Tungsten matrix for hot cathode and preparing method of tungsten matrix
A hot cathode and substrate technology, applied in electrical components, discharge tube/lamp parts, circuits, etc., can solve the problems affecting the emission performance of porous tungsten substrates, the difficulty of the process has not been paid attention to, and the inevitable residual carbon pollution, etc., to achieve The effect of good product consistency, narrow distribution and suitable porosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
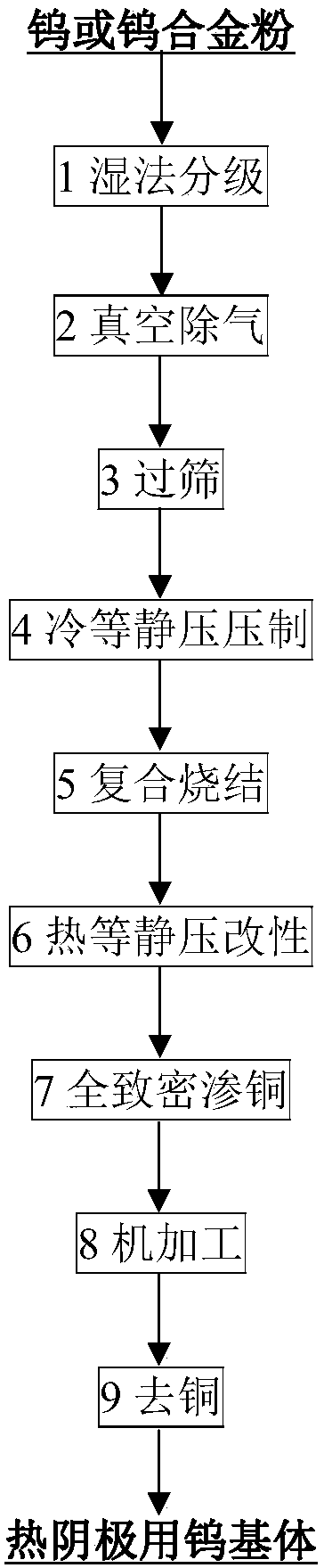
[0054] The technical process of the preparation method of hot cathode tungsten matrix powder of the present invention is as follows figure 1 As shown, it includes the following steps: 1 wet classification; 2 vacuum degassing; 3 sieving; 4 cold isostatic pressing; 5 composite sintering; 6 hot isostatic pressing modification; ; 9 to remove copper; finally obtain a hot cathode tungsten or tungsten alloy substrate with suitable porosity, small pore size and narrow distribution, extremely low closed porosity, and high skeleton strength.
[0055] The preparation method of the tungsten substrate for hot cathodes of the present invention uses wet-classified tungsten or tungsten alloy powder with narrow particle size and medium-fine particles as raw materials, vacuum degassing, sieving, cold isostatic pressing, composite sintering, and then heat etc. Static pressure re-pressure re-firing modification, fully dense copper infiltration, final machining, high-temperature vacuum copper remo...
Embodiment 1
[0066] The tungsten-rhenium alloy powder with an average particle size of 0.5 μm is subjected to wet centrifugal classification, and the laser particle size span (SPAN) of the classified tungsten-rhenium alloy powder is 1.4; after drying at 50°C, the vacuum degree is kept at 5×10 -3 Pa, heat at 400°C for 2 hours for deep degassing and purification; pass through a 200-mesh sieve; put the tungsten-rhenium alloy powder evenly into the In the soft rubber mold, cold isostatic pressing under 250MPa pressure for 1min to obtain a tungsten-rhenium alloy compact with a relatively regular shape; place the tungsten-rhenium compact in a high-temperature tungsten mesh furnace, and sinter at a low temperature of 800°C in a high-purity hydrogen atmosphere 60min, then, directly switch the hydrogen atmosphere to 2×10 -3 Pa high vacuum, sintering at 1700°C for 10 minutes at high temperature to obtain a porous tungsten-rhenium alloy skeleton with suitable porosity and pore size distribution; Th...
Embodiment 2
[0068] The tungsten-iridium alloy powder with an average particle size of 2.4 μm is subjected to wet overflow classification, and the laser particle size span (SPAN) of the classified tungsten-iridium alloy powder is 1.2; after drying at 75°C, the vacuum degree is kept at 1×10 -4 Pa, heat at 500°C for 6 hours for deep degassing and purification; pass through a 150-mesh sieve; put the tungsten-iridium alloy powder evenly into the In the soft rubber mold, the tungsten-iridium alloy compact is obtained by cold isostatic pressing under 200MPa pressure for 10 minutes; the tungsten-iridium compact is placed in a high-temperature tungsten mesh furnace, and sintered at a low temperature of 1000°C in a high-purity hydrogen atmosphere 90min, then, directly switch the hydrogen atmosphere to 4×10 -3 Pa high vacuum, sintering at 1800°C for 30 minutes at high temperature to obtain a porous tungsten-iridium skeleton with suitable porosity and pore size distribution; The tungsten-iridium all...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com