A method for preparing fluorine-containing hierarchical porous structure polymer based on etching polylactic acid
A technology of structural polymers and porous polymers, applied in chemical instruments and methods, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problems of long etching polylactic acid, complicated operation steps, high energy consumption, etc., and increase porosity and specific surface area Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
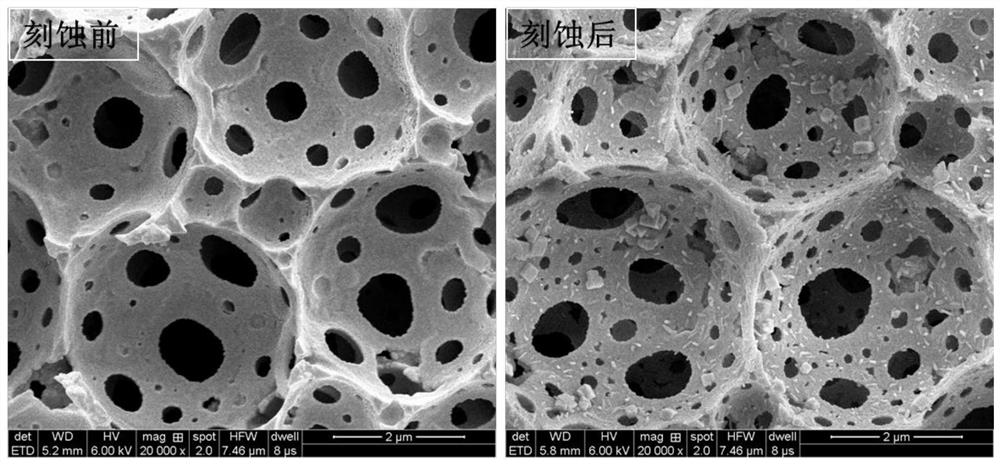
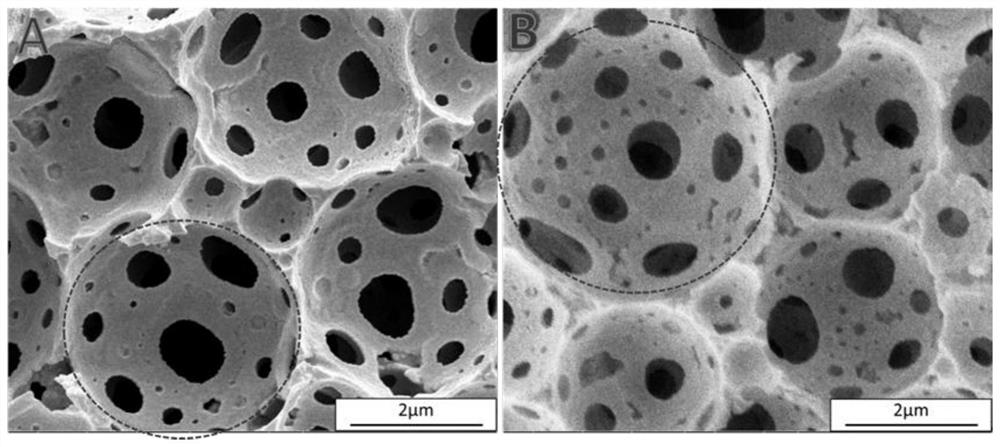
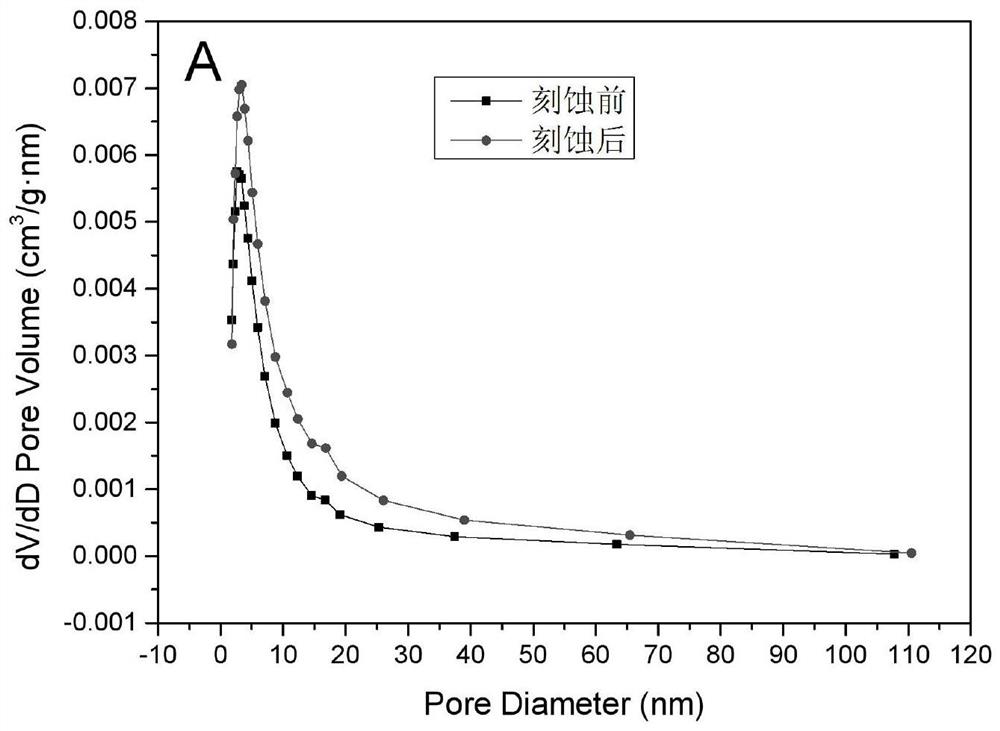
[0053] An oil phase was prepared by mixing 2.0020 parts of trifluoroethyl methacrylate, 1.0100 parts of divinylbenzene, 0.2030 parts of b246, 0.7501 parts of PLA-11000 and 0.0311 parts of azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN). 18.00 parts of an aqueous calcium chloride solution was used as the aqueous phase. Stir the oil phase at a speed of 400 rpm, slowly drop the water phase into the oil phase, stir and mix thoroughly, increase the stirring speed to 500 rpm after the addition, and stir for 30 minutes. The temperature is raised to 65°C in the reactor to initiate polymerization, and the reaction is stopped after 24 hours of polymerization, and the polymerization product is taken out and dried to obtain a fluorine-containing porous polymer material. The obtained porous material has an average pore diameter of 2.90 μm and a density of 0.1783 cm 3 / g, the porosity is 89.55%, and the internal specific surface area is 17.9376m 2 / g.
[0054] Take 0.3484g of the obtained porous material ...
Embodiment 2
[0062] An oil phase was prepared by mixing 2.0612 parts of hexafluorobutyl methacrylate, 1.0027 parts of divinylbenzene, 0.2988 parts of b246, 0.7500 parts of PLA-11000 and 0.0309 parts of azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN). 18.00 parts of an aqueous calcium chloride solution and 0.0410 parts of potassium persulfate were mixed to obtain an aqueous phase. Stir the oil phase at a speed of 400 rpm, slowly drop the water phase into the oil phase, stir and mix thoroughly, increase the rotation speed to 500 rpm and continue stirring for 30 minutes after the addition is complete. Then the emulsion was transferred into the reactor and the temperature was raised to 65°C to initiate polymerization, and the reaction was stopped after 24 hours of polymerization, and the polymerization product was taken out and dried to obtain a fluorine-containing porous polymer material. The obtained porous material has an average pore diameter of 2.77 μm and a density of 0.1698 cm 3 / g, the porosity is 92.7...
Embodiment 3
[0067] An oil phase was prepared by mixing 2.0020 parts of trifluoroethyl methacrylate, 1.0100 parts of divinylbenzene, 0.3030 parts of b246, 1.0020 parts of PLA-11000 and 0.0310 parts of azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN). 18.00 parts of an aqueous calcium chloride solution was used as the aqueous phase. Stir the oil phase at a speed of 400 rpm, slowly drop the water phase into the oil phase, stir and mix thoroughly, increase the stirring speed to 500 rpm after the addition, and stir for 30 minutes. Transfer the emulsion into a reactor and raise the temperature to 65°C to initiate polymerization, stop the reaction after 24 hours of polymerization, take out the polymer product and dry it to obtain a fluorine-containing porous polymer material.
[0068] The obtained porous material has an average pore diameter of 2.65 μm and a density of 0.1683 cm 3 / g, the porosity is 91.85%, and the internal specific surface area is 21.1712m 2 / g.
[0069] Take 0.3508g of the obtained porous mate...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com