate.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
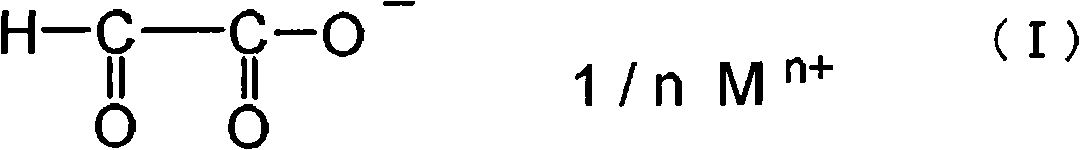
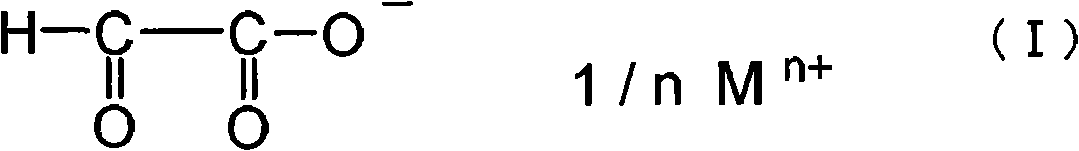
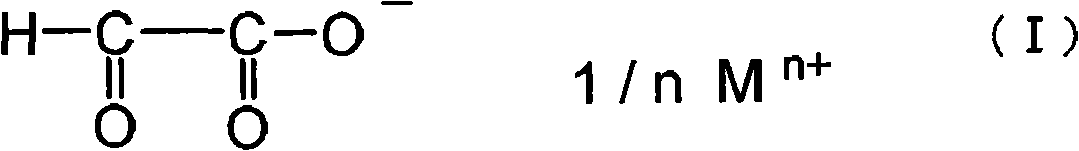
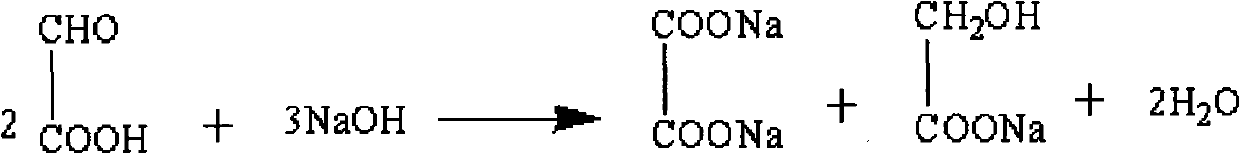
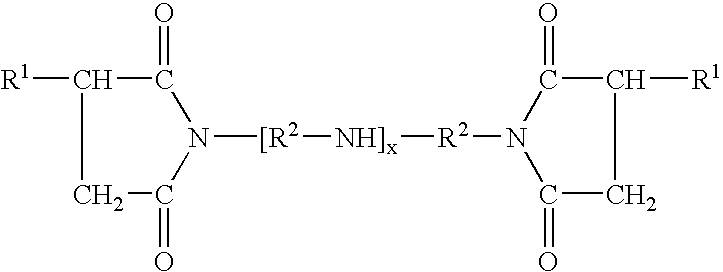
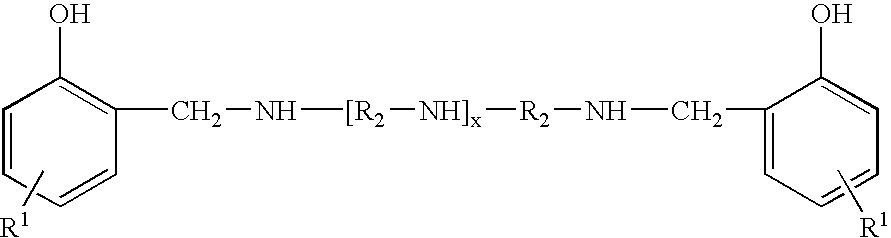
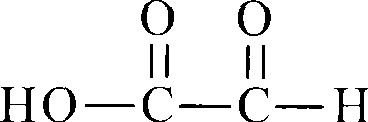
![Recombinant microorganism having ability to produce [lactate-co-glycolate] copolymer from glucose, and method for preparing [lactate-co-glycolate] copolymer using same Recombinant microorganism having ability to produce [lactate-co-glycolate] copolymer from glucose, and method for preparing [lactate-co-glycolate] copolymer using same](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/32068b8a-fa34-41a9-b805-59a3e0f405e2/US08883463-20141111-D00001.png)
![Recombinant microorganism having ability to produce [lactate-co-glycolate] copolymer from glucose, and method for preparing [lactate-co-glycolate] copolymer using same Recombinant microorganism having ability to produce [lactate-co-glycolate] copolymer from glucose, and method for preparing [lactate-co-glycolate] copolymer using same](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/32068b8a-fa34-41a9-b805-59a3e0f405e2/US08883463-20141111-D00002.png)
![Recombinant microorganism having ability to produce [lactate-co-glycolate] copolymer from glucose, and method for preparing [lactate-co-glycolate] copolymer using same Recombinant microorganism having ability to produce [lactate-co-glycolate] copolymer from glucose, and method for preparing [lactate-co-glycolate] copolymer using same](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/32068b8a-fa34-41a9-b805-59a3e0f405e2/US08883463-20141111-D00003.png)
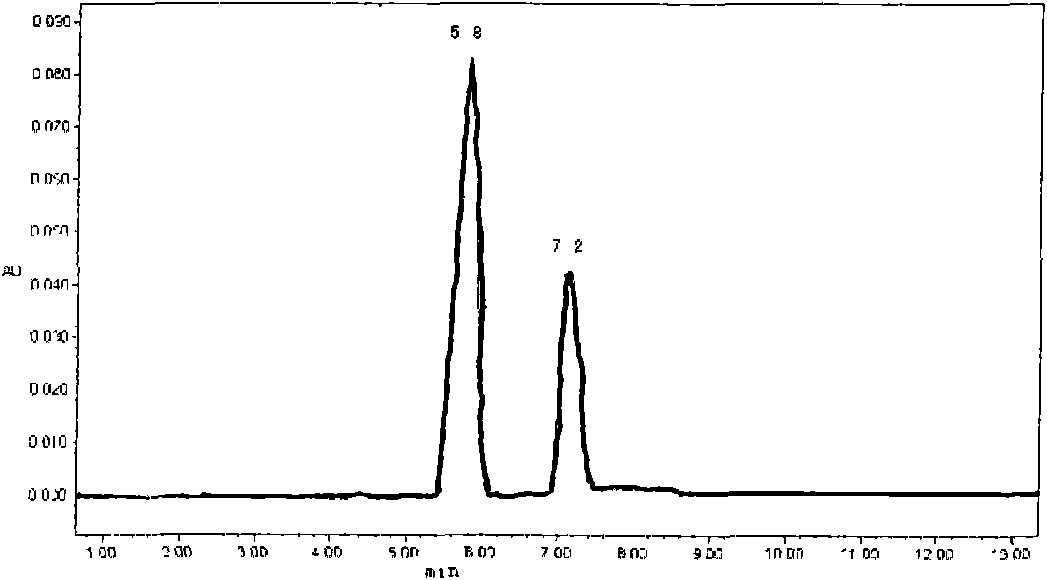
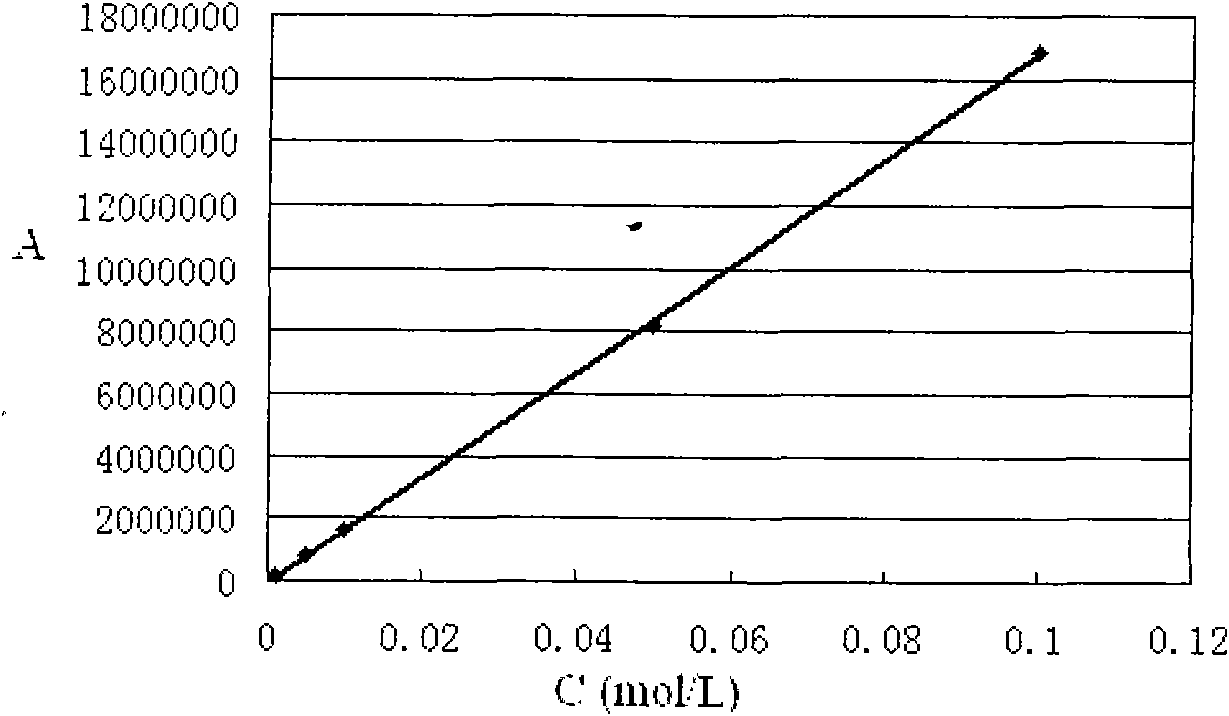
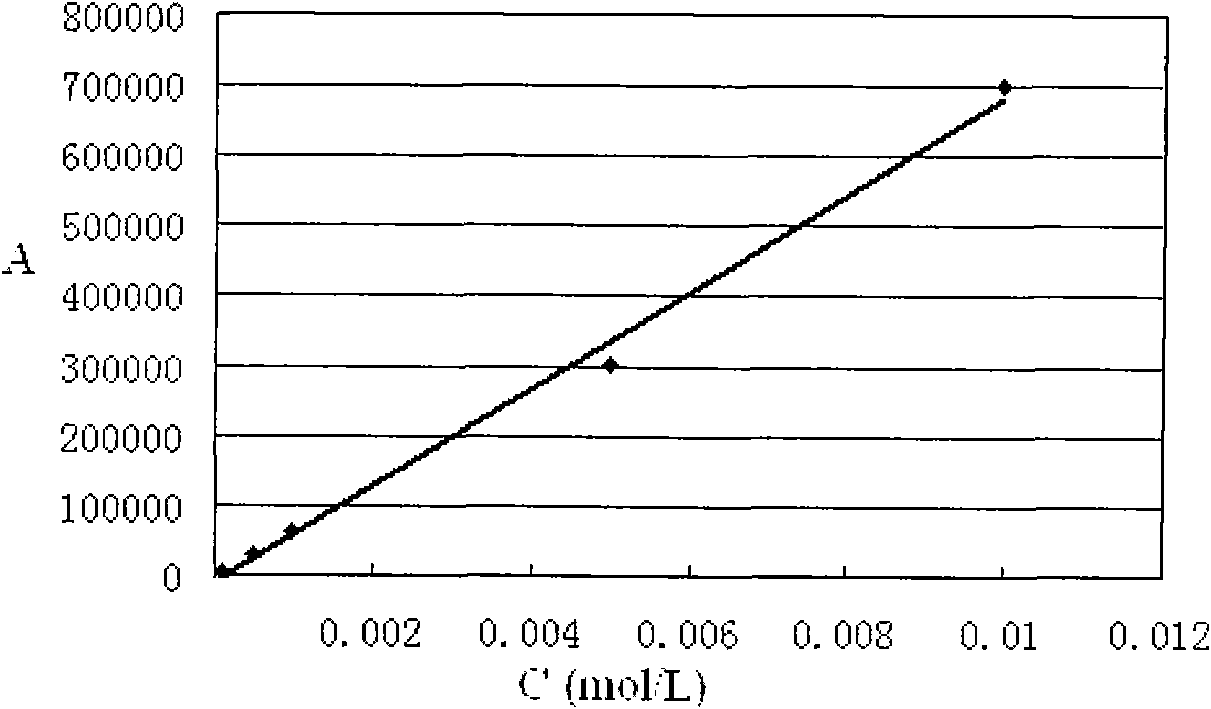
![Method for synthesizing (2S,3S)-3-amino-bicyclo[2.2.2]octane-2-carboxylate Method for synthesizing (2S,3S)-3-amino-bicyclo[2.2.2]octane-2-carboxylate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5edfc6d3-872b-47e7-b397-e873b6d331fd/RE-RE-GDA0001945285370000011.png)
![Method for synthesizing (2S,3S)-3-amino-bicyclo[2.2.2]octane-2-carboxylate Method for synthesizing (2S,3S)-3-amino-bicyclo[2.2.2]octane-2-carboxylate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5edfc6d3-872b-47e7-b397-e873b6d331fd/RE-RE-GDA0001945285370000012.png)
![Method for synthesizing (2S,3S)-3-amino-bicyclo[2.2.2]octane-2-carboxylate Method for synthesizing (2S,3S)-3-amino-bicyclo[2.2.2]octane-2-carboxylate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5edfc6d3-872b-47e7-b397-e873b6d331fd/RE-RE-GDA0001945285370000031.png)