Separation, identification and applications of bacterial cellulose production strain
A technology of bacterial cellulose and strains, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve problems such as difficult adjacent species and strains, and achieve the effects of excellent bioaffinity, rapid film production, and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Embodiment 1: Screening of film-producing strains
[0040] (1) Pick about 1 cm of pulp with decayed tissue from rotten apples, pears, citrus, melons, and mangoes 3 For small pieces, rinse in 10 mL sterile water.
[0041] (2) Pipette 100 μL of rinse liquid into the PA bottle containing 10 mL of primary screening liquid medium. After static culture at 30°C for 4 days, a thin film appeared; transfer the film to sterile water with sterilized tweezers and rinse once to wash off the bacteria on the surface, then transfer the film to a 5mL centrifuge tube, and use sterile Mash the tip of the bacterial pipette as much as possible; add 4 mL of sterilized water and mix well; absorb 100 μL of the liquid and perform 5-fold gradient dilution to finally obtain 1-fold, 5-fold, 25-fold, 125-fold, and 625-fold diluted bacterial suspensions. Take 100 μL of each serial dilution and spread it on the primary screening solid medium. Among them, the composition of the primary screening liq...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2: Morphological observation of bacterial strain
[0045] Colony morphology: cultured at 30°C, cultured on a primary screening solid plate medium for 72 hours, the colony is round, off-white, 2-3 mm in diameter, raised, with dry, uneven surfaces, irregular edges, and easy to pick. The bacterial colony increases with time, and after 10 days, the diameter can reach more than 8 mm, forming a cellulose film block on the surface of the culture medium.
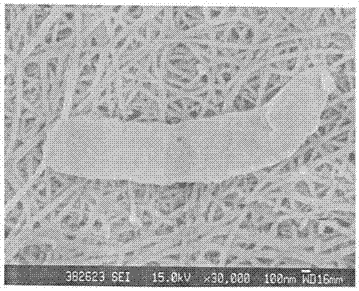
[0046] Cell morphology: The bacterial cells were observed by scanning electron microscope. The HEC-004 strain was rod-shaped, with a width of about 0.4-0.8 μm and a length of about 4 μm (see figure 1 ); the strain was Gram negative.
Embodiment 3
[0047] Embodiment 3: the identification of strain
[0048] The main steps of amplifying the 16S rDNA, dnaK, groEL and rpoB genes of the HEC-004 strain are as follows:
[0049] A single colony was picked from the HS solid plate and inoculated into the primary screening liquid medium containing 1% cellulase, and cultured at 30°C and 150rpm for 48h.
[0050] Use a 1.5mL centrifuge tube to collect 1mL of the culture solution, and centrifuge at 12000rpm to collect the bacteria and remove the supernatant. The cell pellet was resuspended and washed with sterilized water, and the supernatant was removed after centrifugation. Repeat the cell wash once, and finally suspend the cells in 100 μL of water.
[0051] 16S rDNA, dnaK, groEL, rpoB were amplified by PCR method. The PCR system is: 1 μL of bacterial solution, PCR Master Mix (Takara, Japan) 25 μL, forward primer 2 μL, reverse primer 2 μL, add deionized water to 50 μL. PCR program: 95°C for 10 minutes; 30 cycles of 95°C for 30s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com