Method for enhancing membrane treatment on nickel-containing electroplating waste water
A technology for nickel electroplating and nickel wastewater, applied in water/sewage treatment, metallurgical wastewater treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc. The effect of improving the removal rate and improving the utilization efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
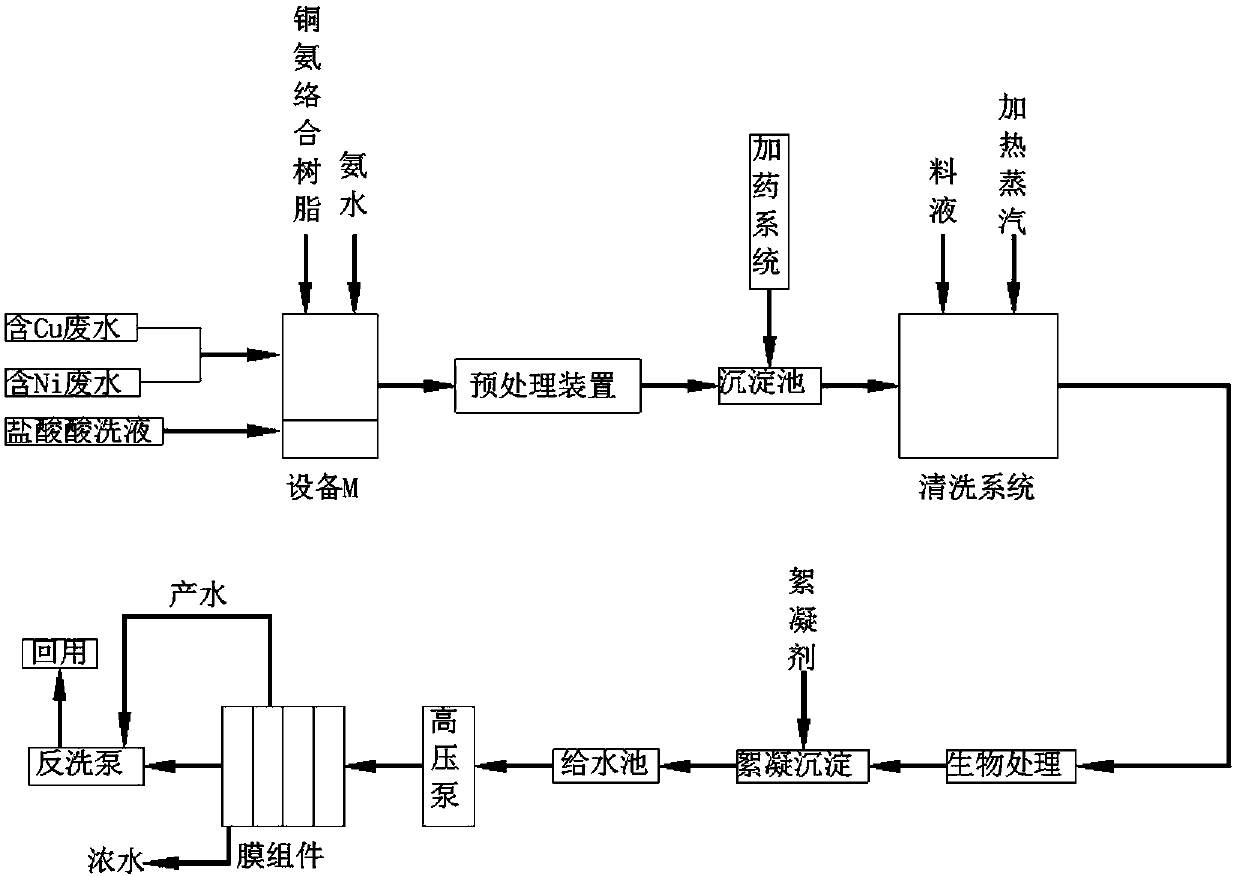
[0022] A method for improving the membrane method to treat nickel-containing electroplating wastewater, comprising the following specific steps:
[0023] 1) Treat the electroplating wastewater separately, in which the copper-containing wastewater and the nickel-containing wastewater are concentrated in a pipeline A, and the hydrochloric acid pickling waste liquid flows into the pipeline B, where the pipeline A and the pipeline B are respectively located at the top and bottom of the raw liquid inflow equipment M On both sides, copper-ammonia complex resin and ammonia water with a volume ratio of 3.5:0.7 are added to the upper side of the equipment M to comprehensively treat copper-containing wastewater and nickel-containing wastewater.
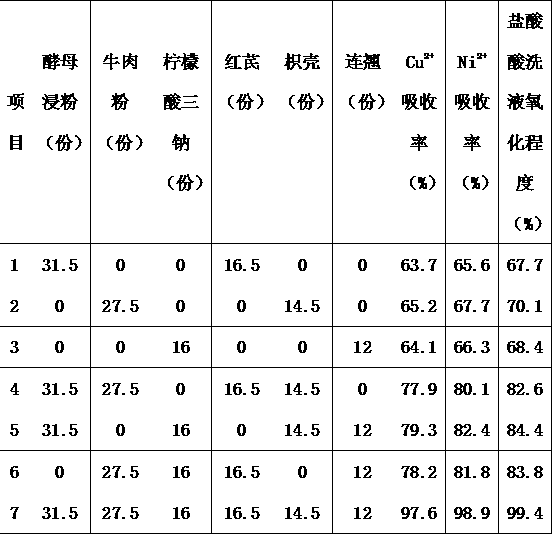
[0024] 2) Flow the copper-containing wastewater, nickel-containing wastewater and hydrochloric acid pickling waste treated in step 1) together into the pretreatment device, and add different groups of yeast extract powder, beef powder and trisod...
Embodiment 2
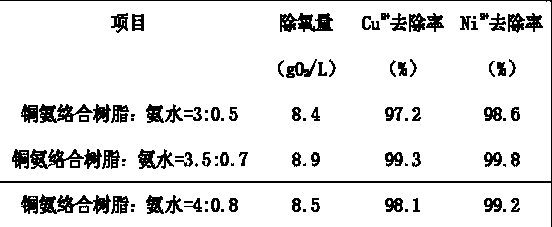
[0027] Utilize cuproammonia complex resin and ammonia water to make following comparison experiment to the removal rate of waste water in the present invention, the removal rate of copper ion and nickel ion, because the water that is saturated with dissolved oxygen under atmospheric pressure in influent, so the dissolved oxygen in effluent water The concentration is negligible relative to the influent water, so the calculation formula of the working oxygen removal capacity can be simplified as:
[0028] C=
[0029] In the formula, C-resin working oxygen removal capacity, gO 2 / L;
[0030] DO- saturated dissolved oxygen concentration of water under test temperature and pressure conditions, mg / L;
[0031] V- the qualified water volume prepared by the test column during the life test, L;
[0032] Vr-the volume of resin loaded on the test column, L.
[0033] The results of the comparative experiments are shown in Table 1:
[0034]
[0035] As can be seen from Table 1, th...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Under the experimental conditions of the present invention, compared with traditional waste water treatment copper ion, nickel ion rejection rate, membrane flux recovery rate etc. have all had bigger improvement, as shown in table 2:
[0039]
[0040] From the above table we can know that Cu in the present invention 2+ The rejection rate is 94.3%~96.1%, Ni 2+ The rejection rate is 95.5%-97.2%, and the membrane flux recovery rate reaches 90.4%-92.2%, which is obviously better than conventional wastewater treatment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com