DMAP removal method for synthesis of cholesterol-grafted amphiphilic high-molecular material
An amphiphilic polymer and cholesterol technology, applied in the field of polymer materials, can solve the problems of difficult removal and low purification efficiency of DMAP, and achieve the effects of controllable results, favorable for industrial production and high purification efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Embodiment 1: the establishment of DMAP standard curve
[0019] Weigh 10.0mg of DMAP into a 10mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark with absolute ethanol, and shake well to obtain 1.0mg·mL of DMAP stock solution -1 . Take 0.5mL of the above DMAP stock solution into a 50mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark with absolute ethanol, shake well, and obtain a concentration of 10.0μg·mL -1 DMAP solution. Pipette 10.0 μg·mL of the above DMAP -1 Solution 0.5, 1.0, 3.0, 5.0, 7.0, 9.0mL in a 10mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark with absolute ethanol, shake well, the concentration is 0.5, 1.0, 3.0, 5.0, 7.0, 9.0μg·mL -1 DMAP solution, with absolute ethanol as a reference, the absorbance value was measured at 281nm with a UV-Vis spectrophotometer, and a standard curve was drawn.
[0020] Carry out linear regression on the absorbance (A) with the concentration (C), and get the regression equation A=0.1645C+0.0059 (R=0.9999), indicating that DMAP is 0.5~9.0μg·mL -1 The l...
Embodiment 2
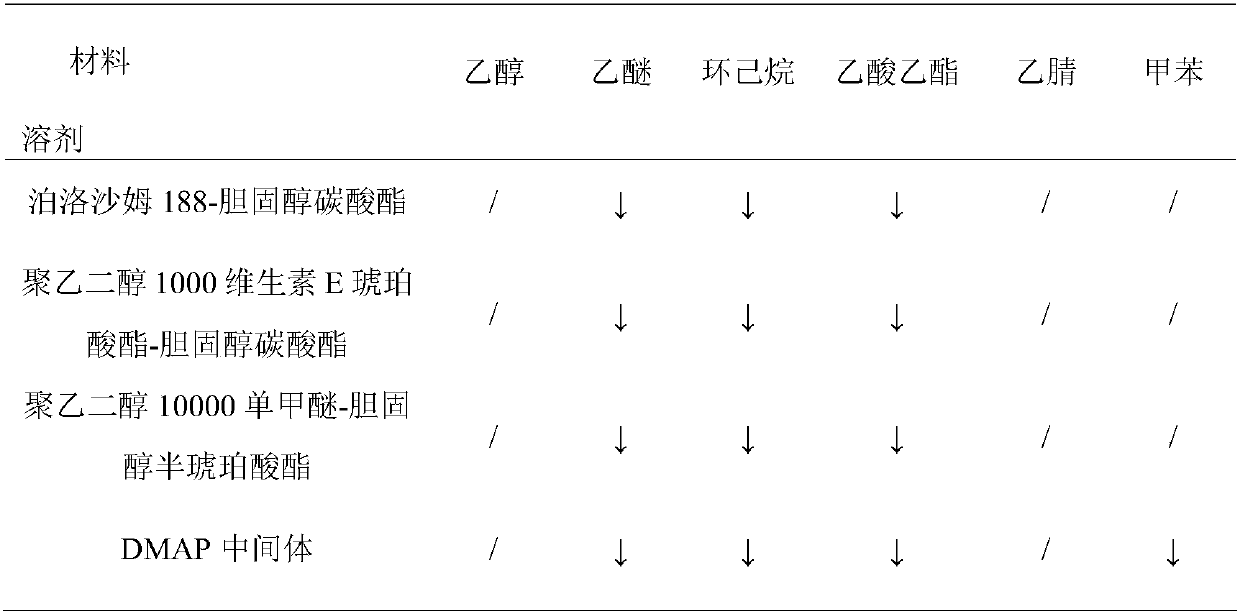
[0021] Example 2: Solubility of different materials and DMAP intermediates in different solvents
[0022]Weigh 5.0 mg of poloxamer 188-cholesterol carbonate, polyethylene glycol 10,000 monomethyl ether cholesterol hemisuccinate, polyethylene glycol 10,000 monomethyl ether cholesterol hemisuccinate, and DMAP in vials, respectively. Add acetonitrile, diethyl ether, cyclohexane, ethyl acetate, acetonitrile and toluene to observe the solubility of different materials and DMAP in various solvents, where " / " means soluble and "↓" means insoluble. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0023] Table 1 Solubility of different materials and DMAP intermediates in solvents
[0024]
[0025] As can be seen from the above table, poloxamer 188-cholesterol carbonate, polyethylene glycol 10000 monomethyl ether cholesterol hemisuccinate, polyethylene glycol 10000 monomethyl ether cholesterol hemisuccinate and DMAP intermediates in ethanol and acetonitrile It is in the dissolved state in ether,...
Embodiment 3
[0026] Example 3: Synthesis of Poloxamer 188-cholesterol carbonate (P188-CHMC) and removal of DMAP
[0027] Take 0.04mmol poloxamer 188 (P188) in a closed container, add 0.02mmol DMAP and 0.14mmol triethylamine (TEA) under nitrogen, slowly add 0.24mmol CHM in dichloromethane (DCM) solution 16mL, Stir and mix in an ice-water bath for 30 minutes, then reflux at 45°C for 36 hours. After the reaction was completed, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure, and a white wax was obtained by precipitation with glacial ether, and the precipitate was washed repeatedly with ether three times (to remove unreacted CHM) to obtain the crude product of P188-CHMC in powder form.
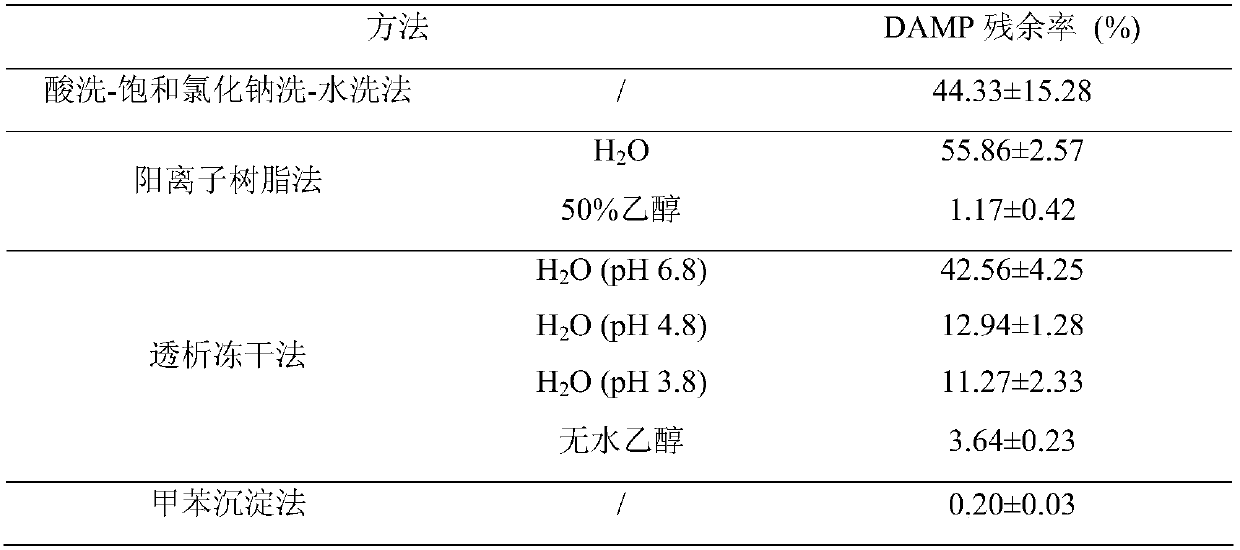
[0028] (1) Acid washing-saturated sodium chloride washing-water washing method: Weigh 50 mg of the crude product of P188-CHMC from which CHM has been removed in a vial, add distilled water, extract with DCM, and then use 100 mmol L -1 Wash 3 times with hydrochloric acid, saturated sodium chloride and ice water...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com