Preparation method of charcoal-loaded zero-valent iron catalytic material
A technology of catalytic materials and zero-valent iron, applied in the direction of catalyst activation/preparation, chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc., can solve problems such as high cost, secondary pollution, weak slow-release ability, etc., and achieve good removal and reducing effect, reducing process cost, reducing the effect of preparation cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] The Fe content is 25%, and the preparation steps of biochar-loaded zero-valent iron catalytic material BC / nZVI are as follows:
[0022] (1) Take 1.8 g of oak chips crushed to below 100 mesh and add them to the polytetrafluoroethylene bottle of the autoclave, and then add 18 mL of deionized water. Under the condition of 200 ° C for 20 minutes, the hydrothermal charcoal HC was obtained by filtration and drying.
[0023] (2) Add HC to 100 mL of Fe(NO 3 ) 3 solution, stirred for 12h, filtered and dried.
[0024] (3) Load the supported HC obtained in (2) into a porcelain boat, put the porcelain boat into a tube furnace, and carbonize at 800°C for 40 minutes in a nitrogen atmosphere.
[0025] (4) After cooling the dried sample in (3), grind and sieve to obtain the biochar-loaded zero-valent iron catalytic material BC / nZVI.
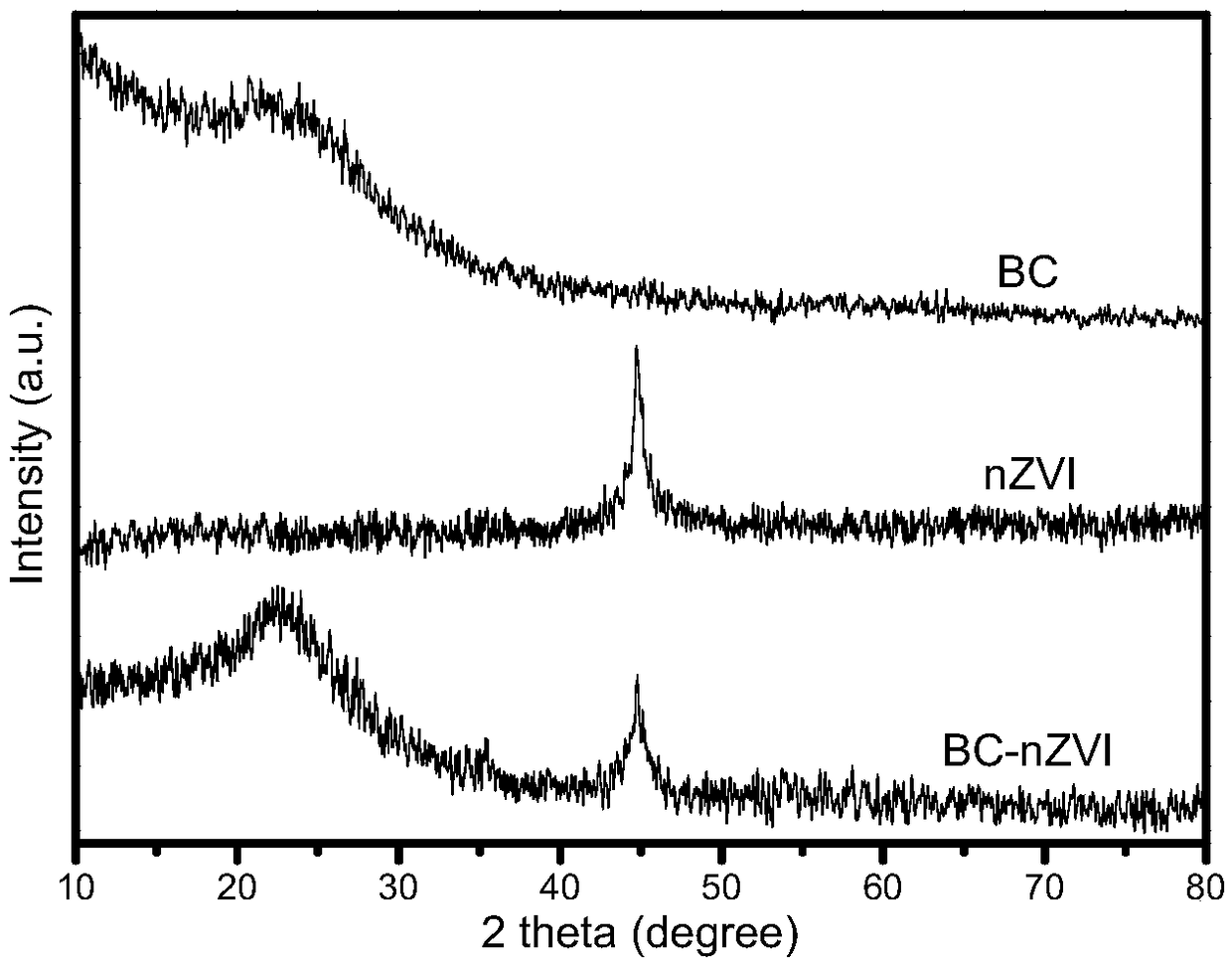
[0026] figure 1 XRD patterns of biochar BC, nanometer zero-valent iron nZVI, and biochar-supported zero-valent iron catalytic material BC / nZVI. Dep...
Embodiment 2
[0028] The Fe content is 20%, and the preparation steps of biochar-loaded zero-valent iron catalytic material BC / nZVI are as follows:
[0029] (1) Take 1.8 g of oak chips crushed to below 100 mesh and add them to the polytetrafluoroethylene bottle of the autoclave, and then add 18 mL of deionized water. Under the condition of 200 ° C for 20 minutes, the hydrothermal charcoal HC was obtained by filtration and drying.
[0030] (2) Add HC to 100 mL of Fe(NO 3 ) 3 solution, stirred for 12h, filtered and dried.
[0031] (3) Load the supported HC obtained in (2) into a porcelain boat, put the porcelain boat into a tube furnace, and carbonize at 800°C for 40 minutes in a nitrogen atmosphere.
[0032] (4) After the sample dried in step (3) is cooled, it is ground and sieved to obtain the biochar-loaded zero-valent iron catalytic material BC / nZVI.
Embodiment 3
[0034] The Fe content is 30%, and the preparation steps of biochar-loaded zero-valent iron catalytic material BC / nZVI are as follows:
[0035] (1) Take 1.8 g of oak chips crushed to below 100 mesh and add them to the polytetrafluoroethylene bottle of the autoclave, and then add 18 mL of deionized water. Under the condition of 200 ° C for 20 minutes, the hydrothermal charcoal HC was obtained by filtration and drying.
[0036] (2) Add HC to 100 mL of Fe(NO 3 ) 3 solution, stirred for 12h, filtered and dried.
[0037] (3) Load the supported HC obtained in (2) into a porcelain boat, put the porcelain boat into a tube furnace, and carbonize at 800°C for 40 minutes in a nitrogen atmosphere.
[0038] (4) After the sample dried in step (3) is cooled, it is ground and sieved to obtain the biochar-loaded zero-valent iron catalytic material BC / nZVI.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com