Method for preparing NaV2O5 from vanadium-enriched liquid obtained by extracting vanadium from shale
A technology of vanadium-enriched liquid and vanadium liquid, applied in chemical instruments and methods, vanadium compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of ammonia nitrogen wastewater and waste gas environmental pollution, increase process energy consumption, low conversion efficiency, etc., to avoid ammonia nitrogen Effects of waste water, shortened preparation time, and reduced energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Preparation of NaV from a vanadium-rich liquid for extracting vanadium from shale 2 o 5 method, including the following steps:
[0031] 1) According to the molar ratio of oxalate and vanadium in the vanadium-rich solution is 0.25, oxalic acid is dissolved in the shale vanadium-rich solution with a vanadium concentration of 17.52g / L, and the pH of the solution is adjusted to 3.0 with sulfuric acid to obtain the to-be-reacted liquid;
[0032] 2) Transfer the liquid to be reacted to a high-temperature and high-pressure reactor, react for 7 hours at a temperature of 180° C., and obtain a slurry after natural cooling;
[0033]3) The slurry is separated into solid and liquid to obtain solid and liquid, and the solid is vacuum-dried at 60°C to obtain NaV 2 o 5 ;
[0034] NaV in this example 2 o 5 The conversion rate is 98.64%, and the purity is 99.07%.
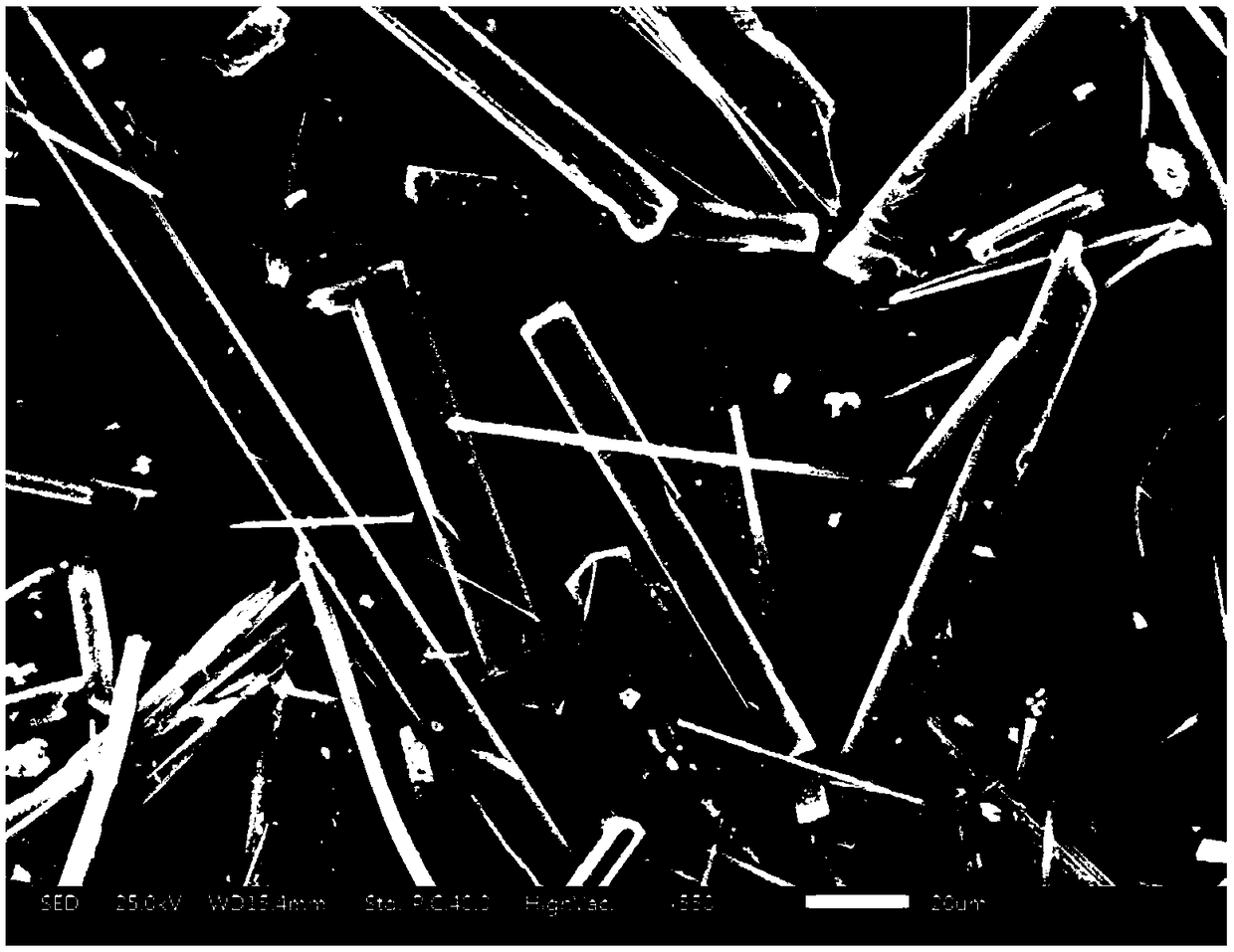
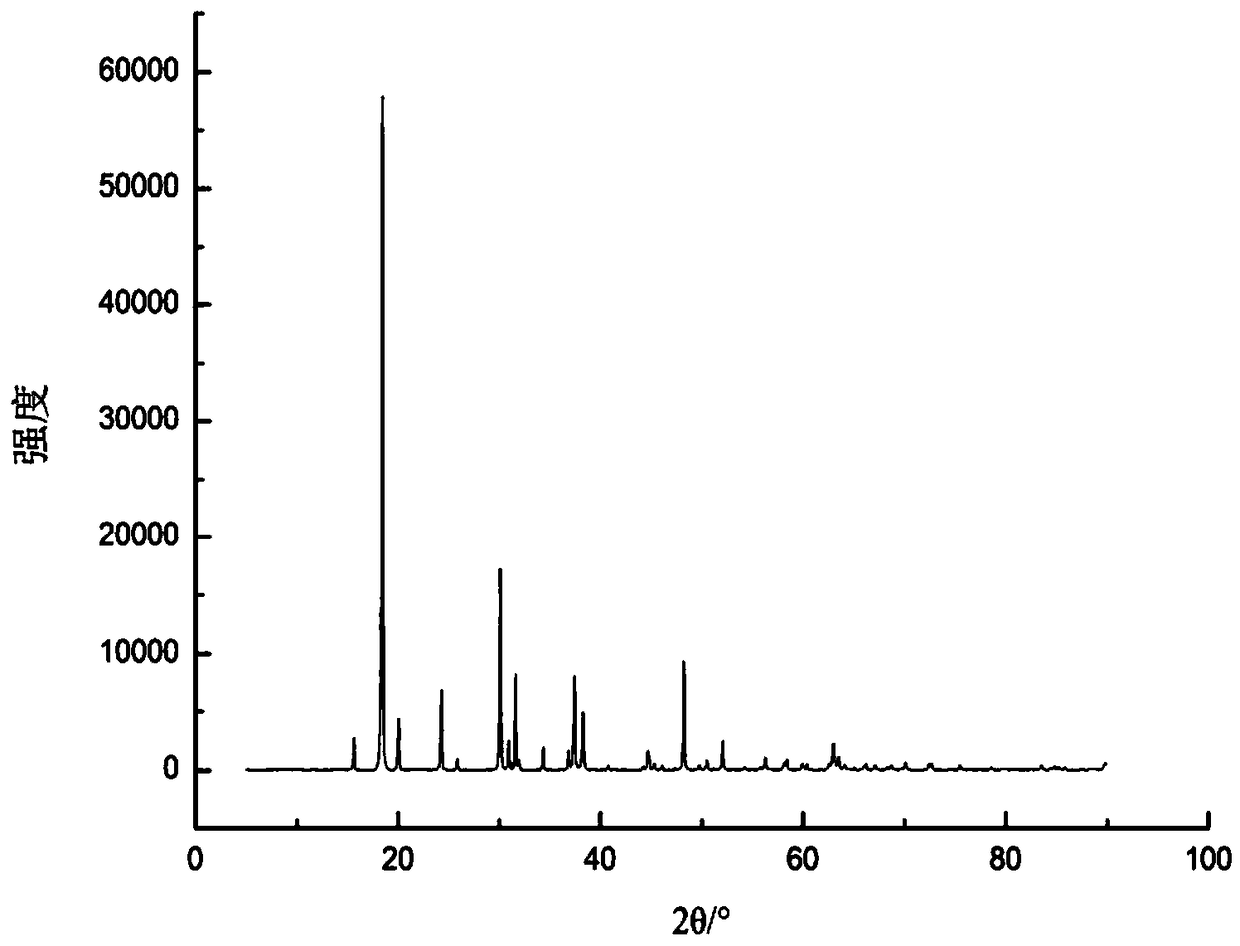
[0035] The NaV obtained by the preparation method of this embodiment 2 o 5 Refer to the attached X-ray diffraction...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Preparation of NaV from a vanadium-rich liquid for extracting vanadium from shale 2 o 5 method, including the following steps:
[0039] 1) According to the molar ratio of oxalate and vanadium in the vanadium-rich solution being 1.0, potassium oxalate is dissolved in the shale vanadium-rich solution with a vanadium concentration of 19.68g / L, and the pH of the solution is adjusted to 5.0 with sulfuric acid to obtain The reaction solution;
[0040] 2) Transfer the liquid to be reacted to a high-temperature and high-pressure reactor, react for 6 hours at a temperature of 220° C., and obtain a slurry after natural cooling;
[0041] 3) The slurry is separated into solid and liquid to obtain solid and liquid, and the solid is vacuum dried at 80°C to obtain NaV 2 o 5 ;
[0042] NaV in this example 2 o 5 The conversion rate is 99.11%, and the purity is 99.10%.
Embodiment 3
[0044] A vanadium-rich liquid NaV for extracting vanadium from shale 2 o 5 method, including the following steps:
[0045] 1) According to the molar ratio of oxalate root and vanadium in the vanadium-rich solution being 2.0, sodium oxalate is dissolved in the shale vanadium-rich solution with a vanadium concentration of 22.73g / L, and the pH of the solution is adjusted to 7.0 with sulfuric acid to obtain The reaction solution;
[0046] 2) Transfer the liquid to be reacted to a high-temperature and high-pressure reactor, react at a temperature of 230°C for 8 hours, and obtain a slurry after natural cooling;
[0047] 3) The slurry is separated into solid and liquid to obtain solid and liquid, and the solid is vacuum-dried at 60°C to obtain NaV 2 o 5 ;
[0048] NaV in this example 2 o 5 The conversion rate is 99.54%, and the purity is 99.32%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com