Chalcomoracin, a biologically active monomer component in mulberry leaves based on ultraviolet induction, and its preparation method and use
A biologically active and mulberry leaf technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of the monomer component chalcomoracin, can solve problems such as the preparation process is not clear, and achieve the effect of reasonable technical route, reasonable economy, and anti-radiotherapy sensitization of malignant tumors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
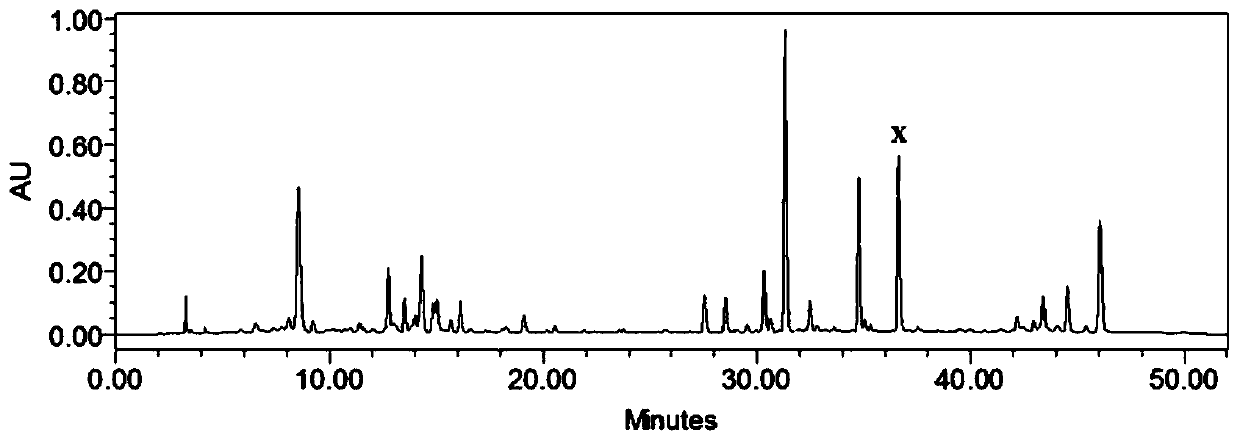
[0024] Example 1: Preparation of Ultraviolet Induced Mulberry Leaf Extract Chalcomoracin
[0025] Freshly picked mulberry leaves were washed and irradiated with ultraviolet light (UV-B band) for 15 minutes, and the irradiated mulberry leaves were dried at 60°C. After the dried mulberry leaves are crushed, add 20 times the volume of petroleum ether, soak for 24 hours, filter, soak the filter residue with 5 times the volume of ethyl acetate for 24 hours, extract twice, filter, combine the extracts, and recover ethyl acetate ester to obtain the total extract extract. Take the total extract extract, add ethanol to dissolve, then add 200 mesh silica gel 2 times the weight of the total extract extract, evaporate the solvent to obtain a mixed sample, take 20 times the 200 mesh silica gel of the mixed sample weight, pack into the chromatographic column, keeping the diameter-to-height ratio at 1:10, performing gradient elution with a dichloromethane-methanol mixed solvent system (99:1...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Embodiment 2: the antitumor effect of UV-induced mulberry leaf extract chalcomoracin (CMR)
[0030] 2.1 In vitro antitumor effect of CMR
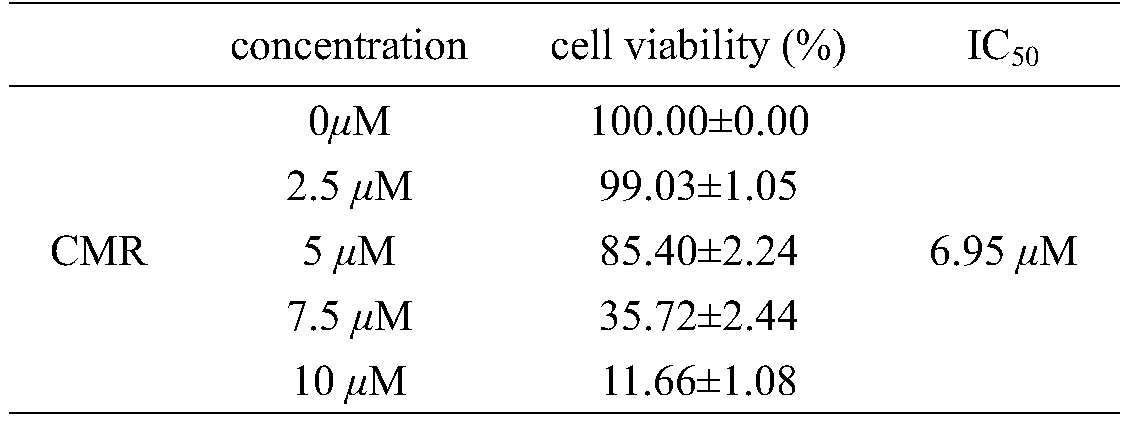
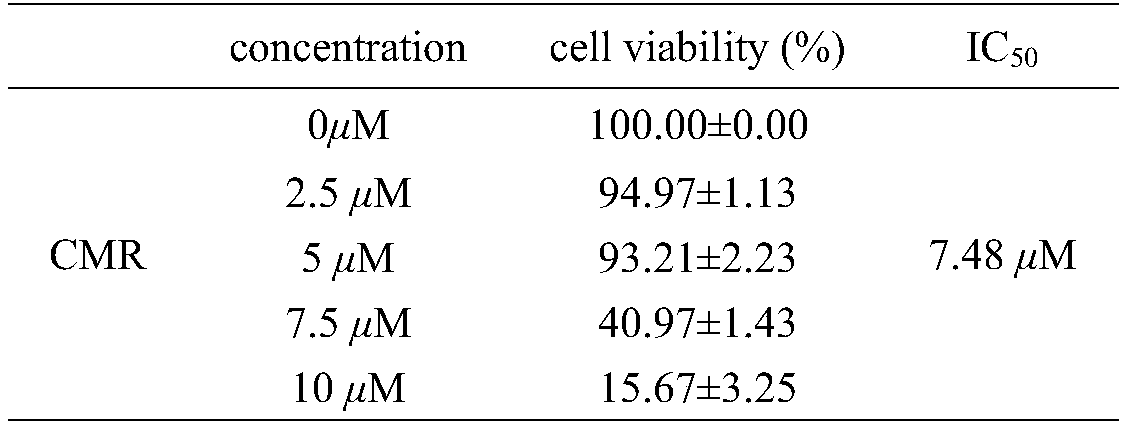
[0031] Human prostate cancer cells (PC-3) and breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231) were inoculated in 96-well plates at 5000 cells / well, and the experiment was divided into control group and different concentrations of UV-induced mulberry leaf extract (CMR) 24 hours after inoculation, the administration group added 100 μL / well of serum-free medium containing different concentrations of CMR, so that the final concentration of CMR was 0, 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10 μM, and incubated for 48 hours, MTT method Check cell viability. The experiment was repeated three times, and the results are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
[0032] Table 1 The effect of UV-induced mulberry leaf extract on the activity rate of PC-3 (mean ± standard deviation)
[0033]
[0034] Table 2 The effect of ultraviolet-induced mulberry leaf extract on the activity rate of MDA-...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Embodiment 3: The radiotherapy sensitization effect of CMR
[0041] The lung cancer PC-9 cell suspension was inoculated into 500 cells / well of 6-well culture plate, and the cells were divided into control group and irradiation group (IR group, irradiation doses were 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8G, respectively). , CMR group (with concentrations of 0, 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10 μM) and IR+CMR group. After irradiation and drug treatment, the culture was continued for two weeks, and the supernatant was discarded and stained with crystal violet to count the number of colonies. Calculated according to the following formula: Cell Survival Fraction (SF)=clonal formation rate of the experimental group / clonal formation rate of the control group, clone formation rate=number of clones / number of inoculated cells×100%. The average lethal dose (D0), quasi-localized dose (Dq), cell survival fraction (SF2) after 2Gy irradiation was calculated by software fitting, the cell survival curve was drawn, and the ex...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com