Preparation method of antibacterial composite bacterial cellulose membrane
The technology of bacterial cellulose film and bacterial cellulose is applied in the field of preparation of antibacterial composite bacterial cellulose film, which can solve the problems of affecting the quality of wound healing and recovery, and cannot prevent wound infection, and achieves low cost and good antibacterial effect. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Embodiment 1: fermentation and processing of bacterial cellulose film
[0028] 1) culture medium
[0029] Seed medium: 10g of glucose, 10g of yeast extract, 1000mL of distilled water, sterilized at 115°C for 20min, and added 3% absolute ethanol (V / V) when cooling to about 50°C.
[0030] Fermentation medium: glucose 20g, yeast extract 10g, peptone 7g, disodium hydrogen phosphate 7.5g, citric acid 0.5g, distilled water 1000mL, sterilized at 115°C for 20min.
[0031] 2) Acetobacter xylinum cellulose fermentation
[0032] Pick Acetobacter xylinus (Gluconacetobacter xylinus) TJU-S8 from the slant and inoculate it in 100 mL of seed medium, culture at 30° C. with shaking at 120 r / min for 18 hours, and prepare seed liquid.
[0033] The seed solution was inserted into the fermentation medium at a ratio of 10%, and cultured statically at 30° C. for 7 days to obtain the bacterial cellulose membrane.
[0034] 3) Extraction of bacterial cellulose
[0035] The bacterial cellulose...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2: bacterial cellulose composite film preparation
[0037] The dried bacterial cellulose membrane was cut into discs with a diameter of 10 mm. Place in 0.6% chitosan / carboxymethyl chitosan-citric acid aqueous solution, stir and incubate at room temperature for 24 hours, take it out for vacuum freeze-drying for 12 hours, and store in a dehumidifier. In this example, a bacterial cellulose composite membrane with an ultrafine network structure and evenly distributed pores was obtained.
Embodiment 3
[0038] Embodiment 3: Bacterial cellulose composite membrane structural characteristic analysis
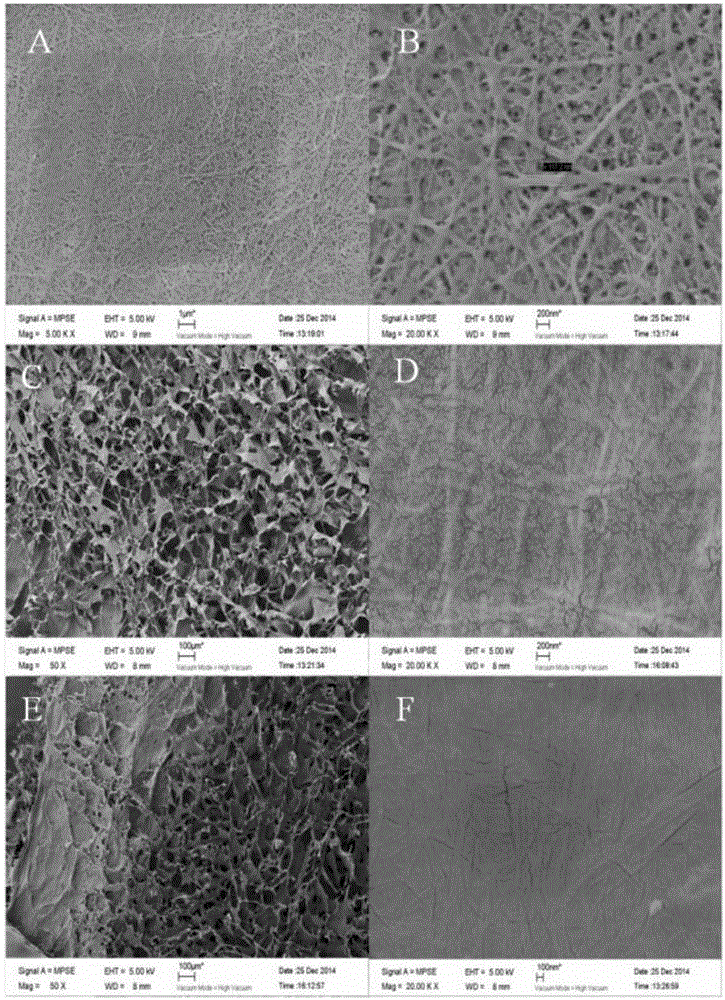
[0039] 1) Scanning electron microscope analysis
[0040] Cut the treated bacterial cellulose into 5mm 2 The small squares on the left and right are sprayed with gold coating on the ion gold plating instrument. The microstructure of the coated samples was observed with a scanning electron microscope.
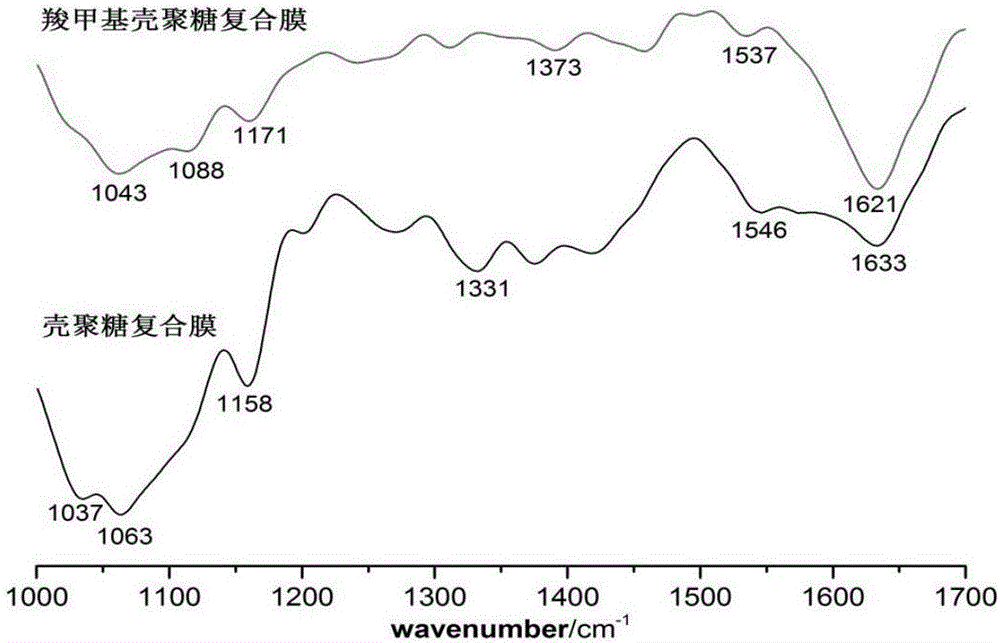
[0041] 2) Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic analysis
[0042] The infrared absorption spectrum of bacterial cellulose was measured by Fourier transform infrared spectrometer. Mix the dried bacterial cellulose sample with KBr and grind it, and press it into thin slices for detection, the range is 4000-500cm -1 .
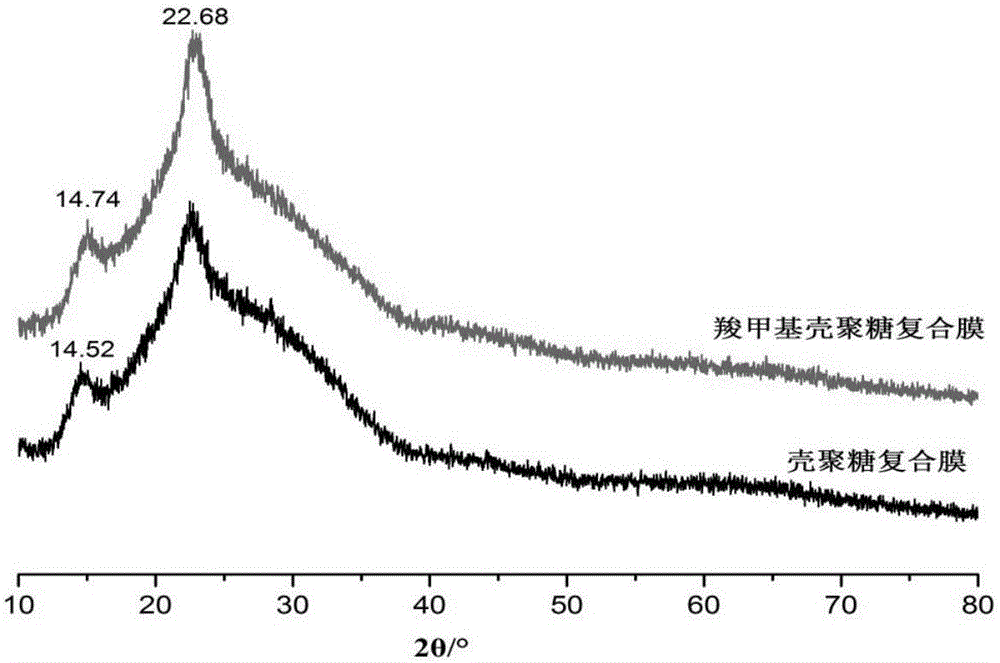
[0043] 2) X-ray diffraction analysis
[0044] Use an X-ray diffractometer to fix the dried bacterial cellulose on the frame, keep it flat, copper target, test voltage 40KV, test current 15mA, rate 10° / min, cloth width 0.02°, 2θ 10-80 ° large-scale scanning; then...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| crystallinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com