A method of resource utilization of waste plastics in urban solid waste to promote iron ore reduction
A technology for recycling waste plastics, which is applied in the fields of ecological environmental protection and comprehensive utilization of resources, and can solve the problems of not considering the crushing of waste plastics, the low metallization rate of pellets, and the difficulty in application.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
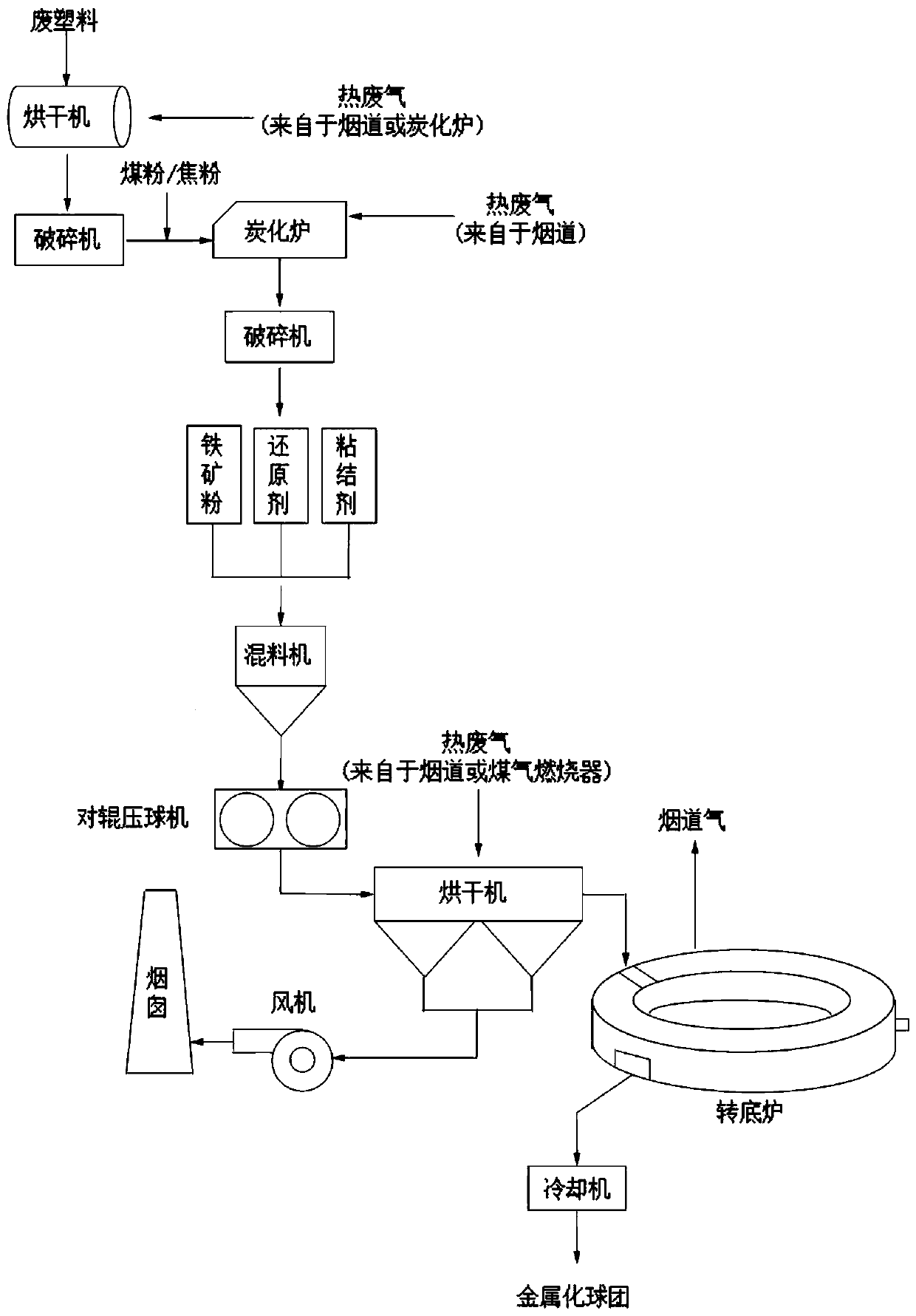
[0029] according to figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a method for low-temperature carbonization-iron ore reduction synergistic resource utilization of waste plastics in urban solid waste, using polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride film waste plastics, which are the main components of waste plastics in municipal solid waste, as raw materials, Break it into fragments with a side length of 10-20 mm, mix the two at a mass ratio of 1:1, and mix them evenly with anthracite powder (see Table 1 for the composition of anthracite). The proportion of waste plastics in the mixed reducing agent is 20%, coal If the particle size of the powder is less than 0.2mm, heat the mixture at 450°C for 20 minutes, discharge it after cooling, and then crush it to 0.2mm to obtain a mixed reducing agent.
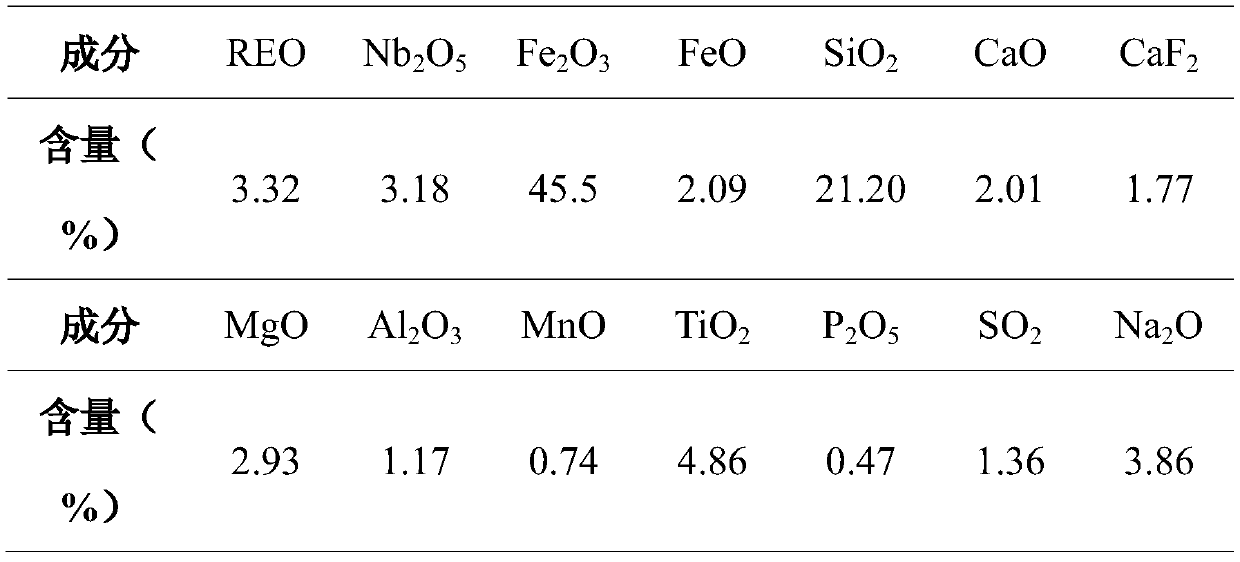
[0030] will contain Nb 2 o 5 3.18% low niobium ferroniobium concentrate ore powder containing titanium (see Table 2 for the composition of ferroniobium concentrate), weight is the mix...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The mixed reducing agent was prepared by the method described in Example 1. The high-phosphorite ore powder with a phosphorus content of 0.38%, the weight of high-phosphorite (see Table 3 for the composition of high-phosphorite) 16% mixed reducing agent (preparation method is the same as in Example 1, and anthracite coal powder is set Be the control group of reductant), weight is the CaCO of pyrite weight 39% 3 , the fluorspar whose weight is 5% of the iron ore weight, and the binder whose weight is 2% of the iron ore weight are transported to the mixer through a belt for mixing, and the moisture content of the mixed material is adjusted to 7%. The mixed material is conveyed to the double-roller ball pressing machine through the belt to make carbon-containing pellets, the pressure is 15MPa, and the size of the pellets is 40×30×20mm pillow-shaped ellipsoid. The raw balls are dried and spread on the carbonaceous refractory material of the rotary hearth furnace in a singl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com