Molybdenum carbide modified tubular carbon nitride photocatalytic material and its preparation method and application
A catalytic material, molybdenum carbide technology, applied in the field of materials, can solve the problems of insignificant photocatalytic performance, limited large-scale application, low utilization rate of visible light, etc., achieve superior photocatalytic activity, achieve effective separation, easy transfer and separation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] A kind of tubular carbon nitride (Mo) modified by molybdenum carbide of the present invention 2 C / TCN) photocatalytic material, its preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0055] (1) Preparation of tubular carbon nitride:
[0056] 1.1. Grind 8.56g of urea and 6g of melamine, dissolve in 70ml of deionized water, and stir at a constant speed for 2 hours to obtain a uniform mixed solution.
[0057] 1.2. Transfer the above mixed solution to a 100mL autoclave, and keep it warm at 180°C for 24 hours. After natural cooling, rinse with water and ethanol three times respectively, filter, and dry at 100°C for 12h to obtain the carbon nitride precursor .
[0058] 1.3. Put the carbon nitride precursor into a crucible, place it in a muffle furnace, heat it up to 550°C at a heating rate of 2.3°C / min, and keep it at 550°C for 4 hours. The whole process is carried out under the protection of nitrogen. After natural cooling, it was taken out and ground with a mortar to ob...
experiment example 1
[0066] Experimental Example 1: The monomeric carbon nitride in Comparative Example 1 and the tubular carbon nitride in Example 1 were scanned by an electron microscope.
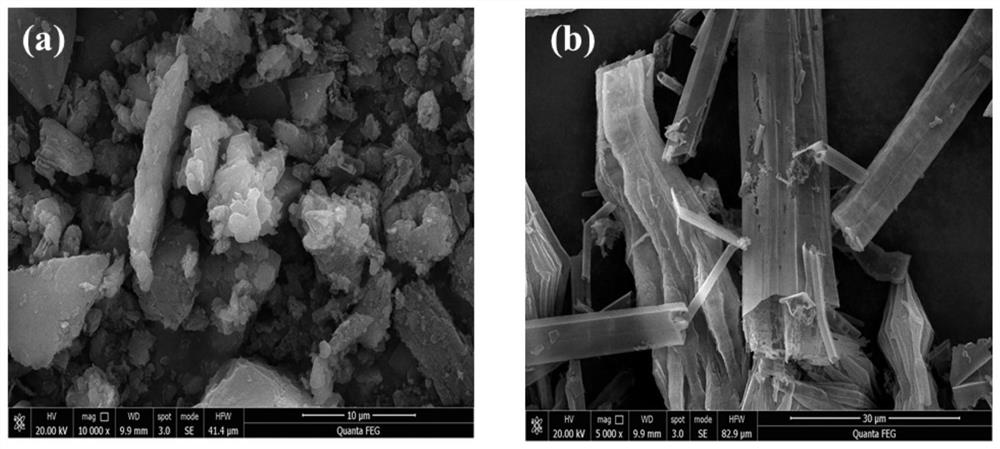
[0067] figure 1 It is a scanning electron microscope (SEM) illustration of the monomer carbon nitride of Comparative Example 1 of the present invention and the tubular carbon nitride of Example 1, wherein (a) is monomer carbon nitride, and (b) is tubular carbon nitride .
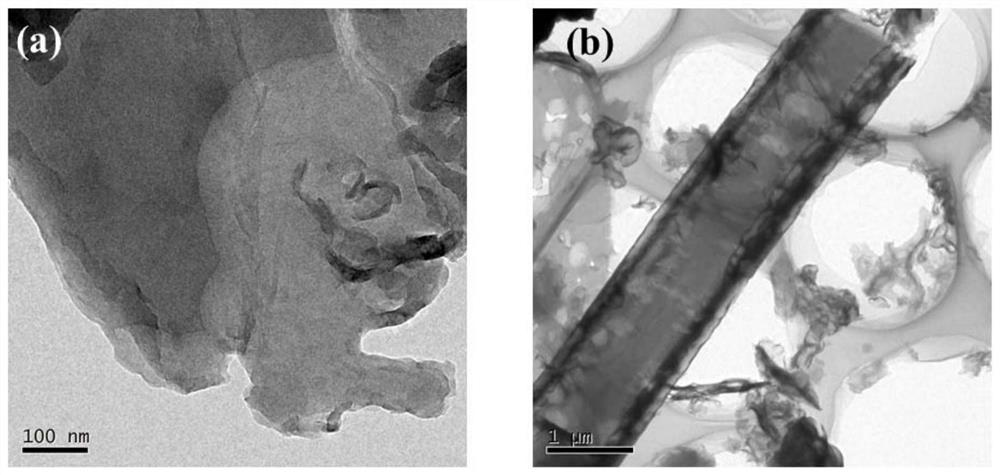
[0068] figure 2 It is a transmission electron microscope (TEM) illustration of the monomeric carbon nitride of Comparative Example 1 of the present invention and the tubular carbon nitride of Example 1, wherein (a) is a monomeric carbon nitride, and (b) is a hollow tubular carbon nitride carbon.
[0069] From figure 1 and figure 2 It can be seen that the monomeric carbon nitride presents a block-like aggregated structure with a small specific surface area and no nanopores on the surface. However, the tubular carbon nitride presents ...
experiment example 2
[0070] Experimental example 2: the monomer carbon nitride of comparative example 1, the tubular carbon nitride in embodiment 1, molybdenum carbide and Mo 2 X-ray scanning of C / TCN composites.
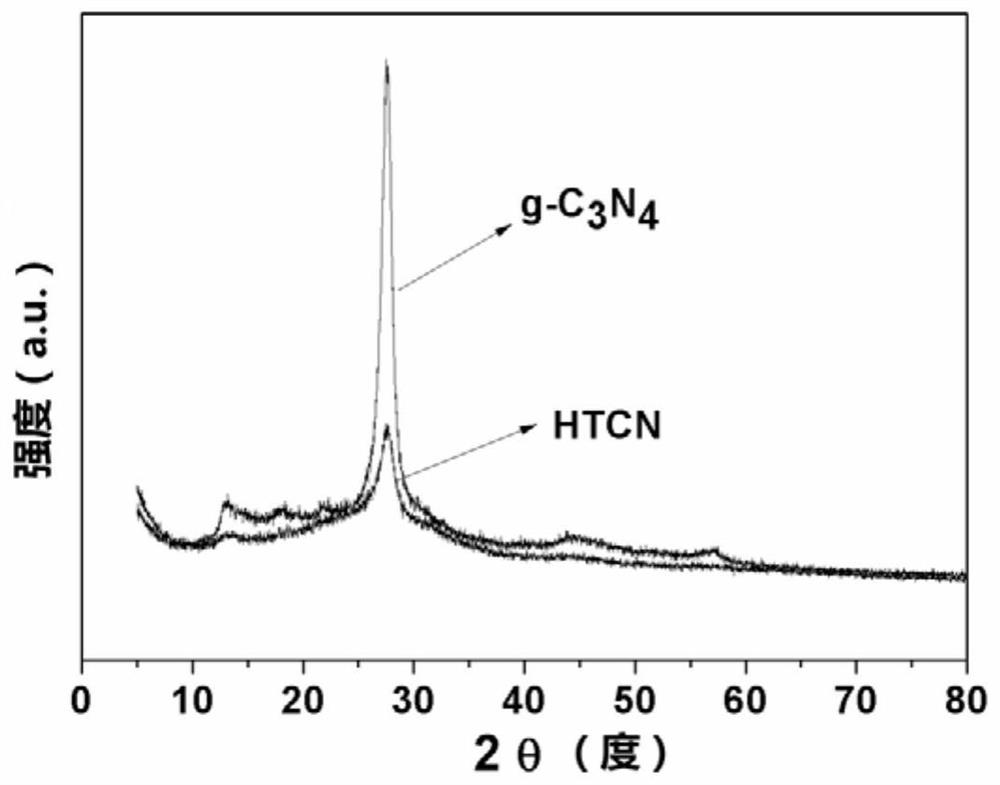
[0071] image 3 It is the X-ray diffraction (XRD) comparative pattern of the monomeric carbon nitride of Comparative Example 1 of the present invention and the tubular carbon nitride of Example 1. From the figure, it can be found that there are two obvious XRD diffraction peaks at 13.1° and 27.2° that belong to the graphitic carbon nitride (100) and (002) crystal planes, confirming that the prepared product is g-C 3 N 4 . Compared with monomeric carbon nitride, the 27.2° peak of tubular carbon nitride becomes wider and its intensity becomes weaker, indicating that its crystal form becomes weaker, its thickness becomes thinner, and a hollow tubular structure is successfully formed.
[0072] Figure 4 Tubular carbon nitride, molybdenum carbide and Mo of embodiment 1 2 C / TCN composit...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com