Edible fungi cultivation nutrient for improving lignin conversion rate and method for cultivating edible fungi using nutrient
A technology for edible fungi and nutrients is applied in the field of edible fungi cultivation nutrients that improve the lignin conversion rate and the field of cultivation of edible fungi by using the nutrients, which can solve the problems of reducing the utilization rate of raw materials, long growth cycle, slow growth of mycelium, etc. The effect of bacterial culture delay period, growth rate improvement, disease resistance and yield promotion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] Each component and mass fraction of cultivation nutrients in the present embodiment are as follows:
[0069] 40 parts by mass of starch, 10 parts by mass of sodium acetate, 28 parts by mass of sea salt, 1 part by mass of betaine, and 21 parts by mass of corn gluten.
[0070] The starch is extracted from corn.
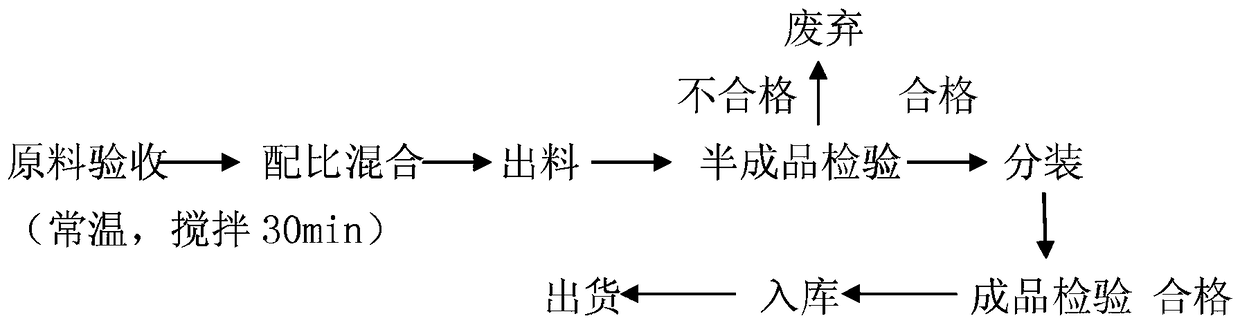
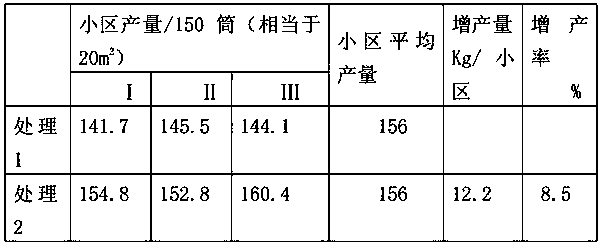
[0071] The above formula is applied to the cultivation of shiitake mushrooms. The cultivation techniques of Treatment 1 and Treatment 2 were used to test respectively, and the mycelium growth (see Table 2) and shiitake mushroom yield (see Table 3) of the experimental group and the control group were obtained.
[0072] Wherein, described treatment 1 adopts conventional nutrient material; Described treatment 2 adopts the cultivation nutrient of conventional nutrient material+above-mentioned formula, wherein, the cultivation nutrient of above-mentioned formula accounts for 2% of total nutrient material, other conditions are all the same, repeat the test three time...
Embodiment 2
[0081] The following formula was applied to the cultivation of oyster mushrooms.
[0082] 18 parts of flour, 30 parts of soybean protein, 45 parts of industrial salt, 0.2 parts of betaine and 25.8 parts of sodium acetate. The starch is extracted from sweet potato.
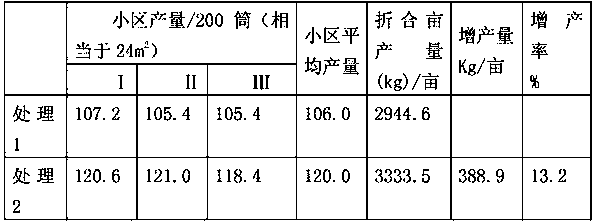
[0083] The cultivation techniques of Treatment 1 and Treatment 2 were used to test respectively, and the mycelium growth (see Table 4) and shiitake mushroom yield (see Table 5) of the experimental group and the control group were obtained.
[0084] Wherein, described treatment 1 adopts conventional nutrient material; Described treatment 2 adopts the cultivation nutrient of conventional nutrient material+above-mentioned formula, wherein, the cultivation nutrient of above-mentioned formula accounts for 3% of total nutrient material, other conditions are all the same, repeat the test three times.
[0085] The area of the plot in this example is 20 square meters (150 bacterial barrels), and the formula of the conve...
Embodiment 3
[0094] The following formula was applied to the cultivation of black fungus.
[0095] 30 parts of starch, 10 parts of cottonseed protein, 20 parts of table salt, 0.8 parts of betaine and 15 parts of sodium acetate. The starch is extracted from wild acorns.
[0096] The cultivation techniques of Treatment 1 and Treatment 2 were used to test respectively, and the yields of black fungus in the experimental group and the control group were obtained (see Table 6),
[0097] Wherein, described processing 1 is the cultivation nutrient of conventional black fungus culturing material+above-mentioned formula (the cultivating nutrient of above-mentioned formula accounts for 2% of total nutrient material, and the nutrition of the present embodiment is diluted to 600 times of liquid with water);
[0098] Treatment 2: conventional black fungus culture material + treatment 1 moderate amount of water;
[0099] Treatment 3: Conventional black fungus culture material (40 kg of broad-leaved saw...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com