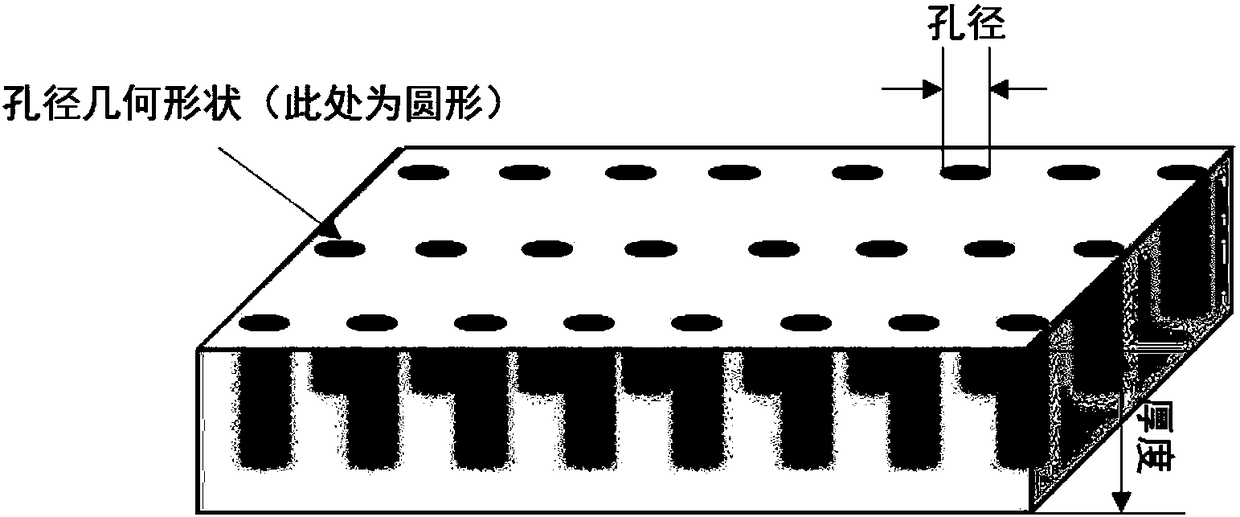
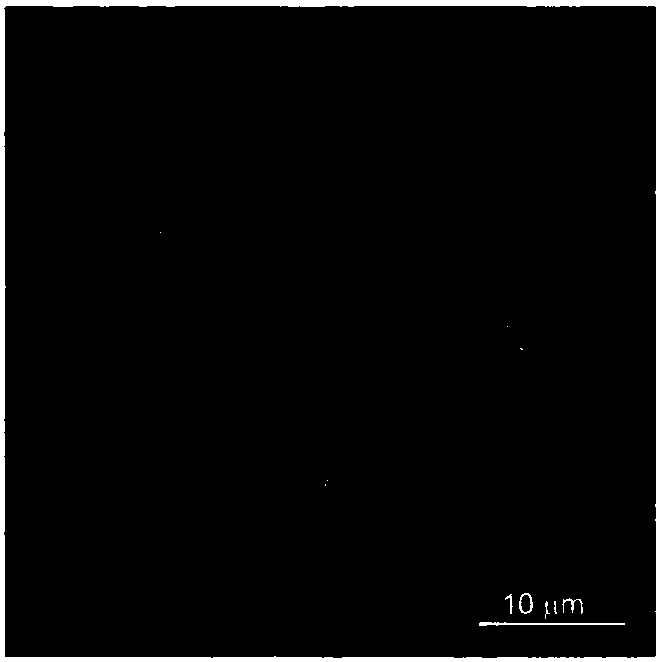Porous aluminum current collector capable of suppressing sodium dendritic crystal
A current collector and porous aluminum technology, which is applied in the field of porous aluminum current collectors, can solve the problems of battery short-circuit coulombic efficiency, continuous consumption of electrolyte, dendrites, etc., achieve uniform distribution of metal ions, improve cycle stability, and increase energy density. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] In a glove box filled with argon gas, porous aluminum and a comparative ordinary aluminum foil are used as negative electrodes. Sodium was used as a reference electrode and a counter electrode, and Celgard 2325 was used as a diaphragm, which was assembled into a button cell, and a blue electrode was used for deposition / dissolution experiments. The electrolytic solution used in the present invention is composed of a certain concentration of sodium salt and an organic solvent. The sodium salt is sodium hexafluorophosphate, and the solvent is diglyme. The deposition current is 0.1~50mA cm -2 , the deposition capacity is 0.5~20mAh cm -2 , when the current density is 0.5mA cm -2 , with a capacity of 0.5mAh cm -2 At the same time, after 1000 hours of cycling, there is still a small voltage hysteresis, while the battery assembled with ordinary aluminum foil is less than 60 cycles, and the voltage hysteresis increases rapidly due to uneven deposition. When the current dens...
Embodiment 2
[0028] The difference from Example 1 is that in this example, the sodium salt is sodium perchlorate, and the solvent is ethylene carbonate and diethyl carbonate with a volume ratio of 1:1. When the current density is 0.25mA cm -2 When , the deposition and dissolution time was controlled at 15 minutes, and after 1200 cycles, there was still a small voltage hysteresis.
Embodiment 3
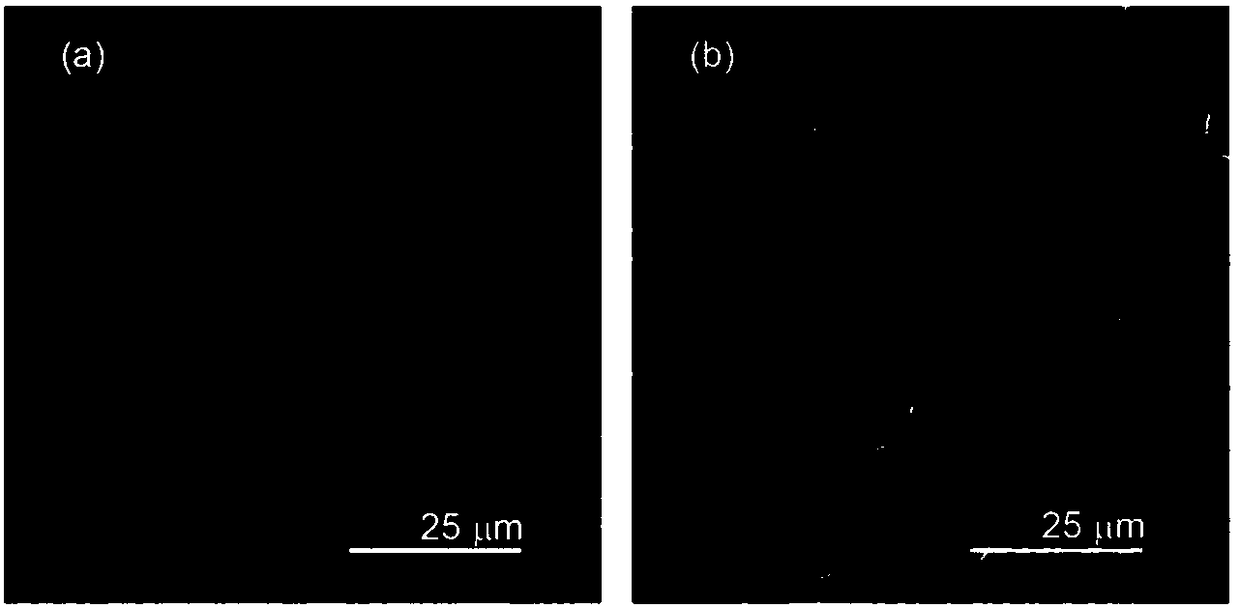
[0030] The difference from Example 1 is that the battery after the deposition of sodium or multiple cycles is disassembled in the glove box, the negative electrode is rinsed and dried, and the deposition morphology of metallic sodium is observed with a cold field emission scanning electron microscope (SEM), as shown in figure 2 shown. Compared with ordinary aluminum foil, the deposition of porous sodium aluminum is significantly improved, and the deposition is more uniform.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com