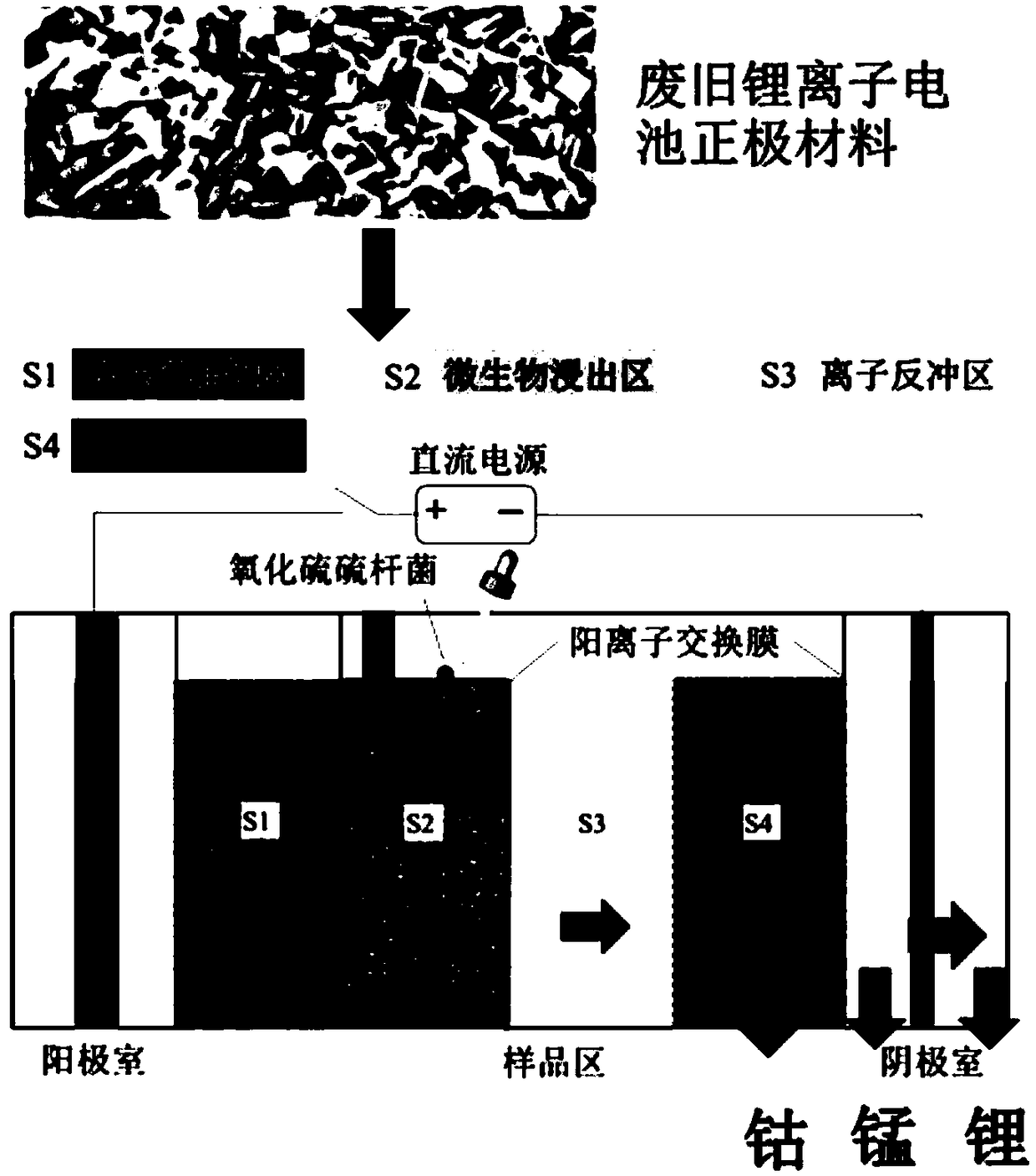
Method for synchronously separating and recycling cobalt, lithium and manganese from cathode material of waste lithium ion battery
A lithium-ion battery and positive electrode material technology, which is applied in the field of waste lithium battery waste treatment and resource recycling, can solve the problems of limited mass transfer of electron acceptors, high impurity content in leachate, and poor microbial tolerance, so as to reduce production capacity and disposal costs, saving resources and energy, and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Example 1 Effect of surface-modified activated carbon addition of different proportions of active agent mixture on the recovery efficiency of cobalt, manganese and lithium
[0025]Disassemble the used lithium-ion battery and take out the positive electrode material foil. The cathode material foil was pulverized, and put into an ultrasonic cleaner together with N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone for cleaning for five minutes. The cathode material fragments were taken out, washed three times with deionized water, and then dried for later use to obtain the cathode material for lithium ion batteries. Soak commercial activated carbon in a mixture containing 8% by mass of 2-ethylhexylphosphonic acid mono-2-ethylhexyl (PC-88A) and 3% by mass of tri-n-octylamine (TOA) In the three groups of mixed solutions containing 10% by mass PC-88A and 5% by mass TOA activator, 12% by mass PC-88A and 7% by mass TOA activator, mechanically stirred for 2 hour, then take it out and rinse it three times ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2 The effect of mixed matrix powder addition in different mixing ratios on cobalt, manganese, and lithium recovery efficiency
[0034] The hematite powder, the pyrite powder, and the positive electrode material of the lithium ion battery were mechanically ball milled for 2 hours respectively. The sample area of the electrolytic cell was equally divided into four sub-areas with a polyethylene grid with a pore size of 0.25 mm. Soak commercial activated carbon in 12% 2-ethylhexylphosphonic acid mono-2-ethylhexyl ester (PC-88A) and 7% tri-n-octylamine (TOA) activator mixture, mechanically stir for 2 hour, then take it out and rinse it three times with deionized water, and dry it for subsequent use to obtain surface-modified activated carbon powder. The lithium-ion battery cathode material, elemental sulfur and pyrite powder prepared in Example 1 were dried at a constant temperature until the water content was less than 2%, and then sieved. In parts by mass, weig...
Embodiment 3
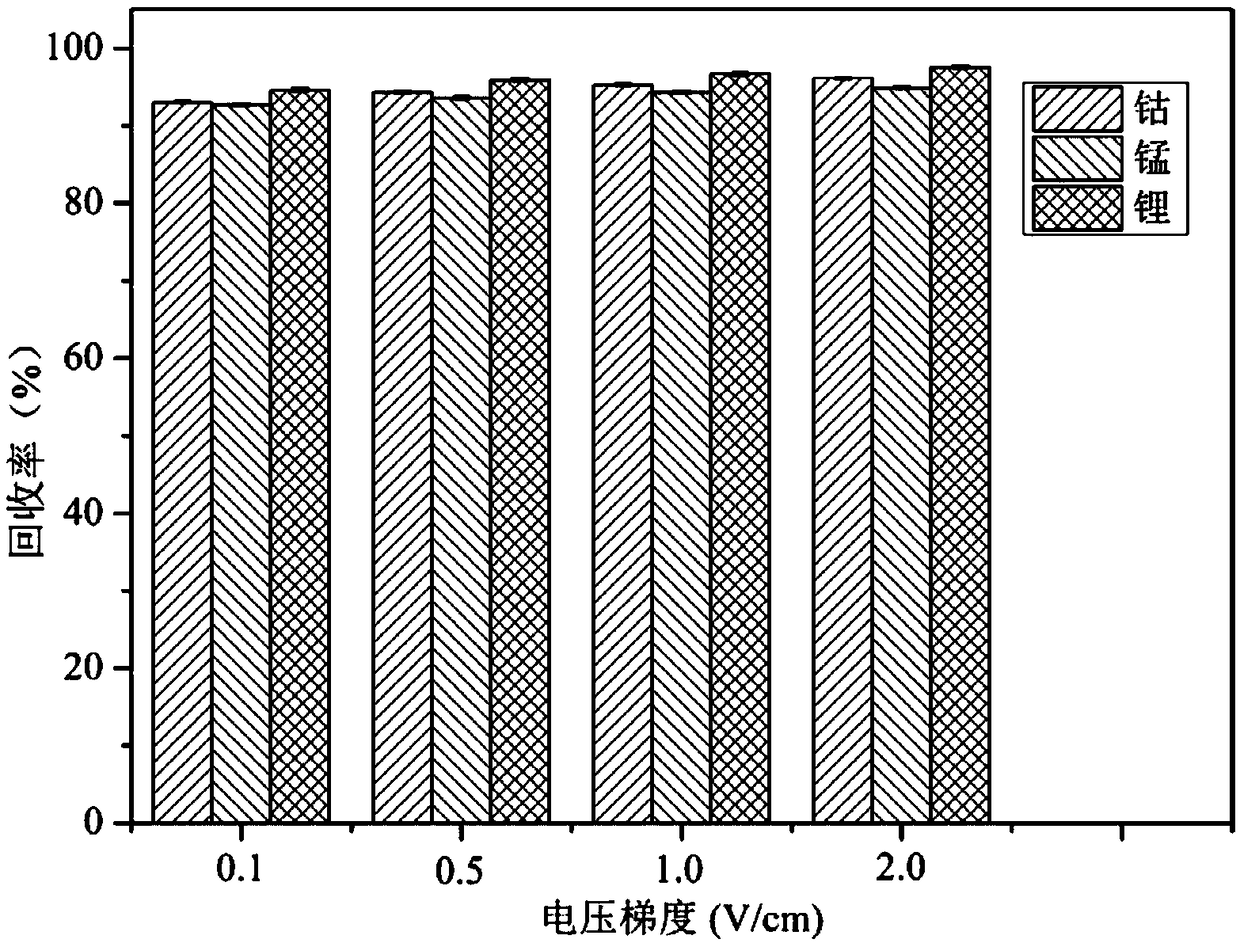
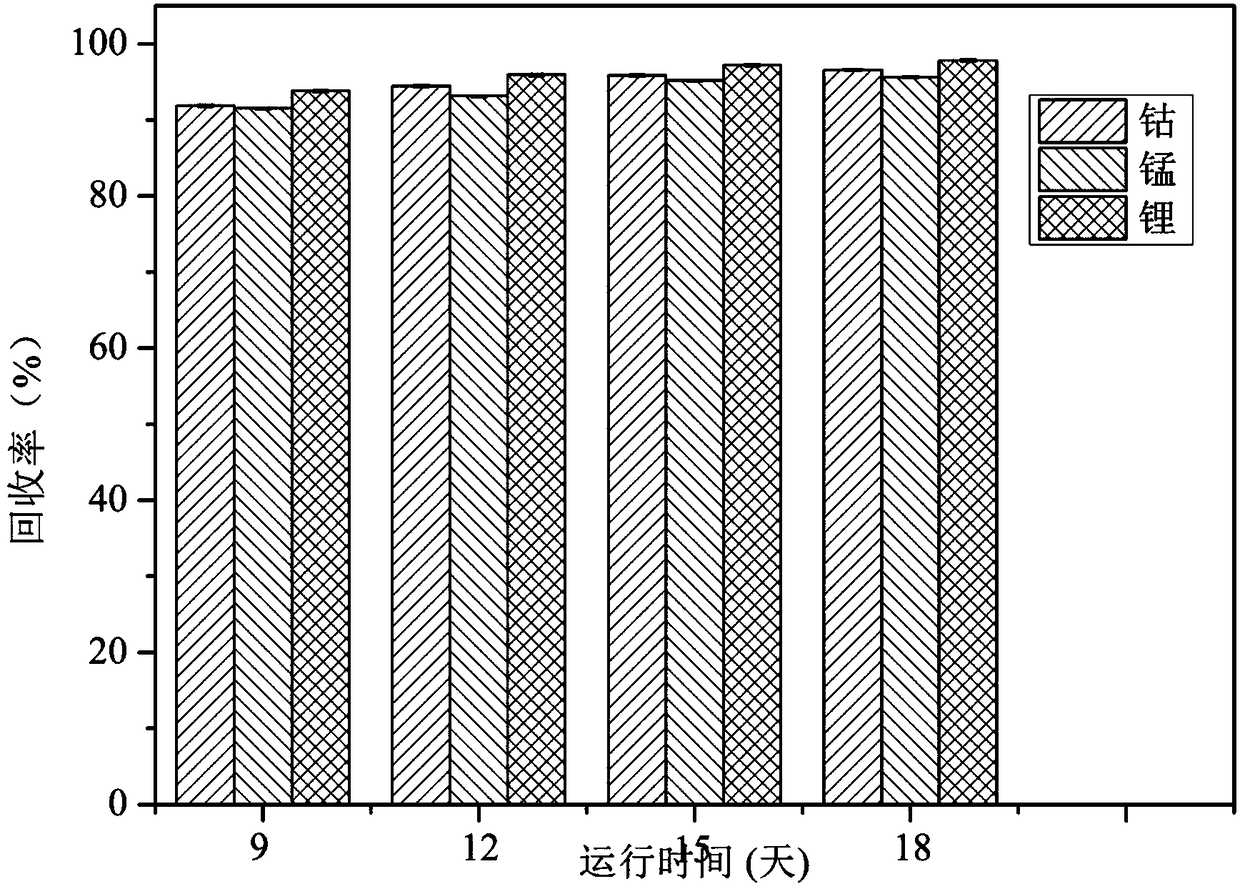
[0040] Embodiment 3 The common influence of voltage gradient and electrolyzer running time on cobalt, lithium, manganese recovery efficiency
[0041] The hematite powder, the pyrite powder, and the positive electrode material of the lithium-ion battery were mechanically milled for 4 hours respectively. The sample area of the electrolytic cell was equally divided into four sub-areas with a polyethylene grid with a pore size of 0.5 mm. Dry the lithium ion battery cathode material, elemental sulfur and pyrite powder prepared in Example 1 at a constant temperature until the water content is less than 2%, and then sieve. In parts by mass, weigh mixed matrix powder: lithium-ion battery cathode material, elemental sulfur, and pyrite powder (5 parts, 5 parts, 90 parts) and stir evenly and add to the S2 area of the electrolytic cell. Fill the hematite powder equal to the mixed matrix powder and the surface-modified activated carbon powder prepared in Example 2 into the S1 and S4 a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com