Method for removing nitrogen and phosphorus in wastewater by utilizing magnesium salt in desulfurization wastewater
A technology for desulfurization wastewater and magnesium salts, applied in water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problem of high operating costs and achieve the effect of improving purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
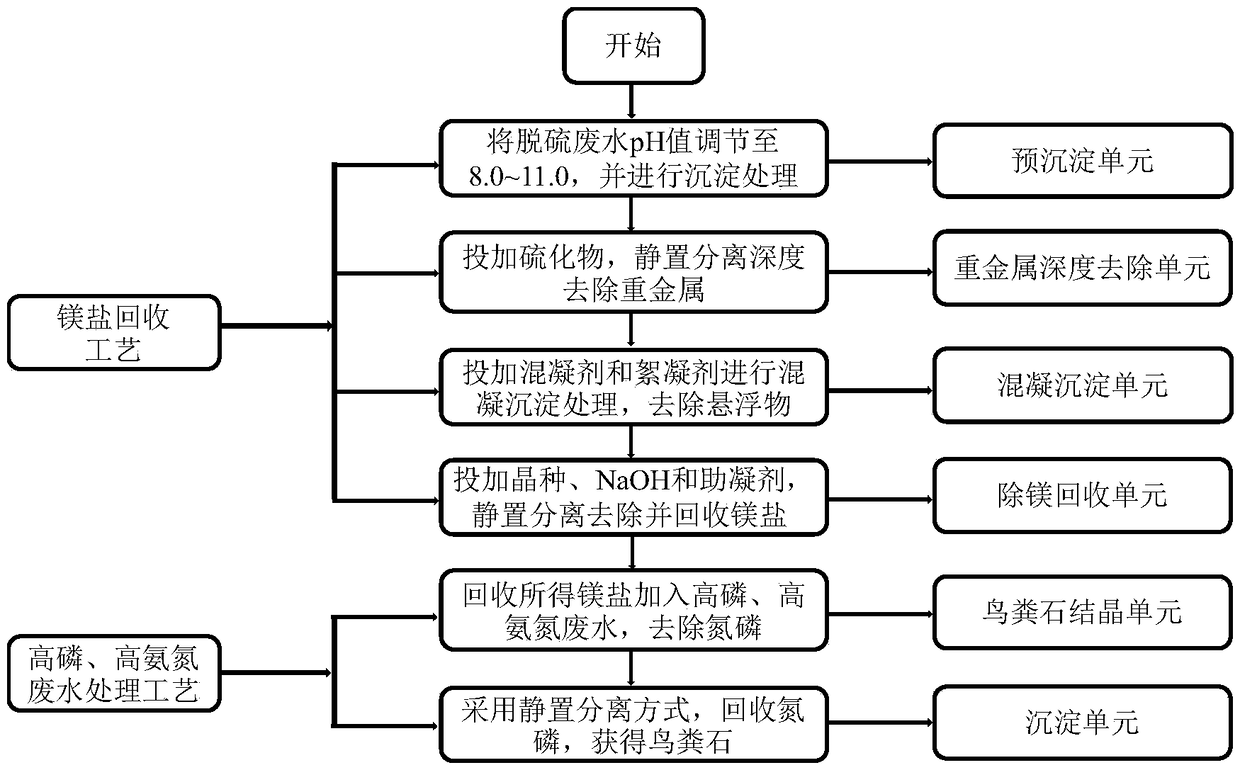
[0042] Removal of magnesium salts from desulfurization wastewater and recovery of condensate polishing to treat ammonia nitrogen in regenerated wastewater. The experiment was carried out on a six-connected mixer, including two parts: magnesium salt recovery and regenerated wastewater treatment. The specific steps are as follows:
[0043] The first part, magnesium salt recovery process
[0044] The first step is to use Ca(OH) 2 Adjust the pH value of the desulfurization wastewater to 9.0-10.0, stir with a stirrer at a speed of 300 rpm for 3 minutes, settle for 0.2-1 hour, and take the supernatant;
[0045] The second step, the organic sulfur of 20~80mg / L waste water and the Na of 10~40mg / L are added in the supernatant described in the first step. 2 S, after stirring with a stirrer at a speed of 300 rpm for 3 minutes, carry out precipitation treatment for 0.2 to 1 hour, and take the supernatant;
[0046] In the third step, add polyaluminium chloride 40~80mg / L in the supernatant ...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Desulfurization wastewater magnesium salt removal and recovery of nitrogen and phosphorus in concentrated dewatered sludge water, the experiment was carried out on a six-connected mixer, including magnesium salt recovery and concentrated dewatered sludge water treatment two parts, the specific steps are as follows:
[0054] The first part is described with the first part in the example 1;
[0055] The second part, concentrated dewatered sludge water treatment
[0056] The first step is to analyze the water quality of the concentrated dewatered sludge water. The content of ammonia nitrogen is 341.62 mg / L, and the content of phosphorus is 64.46 mg / L; the recovered magnesium salt is added to the concentrated dewatered sludge water so that the Mg:P molar ratio is 2 :1, adjust the pH value to 8.0-9.0;
[0057] In the second step, stir at a speed of 150 revolutions per minute for 30 minutes; after standing for 0.2 to 1 hour to separate layers, take the supernatant to measure...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Removal of magnesium salts from desulfurization wastewater and recovery of condensate polishing to treat ammonia nitrogen in regenerated wastewater. The experiment was carried out on a six-connected mixer, including two parts: magnesium salt recovery and regenerated wastewater treatment. The specific steps are as follows:
[0061] The first part, magnesium salt recovery process
[0062] The first step is to use Ca(OH) 2 Adjust the pH value of the desulfurization wastewater to about 11, stir with a stirrer at a speed of 300 rpm for 3 minutes, settle for about 0.1 hour, and take the supernatant;
[0063] In the second step, add 100mg / L of Na in the supernatant described in the first step 2 S, after stirring with a stirrer at a speed of 300 rpm for 3 minutes, carry out precipitation treatment for about 0.1 hour, and take the supernatant;
[0064] The 3rd step, add ferric chloride, polyferric sulfate, ferrous sulfate (mass ratio is 1:1:1) in the supernatant described in t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com