Preparation method of lithium iron phosphate/carbon composite material
A technology of carbon composite materials and lithium iron phosphate, applied in electrical components, electrochemical generators, battery electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of poor electrochemical performance and high rate discharge performance of lithium iron phosphate materials, and achieve easy realization, Improved electrochemical performance and high production efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] (1) Ferric oxide, lithium carbonate, and phosphoric acid are mixed in molar ratio n(Fe):n(PO 4 ):n(Li)=0.98:1.02:1 and malonic acid accounting for 4% of the mass of ferric oxide and glucose calculated as 3% of the theoretical carbon content are added to deionized water, and mixed to form a solid content of 30% slurry and disperse for 60 minutes.
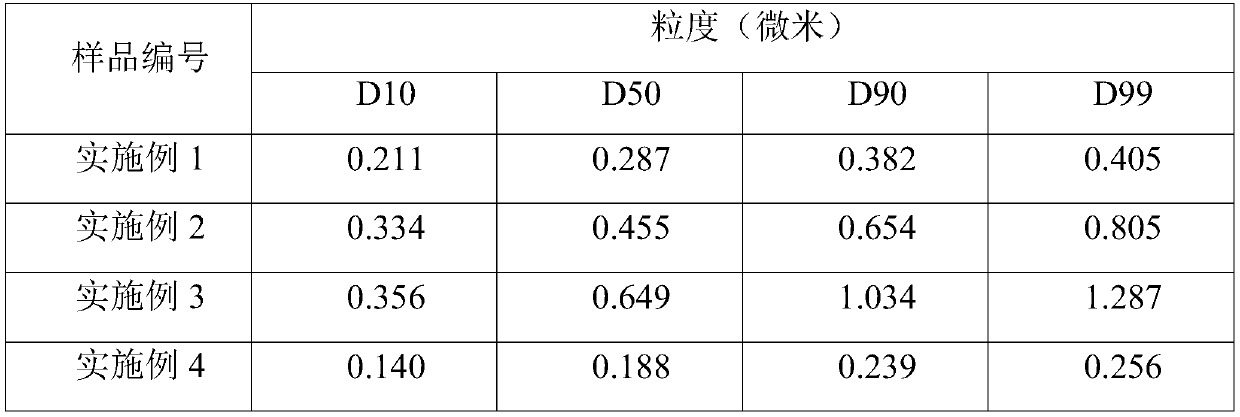
[0027] (2) Put the slurry obtained in step (1) into a sand mill and grind for 45 minutes to obtain a slurry with D50=0.287 microns.
[0028] (3) The slurry obtained in step (2) is passed through a two-phase flow spray dryer, and the inlet is set at 235° C., and the outlet is set at 90° C. for drying and granulation.
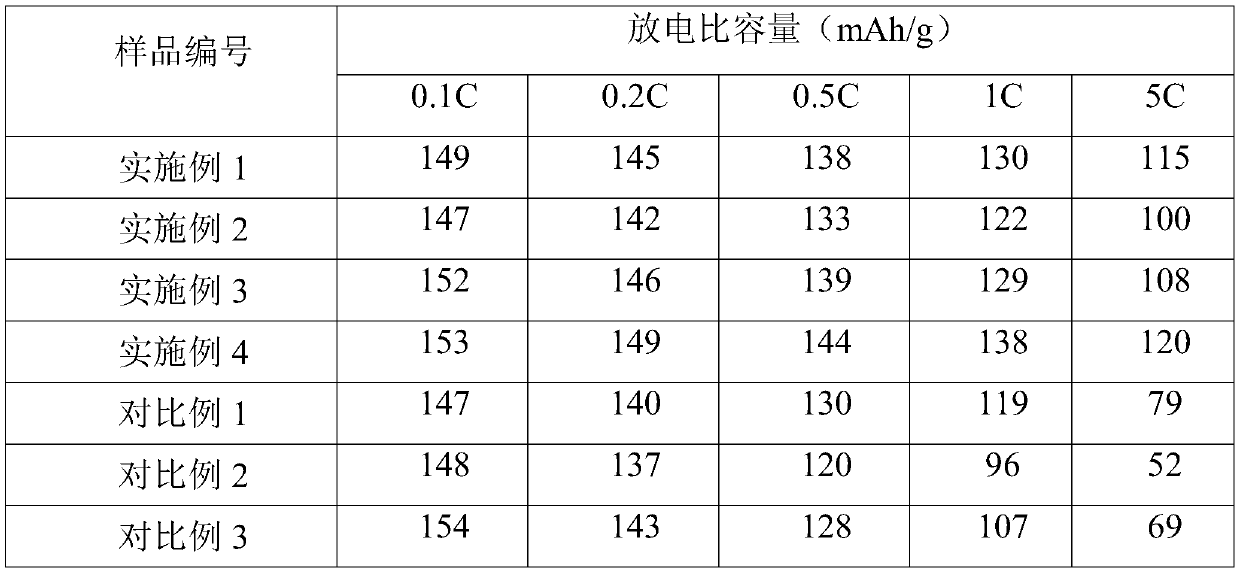
[0029] (4) Sinter the powder obtained in step (3) under the protection of nitrogen according to the system of 400°C for 3 hours and 700°C for 3 hours to obtain an average discharge capacity of 130mAh / g at 1C and an average discharge capacity of 115mAh / g at 5C. g of lithium iron phosphate products.
Embodiment 2
[0031] (1) Ferric hydroxide and lithium dihydrogen phosphate are molar ratio n(Fe):n(PO 4 ):n(Li)=0.98:1:1 and citric acid of 8% of the mass of ferric hydroxide and sucrose calculated on the basis of theoretical carbon content of 3% were added to deionized water and mixed into a slurry with a solid content of 35% And disperse for 120min.
[0032] (2) Put the slurry obtained in step (1) into a sand mill and grind for 30 minutes to obtain a slurry with D50=0.455 μm.
[0033] (3) The slurry obtained in step (2) is passed through a two-phase flow spray dryer, and the inlet is set at 260° C., and the outlet is set at 105° C. for drying and granulation.
[0034] (4) Sinter the powder obtained in step (3) under the protection of nitrogen according to the system of 350°C for 4 hours and 730°C for 1 hour to obtain an average discharge capacity of 122mAh / g at 1C and an average discharge capacity of 100mAh / g at 5C. g of lithium iron phosphate products.
Embodiment 3
[0036] (1) Ferric oxyhydroxide, lithium hydroxide, phosphoric acid in molar ratio n(Fe):n(PO 4 ):n(Li)=0.985:1.03:1 and 3% tartaric acid of iron oxyhydroxide mass and cyclodextrin calculated as 2% of theoretical carbon content are added to deionized water, and mixed into a slurry with a solid content of 25% material and disperse for 60 minutes.
[0037] (2) D50 of the slurry obtained in step (1)=0.649 μm, directly enters the spray drying process.
[0038] (3) The slurry obtained in step (2) is passed through a centrifugal spray dryer, with the inlet at 265°C and the outlet at 95°C for drying and granulation.
[0039] (4) Sinter the powder obtained in step (3) under the protection of nitrogen according to the system of 430°C for 3 hours and 690°C for 2 hours to obtain an average discharge capacity of 129mAh / g at 1C and an average discharge capacity of 108mAh / g at 5C. g of lithium iron phosphate products.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com