Resin-based zero-valent copper catalyst, preparation method and application of resin-based zero-valent copper catalyst in catalytic reduction of para-nitrophenol
A zero-valent copper and resin-based technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, organic compounds/hydrides/coordination complex catalysts, etc. Catalysts are expensive and other issues, to achieve the effects of recycling, saving economic costs, and stable structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Add 100mg of D001 resin into 100mL of 200mg / L cupric chloride solution, shake until adsorption equilibrium, and obtain D001 resin loaded with 13% copper ions. Then add 500mg of sodium borohydride to reduce divalent copper to zero-valent copper, resin-based zero-valent copper catalyst.
[0042] The particle size of D001 cation exchange resin loaded zero-valent copper catalyst obtained in Example 1 is concentrated in 50 μm-1mm, and its scanning electron microscope picture is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the figure shows the surface morphology of the catalyst at magnifications of 1000 μm, 500 μm, and 5 μm.
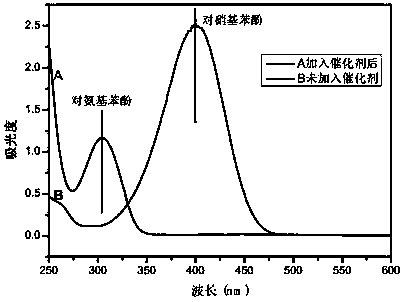
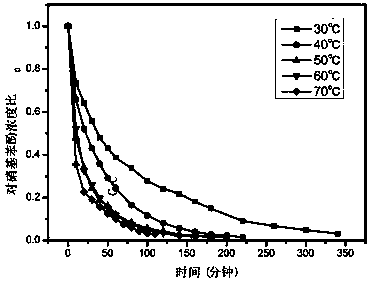
[0043] Add 100mg of the resin-based zero-valent copper catalyst to 100mL 20mg / L p-nitrophenol solution, then add 0.1g sodium borohydride, and catalyze the conversion of p-nitrophenol into p-aminophenol at room temperature. After 2 hours, the catalytic conversion rate can reach up to 90%.
Embodiment 2
[0045]Add 100 mg of macroporous aminophosphoric acid chelating resin to 100 mL of 10 mg / L copper chloride solution, shake to adsorption equilibrium, and obtain macroporous aminophosphoric acid chelating resin loaded with 1% copper ions. Then add 500 mg of sodium borohydride to reduce divalent copper to zero-valent copper to obtain a resin-based zero-valent copper catalyst.
[0046] The obtained resin-based zero-valent copper catalyst was added to 100 mL of 20 mg / L p-nitrophenol solution, and then 0.1 g of sodium borohydride was added to catalyze the conversion of p-nitrophenol into p-aminophenol at room temperature. After 2 hours, the catalytic conversion rate could reach up to 95%.
Embodiment 3
[0048] Add 100mg of polyvinylpyridine resin to 100mL of 80mg / L copper chloride solution, shake to adsorption equilibrium, and obtain polyvinylpyridine nitrogen-containing resin loaded with 7% copper ions. Then add 500 mg of sodium borohydride to reduce divalent copper to zero-valent copper to obtain a resin-based zero-valent copper catalyst.
[0049] The obtained resin-based zero-valent copper catalyst was added to 100 mL of 20 mg / L p-nitrophenol solution, and then 0.1 g of sodium borohydride was added to catalyze the conversion of p-nitrophenol into p-aminophenol at room temperature. After 2 hours, the catalytic conversion rate could reach up to 80%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com