Fluorescent ring-mediated isothermal amplification method based on molecular beacon
A technology of isothermal amplification and molecular beacon probes, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, measurement/testing of microorganisms, resistance to vector-borne diseases, etc., can solve the problem of unrecognizable, difficult to preserve, and unobvious color reaction of HNB and other problems, to achieve the effect of solving the problem of non-specific amplification, huge application value and commercial value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] Embodiment 1, design synthesis and detection method optimization of primer probe
[0071] 1. Primer design and synthesis
[0072] A set of primer combinations for identifying Vibrio cholerae was obtained through a large number of sequence analysis and alignment. The primer set includes front primer (HL-F3), back primer (HL-B3), front inner primer (HL-FIP), back inner primer (HL-BIP) and two accelerated primers (HL-LF, HL-LB) . The primer sequences are as follows (5'→3'):
[0073] HL-F3 (Sequence 1 of the Sequence Listing): CCTAAATGTAGCAAATTGATTTCCT;
[0074] HL-B3 (SEQ ID NO: 2 of the SEQUENCE LISTING): GTCATTAGGTACTACCGAGG;
[0075] HL-FIP (SEQ ID NO: 3 of the Sequence Listing): TCCTTTTTTGTAGGGCTATGTTGTTGTTTGTGTGATTTTTGTGTGC;
[0076] HL-BIP (SEQ ID NO: 4 of the Sequence Listing): ACCATTTGCCTAGCCGTACTACAATAAAGTCACCTTCTTGG;
[0077] HL-LF (SEQ ID NO: 5 of the SEQUENCE LISTING): TGTGTTGCGCGCACAGTA;
[0078] HL-LB (SEQ ID NO: 6 of the Sequence Listing): TGCAGCCCTAC...
Embodiment 2
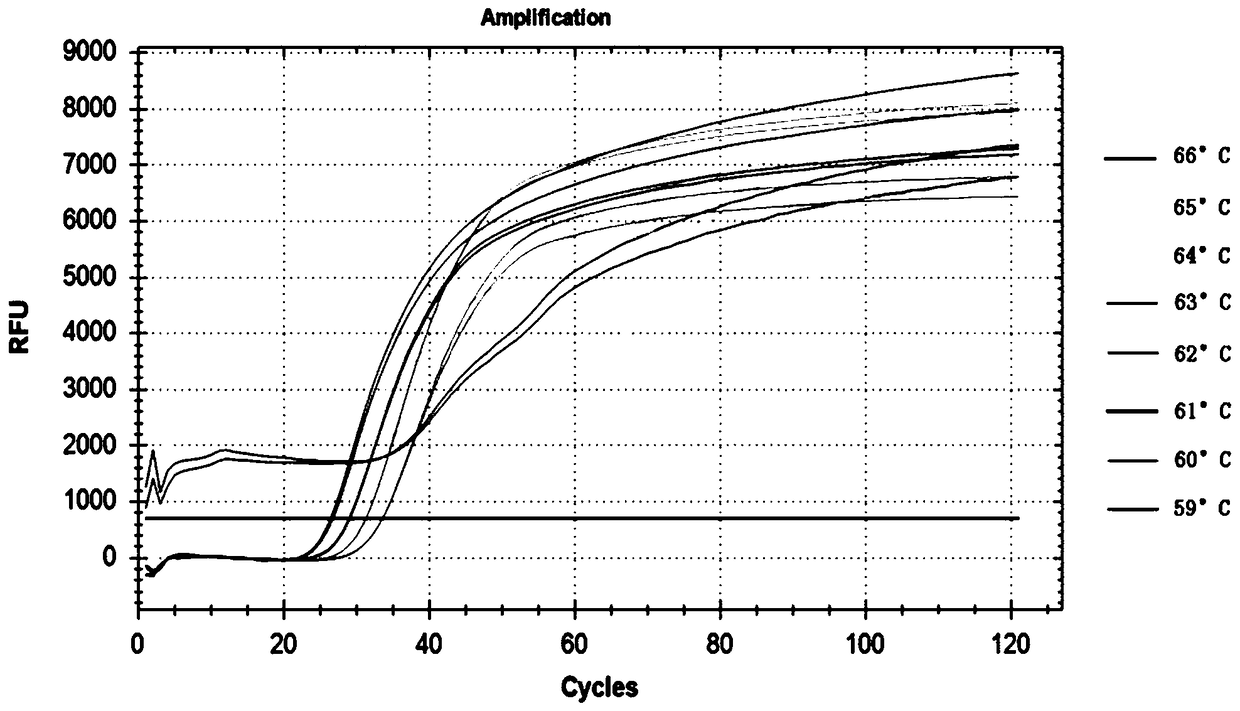
[0113] Embodiment 2, specificity
[0114] The samples to be tested are: Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579 (Bacillus cereus), Pseudomonasaeruginosa ATCC 15692 (Pseudomonas aeruginosa), Enterococcusfaecium ATCC 6569 (Enterococcus faecium), Streptococcus dysgalactiae ATCC 27957 (Streptococcus dysgalactiae), Escherichia coli ATCC (2592 coli), Streptococcus uberis ATCC 9927 (Streptococcus uberis), StreptococcuspneumoniaATCC 49619 (Streptococcus pneumoniae), Salmonella enterica ATCC 14028 (Salmonella enterica), Yersiniaenterocolitica ATCC 9610 (Yersinia enterocolitica), Yersinia enterocolitica ATCC 9610 (colon Yersinia pneumoniae), Vibrio Parahemolyticus ATCC 17802 (Vibrio parahaemolyticus), Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 (Staphylococcus aureus), Shigellaflexneri ATCC 12022 (Frexnerella), staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC 12228 (Epidermal Staphylococcus), Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212 (Enterococcus faecalis), and Vibrio cholera ATCC 11561 (Vibrio cholerae).
[0115] 1. Using the total ...
Embodiment 3
[0124] Embodiment 3, sensitivity
[0125] 1. Dilute the Vibrio cholerae positive plasmid 10 times with sterile water to obtain each dilution.
[0126] 2. Using the dilutions obtained in step 1 as templates, use the primer combination in step 1 of Example 1 to carry out LAMP reaction.
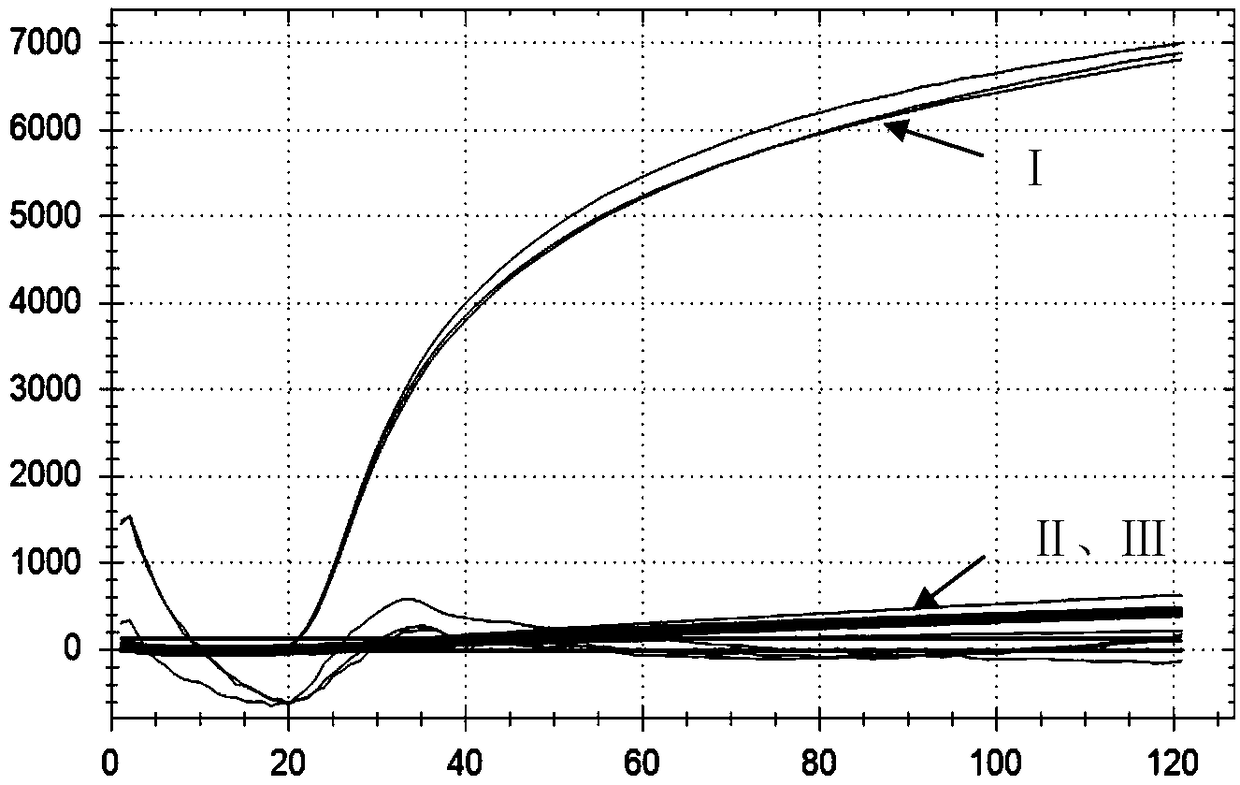
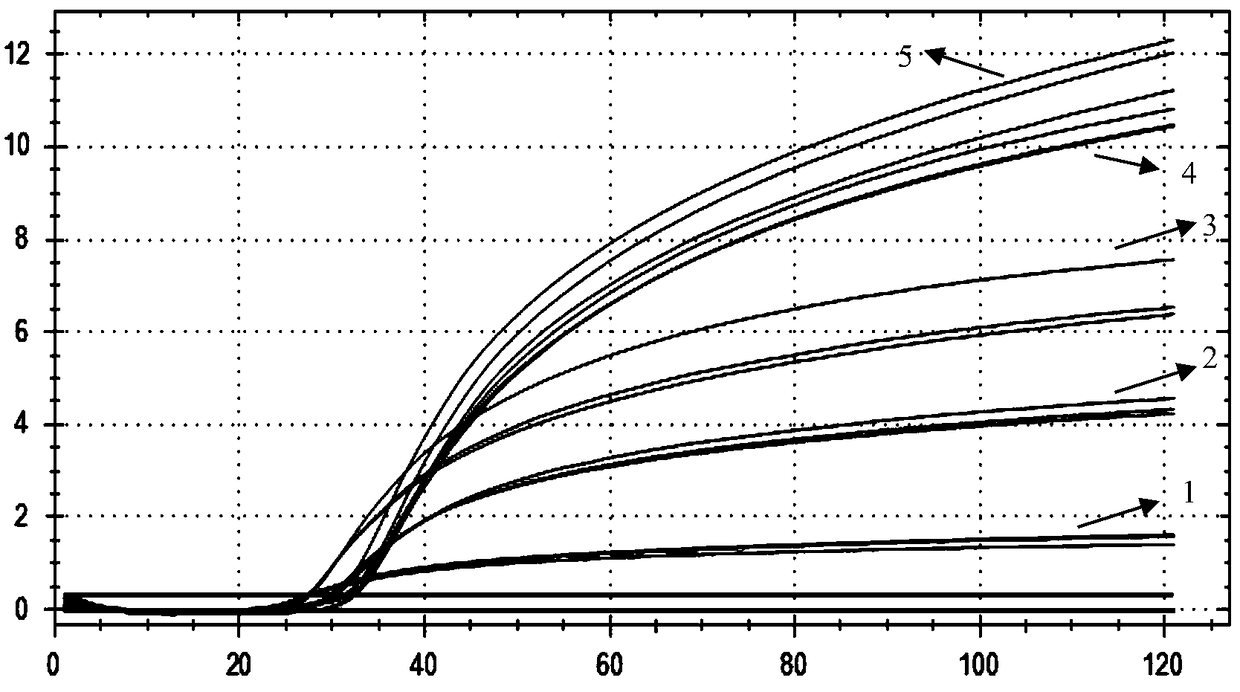
[0127] LAMP reaction system (25 μL): template 2 μL, Tris-HCl (pH=8.8) 20 mM, KCl 10 mM, (NH4) 2 SO 4 10mM, betaine 0.8M, MgSO 4 8mM, dNTP1.4mM, Tween200.25μL, Bst DNA polymerase 8U, primer HL-F35pmol, primer HL-B35pmol, primer HL-FIP 40pmol, primer HL-BIP 40pmol, primer HL-LF 20pmol, primer HL-LB 20pmol, Molecular Beacon Probe LBP 8 pmol.
[0128] LAMP reaction conditions: constant temperature reaction at 63°C for 60 minutes.
[0129] Due to the different dilutions used, the following different reaction systems are formed:
[0130] In reaction system L1, the initial content of plasmid DNA is: 20ng;
[0131] In reaction system L2, the initial content of plasmid DNA is: 2ng;
[0132] In re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com