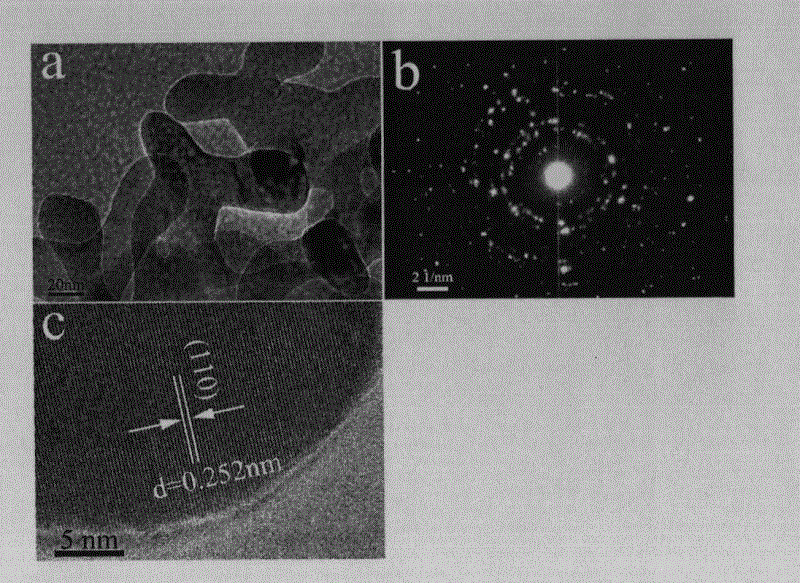
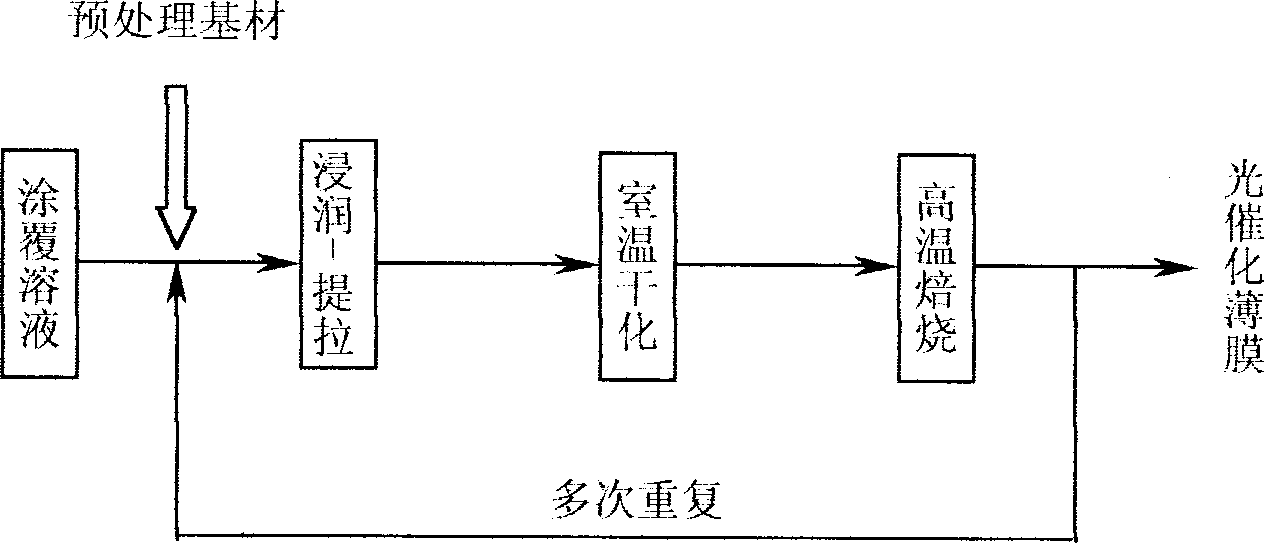
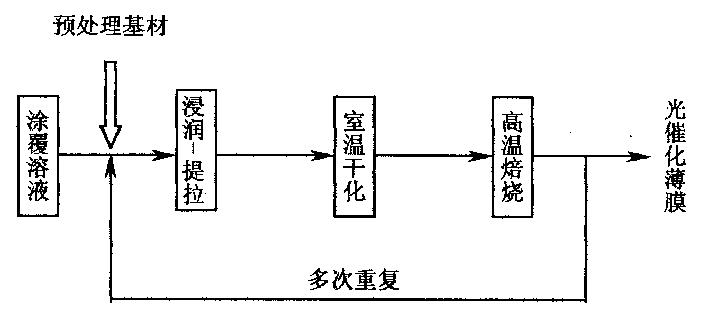
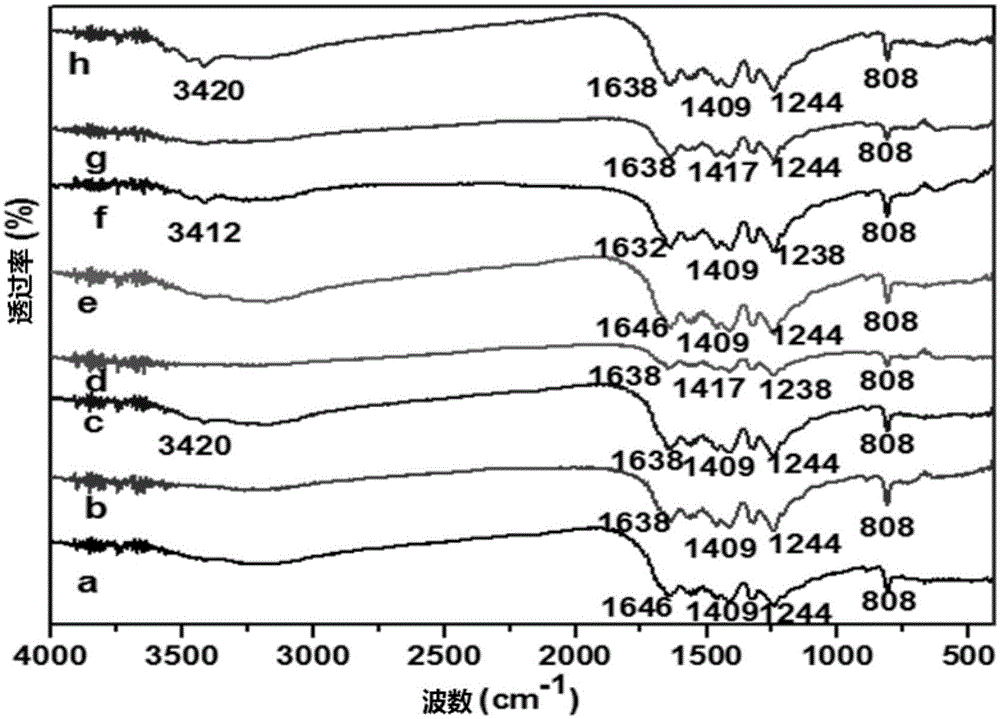
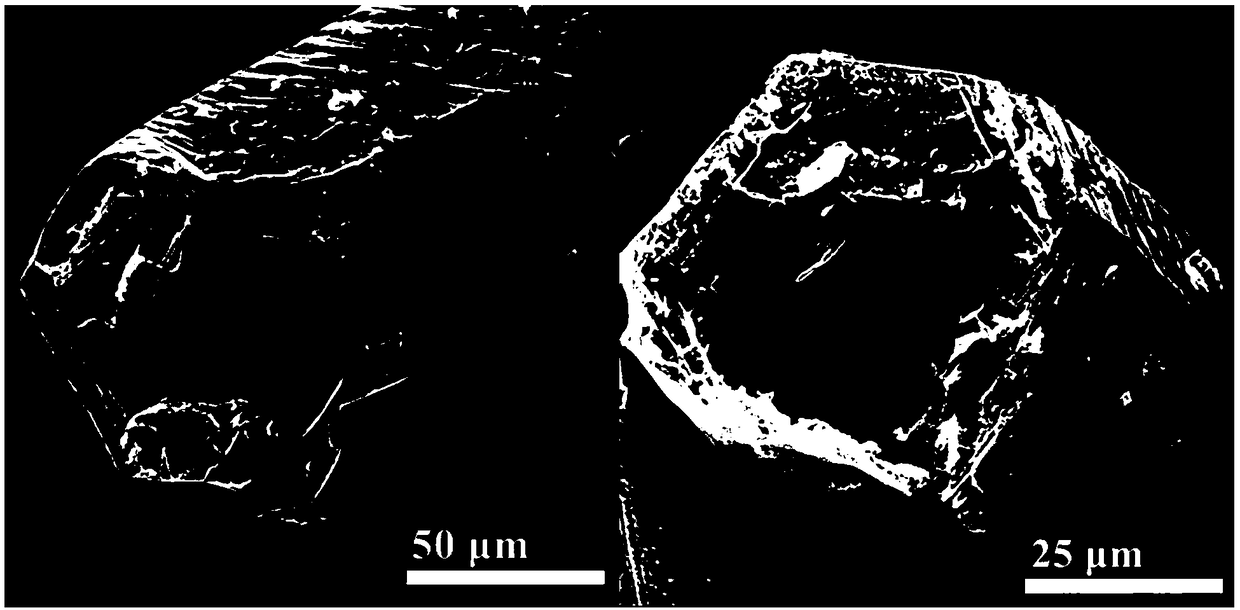
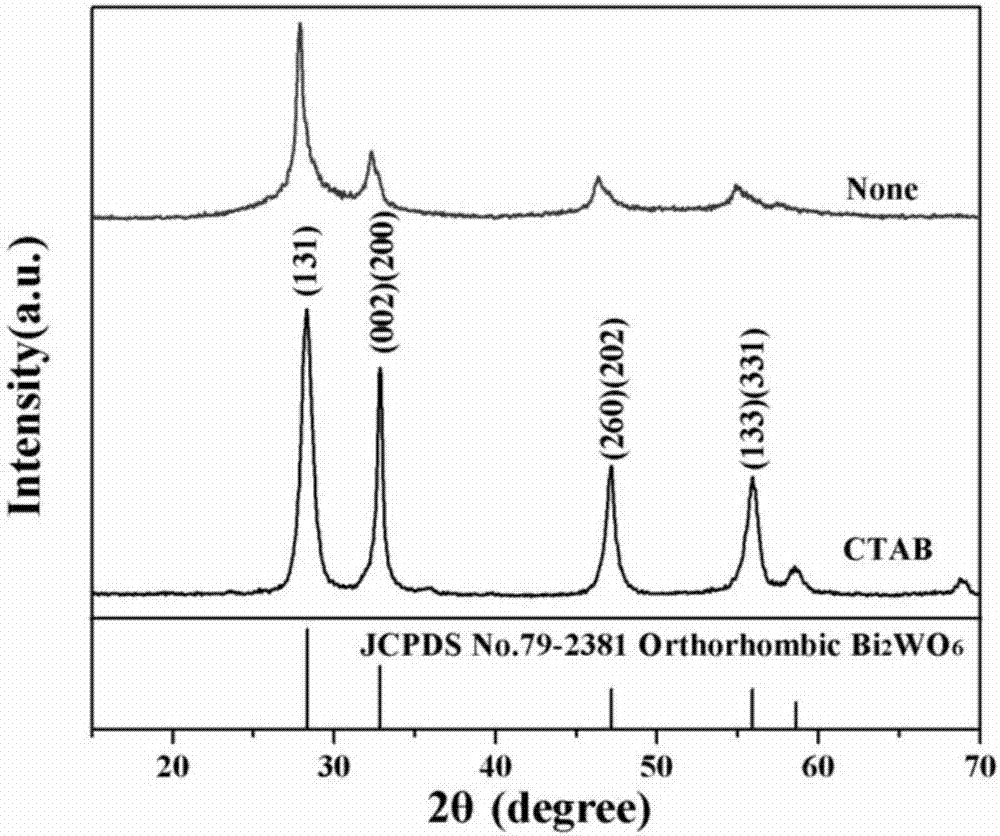
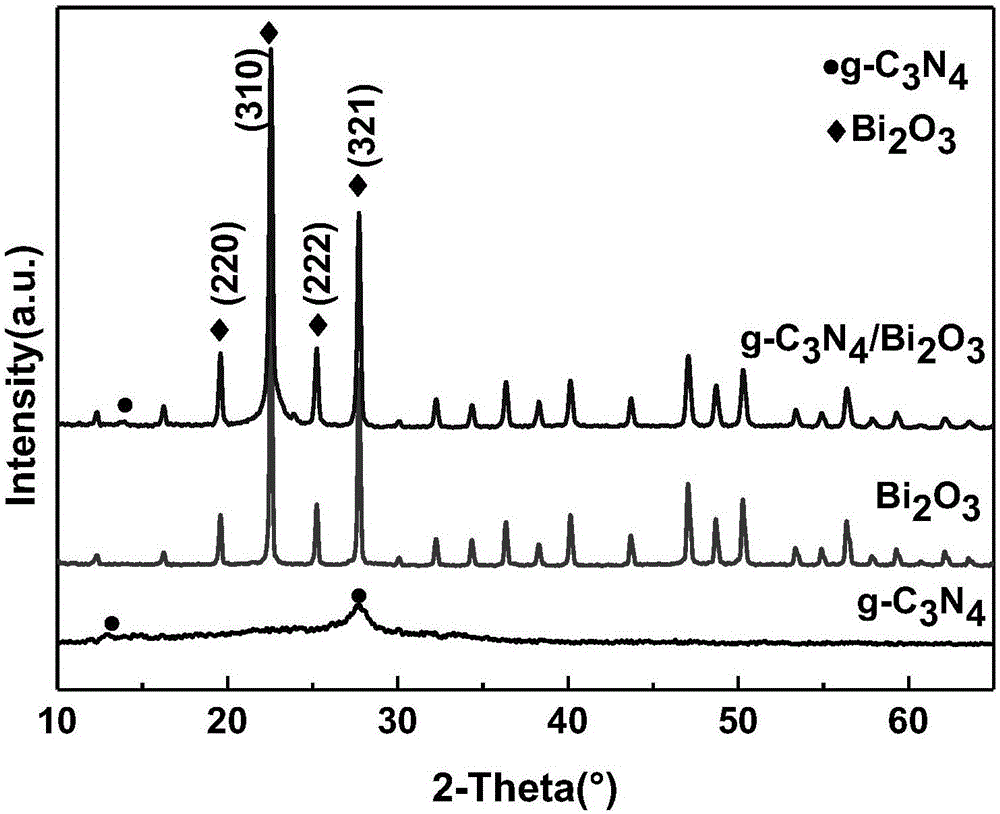
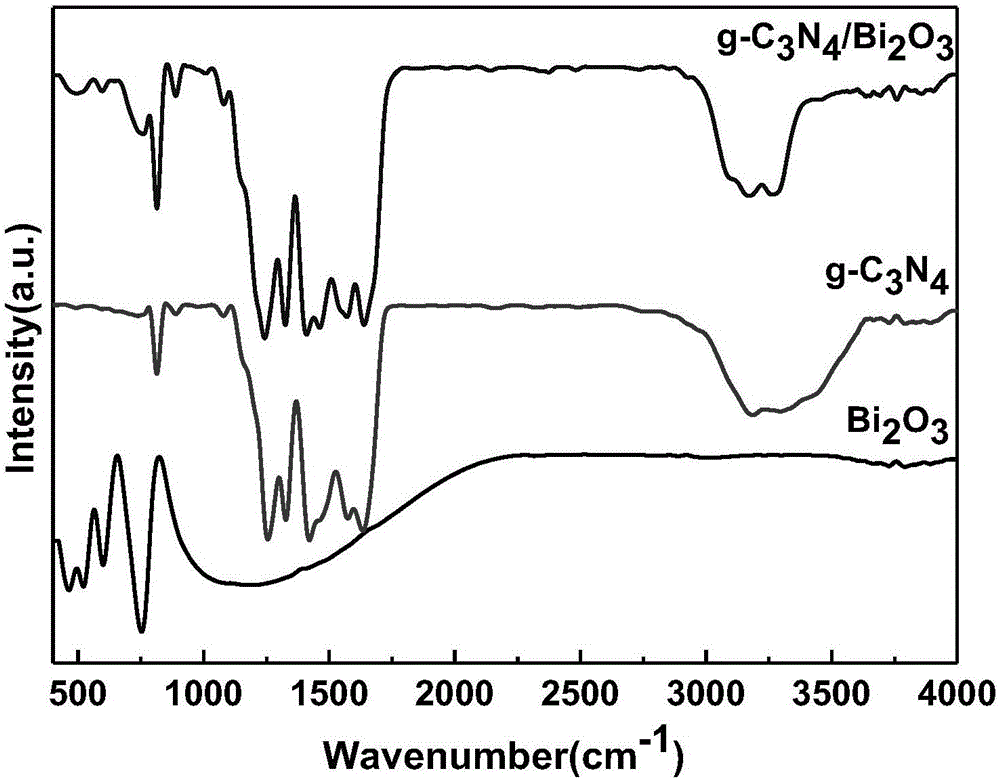
Patents
Literature
423results about How to "Improve photocatalytic degradation performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multi-morphology rare earth doped BiVO4 composite photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102641732ALarge specific surface areaImprove catalytic performanceMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsRare earthPhenol
The invention discloses a multi-morphology rare earth doped BiVO4 composite photocatalyst and a preparation method thereof. The composite photocatalyst comprises the component of Ln(1-x)BiVO4, wherein Ln is equal to La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Gd, Dy, Er and Y, and x is equal to 0.01-0.3mol%. The photocatalyst disclosed by the invention has different morphologies and has the advantages of simple preparation technology, controllable morphology and crystalline phase structure of a target product and big specific surface area, and various organic pollutants, such as toxic and harmful phenols, aldehydes, and dyes, can be decomposed within a wider wavelength range.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE
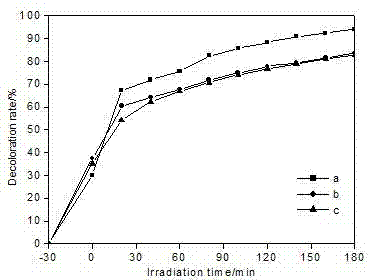
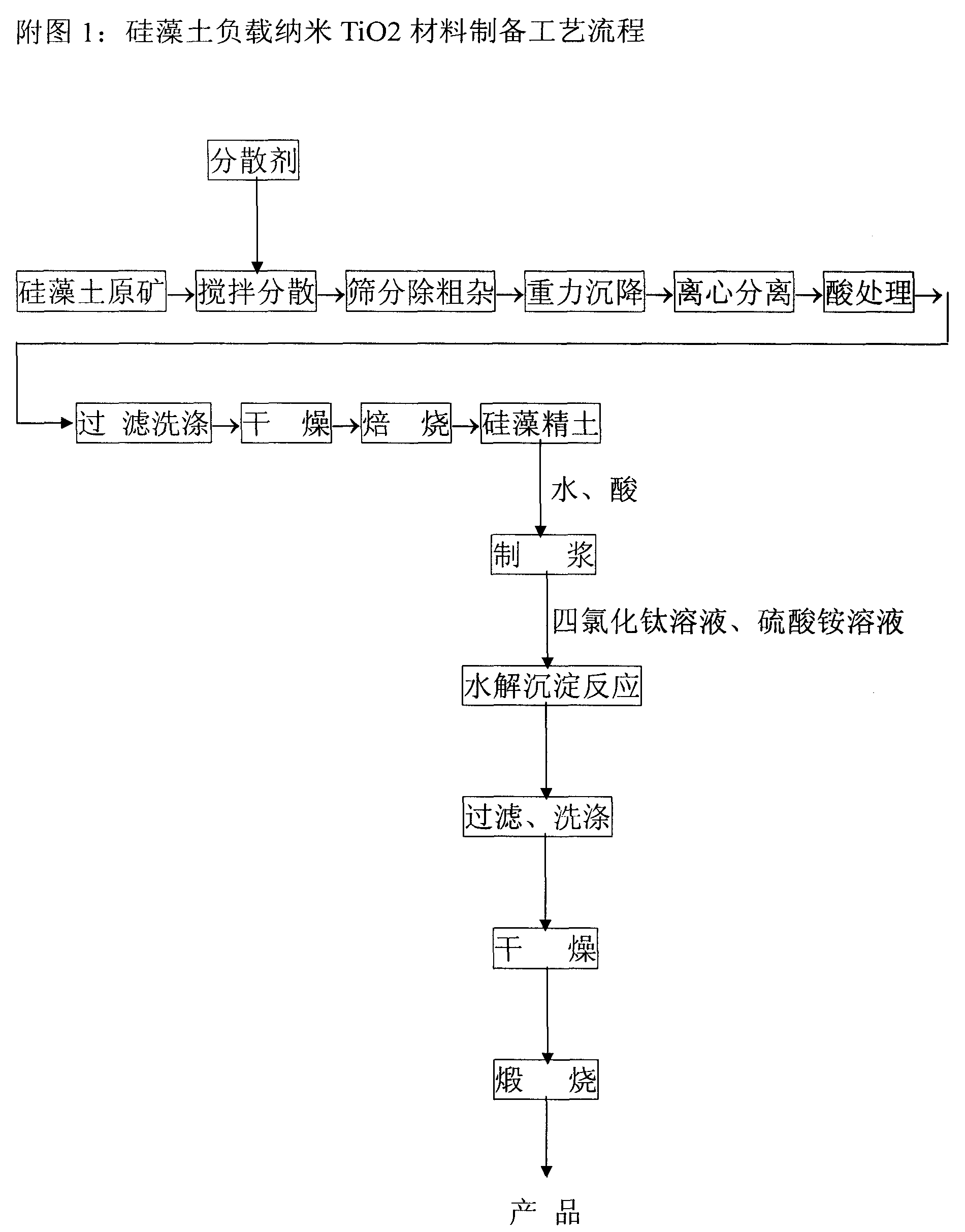
Method for producing tripolite loading nano-TIO2 material capable of being used for water and air purification
InactiveCN101195086AReduce manufacturing costGood photocatalytic effectPhysical/chemical process catalystsForeign matterDecomposition
The invention relates to a process for preparing diatom earth loading nanometer Ti2O material for purifying water and air, which belongs to the field of material process and environmental treatment. Diatom earth raw ore is filled with water and is churned and scattered, is screened, is sunken by gravity, and is eccentrically sunken, sulfuric acid is adopted to dissolve clay-type foreign matters which are left in pore passages after ores which mutually grow with diatom earth like quartz, feldspar, mica, and clay and the like and organic matters which are mixed such as grass roots and barks and the like are removed, and diatom fine soil is attained. Further, diatom fine soil is filtered, dried, and baked, and diatom fine soil after baked is filled with water, and is churned, and is filled with acid to regulate the PH value, and is filled TiCl4 solution, and is filled with ammonia sulfate solution to proceed hydrolytic decomposition deposition reaction, and product yield after the reaction is filtered, washed, dried, and baked to attain the nanometer Ti2O material.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING) +1
Graphene/titanium dioxide composite material, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108160064ASimplify the linkConducive to follow-up reactionsGas treatmentPhysical/chemical process catalystsCvd grapheneTitanium oxide
The invention relates to a graphene / titanium dioxide composite material, a preparation method and application thereof. The graphene / titanium dioxide composite material comprises: graphene and titaniumdioxide particles closely attached to the graphene sheet. According to the invention, graphene and titanium dioxide are selected for compounding to obtain an efficient photocatalyst with the excellent properties of graphene and titanium oxide simultaneously.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of rare-earth element doped modified hollow microsphere bismuth oxyiodide photocatalyst
InactiveCN107597150ABroad absorption spectrumPromote absorptionPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationRare-earth elementNitrate
The invention relates to a preparation method of a rare-earth element doped modified hollow microsphere bismuth oxyiodide photocatalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding bismuth nitrate pentahydrate and nitrate of a rare-earth element into a solvent and sufficiently dissolving to obtain a bismuth nitrate solution containing the rare-earth element; under magnetic stirring, dropwise adding a potassium iodide solution at a uniform speed drop by drop; after finishing dropwise adding, continually carrying out the magnetic stirring to obtain a precursor solution; puttingthe precursor solution into a reaction kettle to react by adopting a solvothermal method; after finishing the reaction, cooling a product to room temperature and taking out the product; washing, drying in vacuum and grinding to obtain the rare-earth element doped modified hollow microsphere bismuth oxyiodide photocatalyst. The method provided by the invention is simple and feasible and has the characteristics of simple process, good experiment reproducibility, low production cost and the like; the prepared rare-earth element doped composite photocatalyst has good photocatalytic degradation performance on organic pollutant and a good application prospect.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of graphene/titanium dioxide photocatalyst
InactiveCN103028387ASimple processEasy to implementPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic dyePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of a graphene / titanium dioxide photocatalyst, which comprises the following steps of (1) preparing a solution A, slowly adding tetrabutyl titanate into chloroform, and obtaining the solution A, (2) preparing a mixed solution B, adding oxidized graphene into a mixed solution of deionized water and ethanol, and obtaining the mixed solution B, (3) stirring the mixed solution B, adding the mixed solution B into the solution A simultaneously, stirring uniformly, and obtaining a mixed solution, and (4) placing the mixed solution into a hydrothermal kettle, conducting the hydrothermal treatment, naturally cooling to a room temperature, separating and washing, and obtaining the graphene / titanium dioxide photocatalyst. The graphene / titanium dioxide photocatalyst prepared by the method has an excellent photocatalytic degradation property for organic dye.
Owner:LIAOCHENG UNIV
Fe2O3 micro-nano porous sphere, preparation method thereof and uses thereof
InactiveCN102616861ALarge specific surface areaImprove thermal stabilityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOther chemical processesMicro nanoOrganic dye
The invention discloses a Fe2O3 micro-nano porous sphere, a preparation method thereof and uses thereof. The porous sphere is formed by Fe2O3 nanoparticles having a nanometer mesoporous alpha-Fe2O3 phase structure therebetween, wherein the diameter of the sphere is 500-5000nm, the specific surface area of the sphere is 15-25m<2> / g, particle sizes of the particles are 20-60nm, and pore diameters of mesopores are 2-50nm. The method comprises the following steps: mixing ferric chloride hexahydrate, ascorbic acid, urea and water, and uniformly stirring them to obtain a mixed liquid; reacting the mixed liquid under conditions that the temperature is 140-180DEG C and the pressure is a self-generated pressure for at least 4h to obtain an intermediate product; separating, washing and drying the intermediate product to obtain porous iron carbonate; and annealing the porous iron carbonate at 450-550DEG C for at least 4h, and naturally cooling the porous iron carbonate to room temperature to prepare the Fe2O3 micro-nano porous sphere. The Fe2O3 micro-nano porous sphere can be placed in water polluted by organic dyes to photocatalytically degrade under visible light, or in water polluted by potassium dichromate to adsorb.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for preparing photocatalytic TiO2 film used to clean water and air
InactiveCN1397377AImprove firmnessImprove photocatalytic degradation performanceDispersed particle separationVacuum evaporation coatingAir cleaningSlurry
A photocatalytic TiO2 film for cleaning water and air is prepared through dissolving the titanium alkoxiode in alcohol solvent, adding water and carbon black to obtain slurry, dipping substrate in it, and gradient calcining several times. It has high catalytic degradation rate to organic pollutant (83-93%).
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Photocatalyst Co3O4-CNI and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105195196AImprove photocatalytic degradation performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic dyePhotocatalytic degradation
The invention provides a photocatalyst Co3O4-CNI and a preparation method and application thereof. According to the photocatalyst Co3O4-CNI, nitrogen-containing organic matter and ammonium iodide serve as raw materials, iodine-doped graphite-phase carbon nitride (abbreviated as CNI) can be prepared through a hydrothermal method, then prepared CNI and a cobalt-containing compound react through a hydrothermal method, and optionally, cooling and smashing are performed so that the photocatalyst Co3O4-CNI can be prepared. The prepared photocatalyst has a good catalytic degradation effect on organic dye and particularly azo type organic dye under visible light.
Owner:FUYANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparing method of zinc oxide nano fiber film used as photocatalyst
InactiveCN101011656ASimple processSuitable for mass productionWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsFiberCellulose acetate
The invention discloses a making method of zinc oxide nanometer fiber as optical catalyst, which comprises the following steps: adopting zinc acetate as primer and fiber acetate as carrier; using organic solvent dimethyl formamide / acetone as co-solvent; adopting electrostatic spinning technique to make composite nanometer fiber film of zinc acetate / fiber acetate; dissolving in the 0.1N NaOH solution; washing; drying; sintering; obtaining the ZnO nanometer fiber film with diameter less than 100nm.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Preparation method of graphene/titania composite material
InactiveCN102600823ASimple processEasy to implementPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationReaction speedMaterials science
The invention discloses a preparation method of a graphene / titania composite material, which comprises the steps of preparing a precursor solution, and heating and stirring the precursor solution and the like. The preparation method of the graphene / titania composite material has the beneficial effects: the process is simple, the implementation is easy, and the opportunity of introducing impurities is reduced, so that the purity of a product can not be affected. The preparation process is mild without protection of a special atmosphere, the required equipment is simple, the reaction speed is quick, and the preparation method is suitable for mass production. Graphene oxide can be reduced by microwave heating, and a toxic reductant is not used.
Owner:LIAOCHENG UNIV
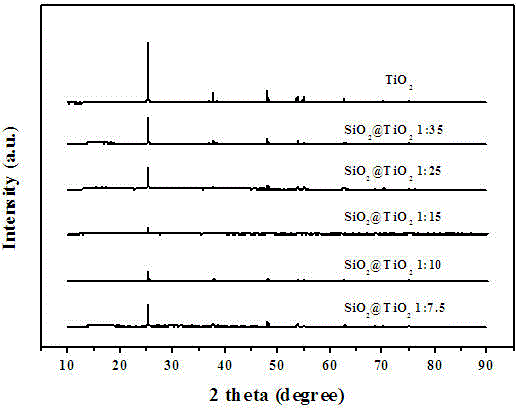
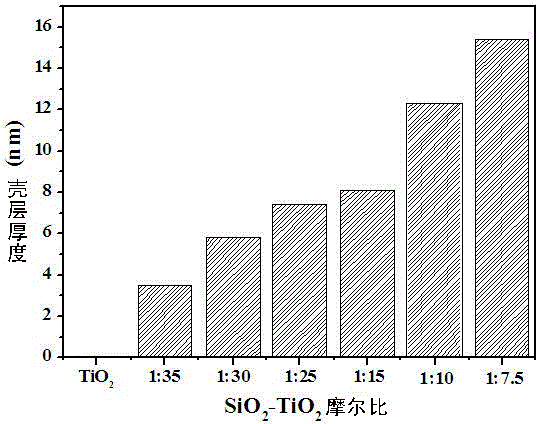
SiO2@TiO2 nuclear shell structure with stable dispersion and controllable photocatalysis, preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN106311199AUniform thicknessThickness is easy to controlPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationDistilled waterRoom temperature
SiO2@TiO2 nuclear shell structure with stable dispersion and controllable photocatalysis preparing method, comprises the steps of 1, adding TiO2 to distilled water to get suspension with concentration of 100-500 g / L, adding 0.1%-0.5% (NaPO3)6 as dispersing agent, and mixing it for 0. 5- 2h; 2, heating the solution obtained from step 1 to 60- 100oC, adding sodium silicate solution and sulfuric acid solution for mixing, to make the molar ratio of sodium silicate and titanium dioxide be 1:(5-45) and reaction system's pH be 8-11, after reaction for 1-3h and ageing for 1.5- 3h at room temperature, using distilled water to clean until the conductivity is less than 20 mS / m, to get SiO2@TiO2 suspension; or drying SiO2@TiO2 suspension at 100-110 oC for at least 24h and grinding it to get SiO2@TiO2 powder.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Preparation method for blue sheet-like titanium dioxide nanomaterial
InactiveCN102895964AEasy to operateImprove photocatalytic degradation performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsTitanium dioxideSewage treatmentSolvent
The invention relates to a preparation method for a blue sheet-like titanium dioxide nanomaterial. The preparation method comprises the following specific steps of: dispersing a titanium source in a solvent; then, adding a morphology control agent; stirring to obtain transparent solution; then, transferring the transparent solution into a reaction kettle for reaction; naturally cooling; washing; centrifuging; and drying to finally obtain the blue sheet-like titanium dioxide nanomaterial. The grain size of the material is 10-30nm; the crystal form of the material is an anatase form; and 400-700nm visible light can be absorbed. The blue sheet-like titanium dioxide nanomaterial prepared by the preparation method has the characteristics that the raw material is broad in source; the preparation method is simple; and the material is controllable in color and adjustable in morphology. One more breakthrough that the titanium dioxide nanomaterial is colored from white is realized. The blue sheet-like titanium dioxide nanomaterial is expected to be applied to the sewage treatment industry.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
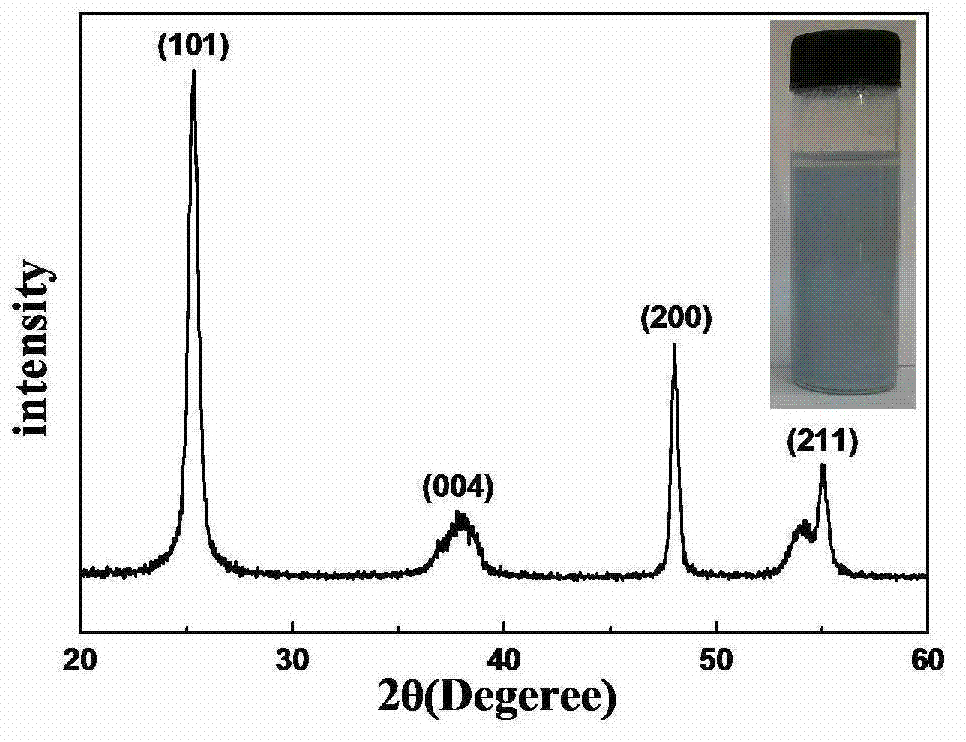
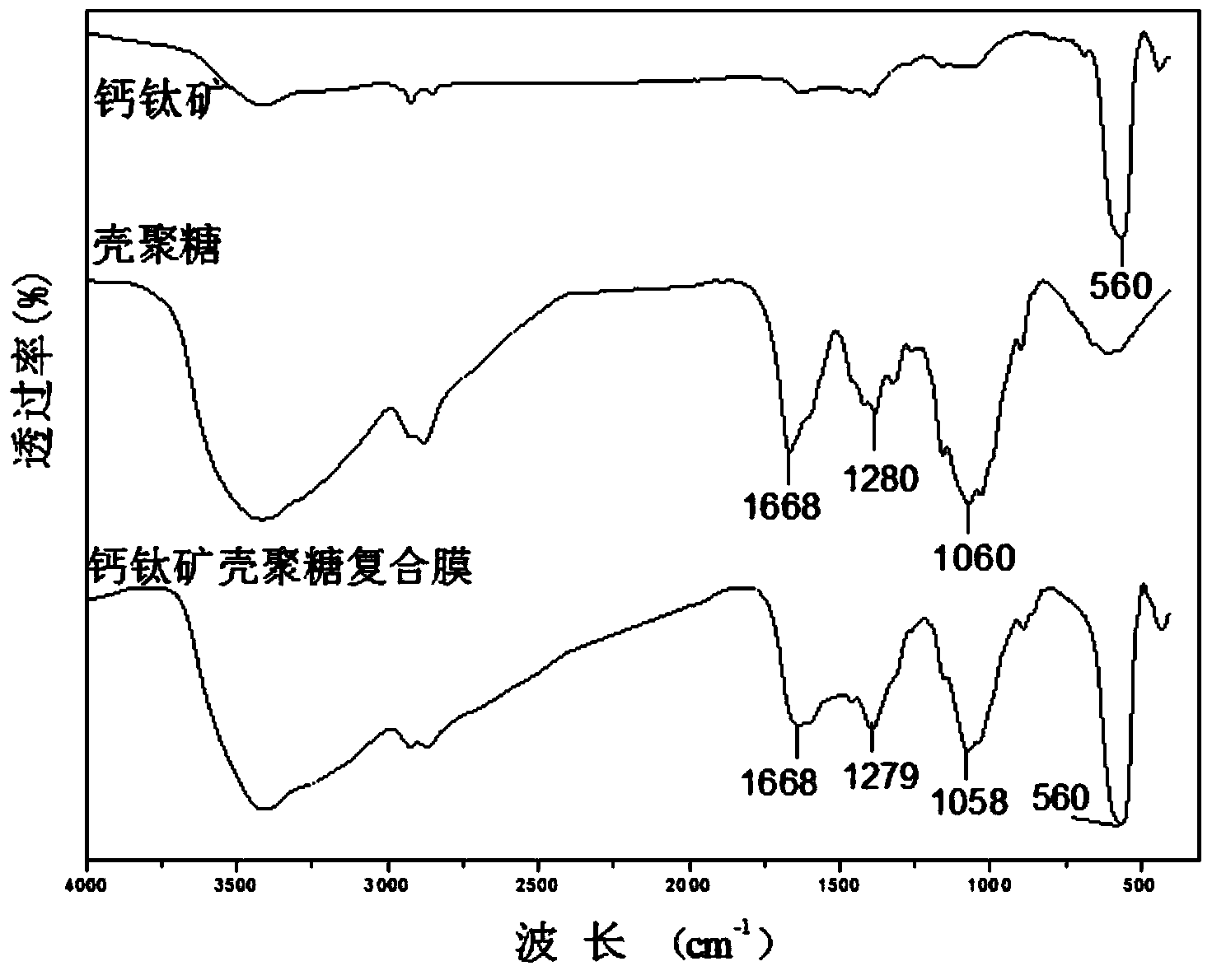
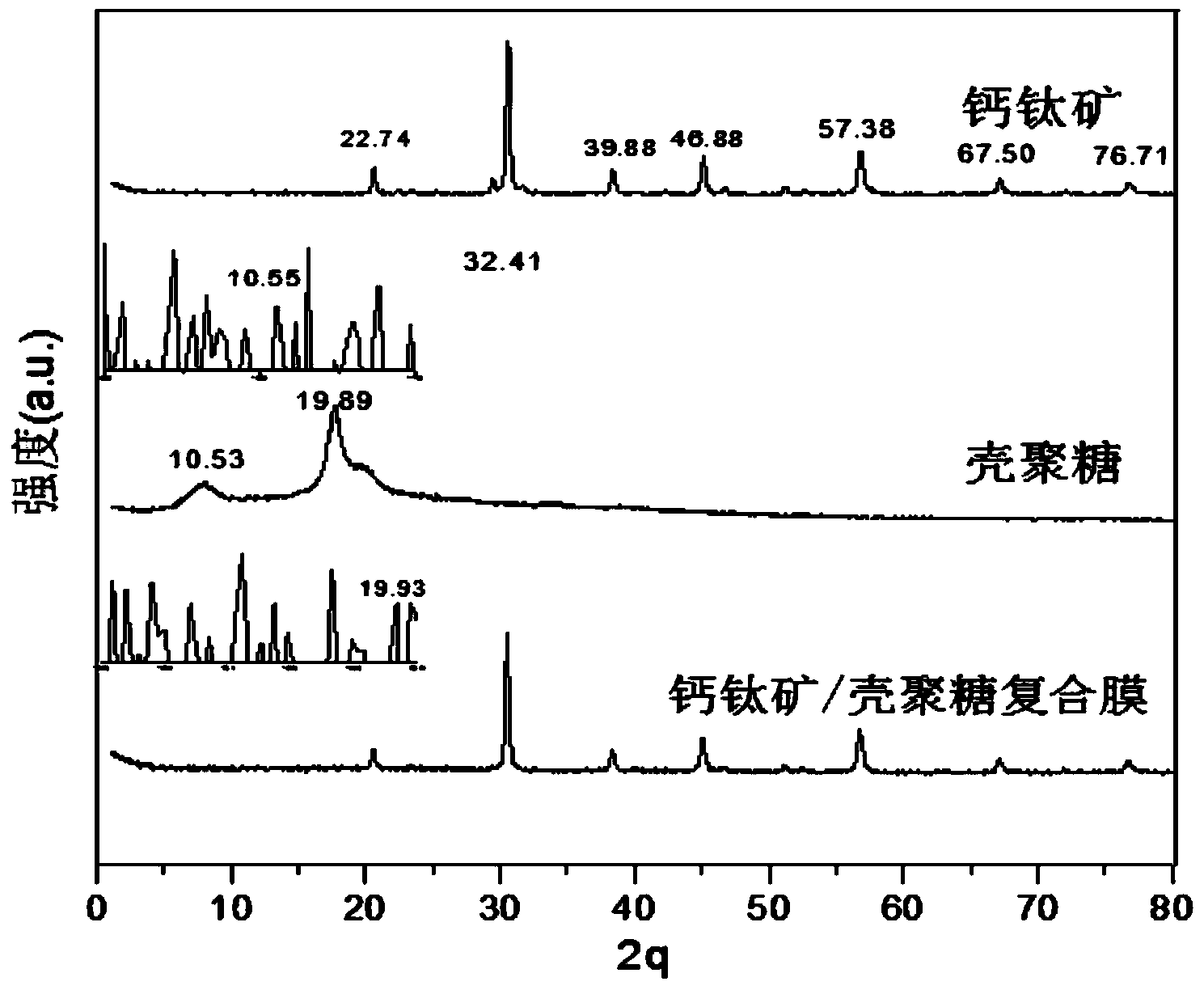
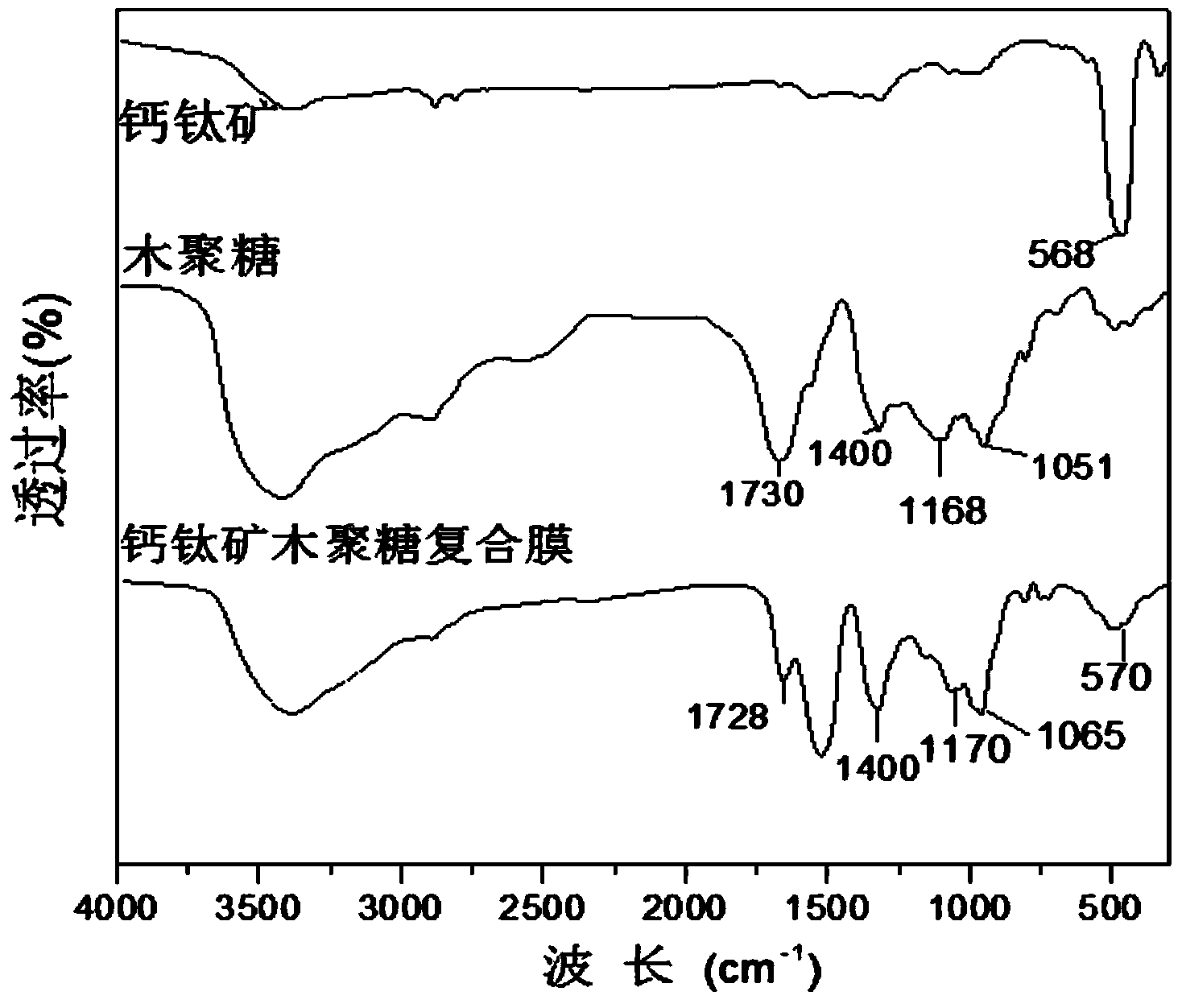
Method for degrading methyl orange by use of perovskite/polysaccharide composite photocatalyst
ActiveCN103936097AGood catalytic degradation effectShorten the timeWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPhotocatalytic degradationMethyl orange
The invention discloses a method for degrading methyl orange by use of perovskite / polysaccharide composite photocatalyst. The method comprises the following steps: preparing perovskite by utilizing nitrate of La, Cu and Fe, adding the perovskite and chitosan into an acetic acid solution, and performing ultrasonic treatment; drying to form a film to obtain a perovskite / chitosan composite photocatalyst; or adding xylan into distilled water, adding sodium hypophosphite and citric acid solution, adding perovskite, performing ultrasonic treatment, dehydrating, crosslinking to form a film, and washing with ethanol to obtain a perovskite / xylan composite photocatalyst; adding the composite photocatalytic material into the methyl orange solution, respectively reacting for 470-490 minutes at normal temperature in ultraviolet radiation. The polysaccharide used in the method is formed by compounding the catalyst and polysaccharide respectively with chitosan and xylan, the methyl orange photocatlytic degrading capability of the polysaccharide can be improved. The polysaccharide has the advantages of high catalytic efficiency, strong photo-response performance, regeneration, recycling and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
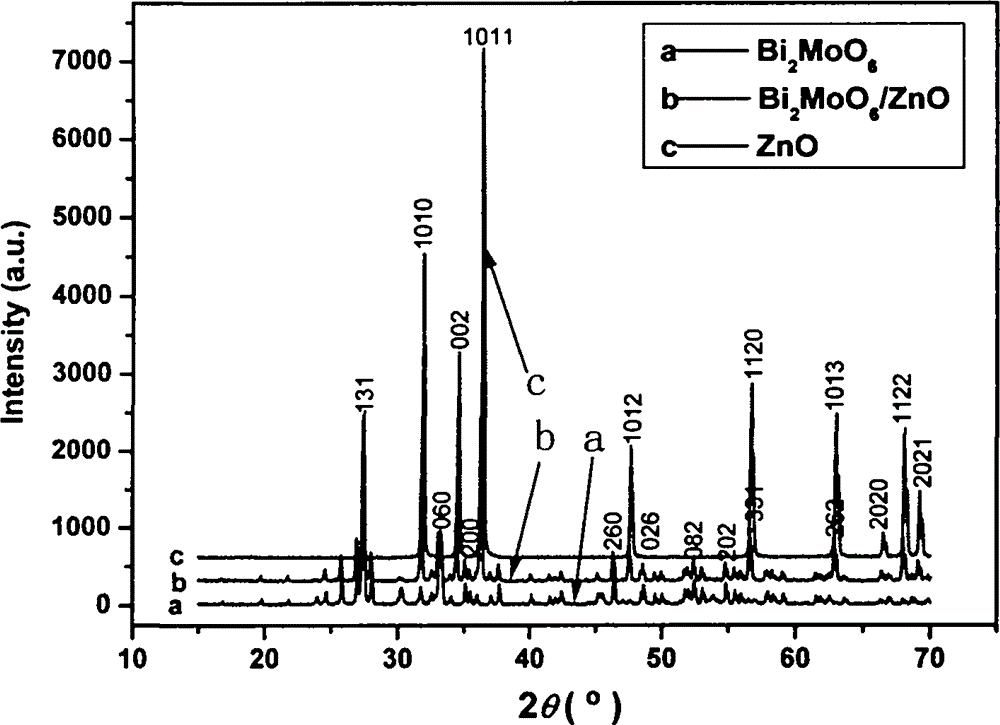
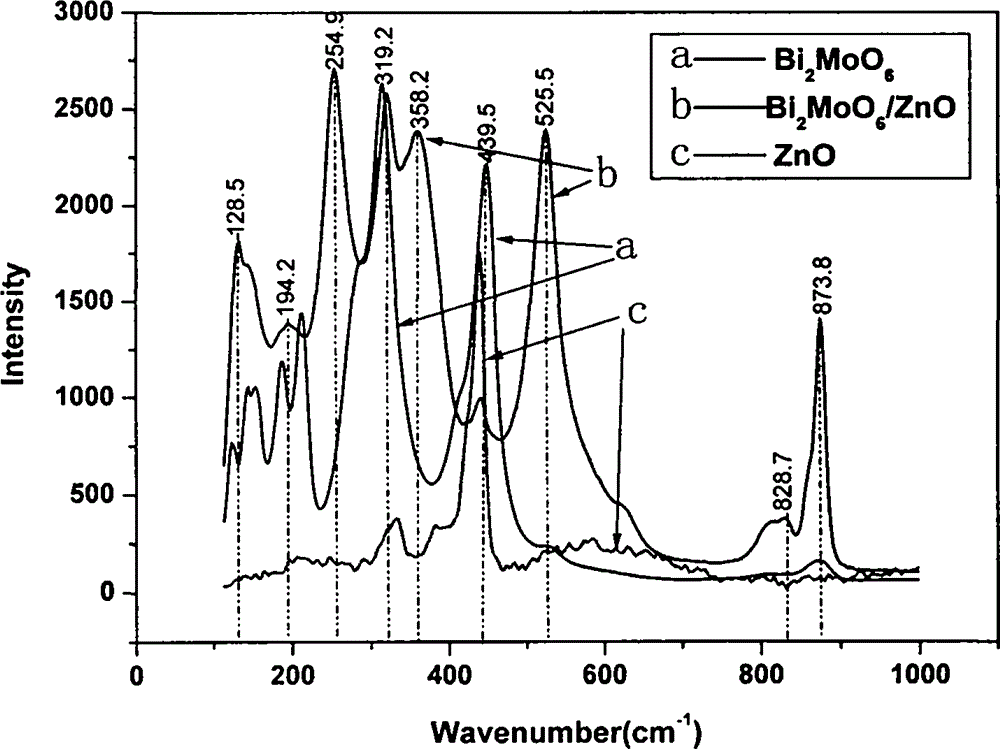
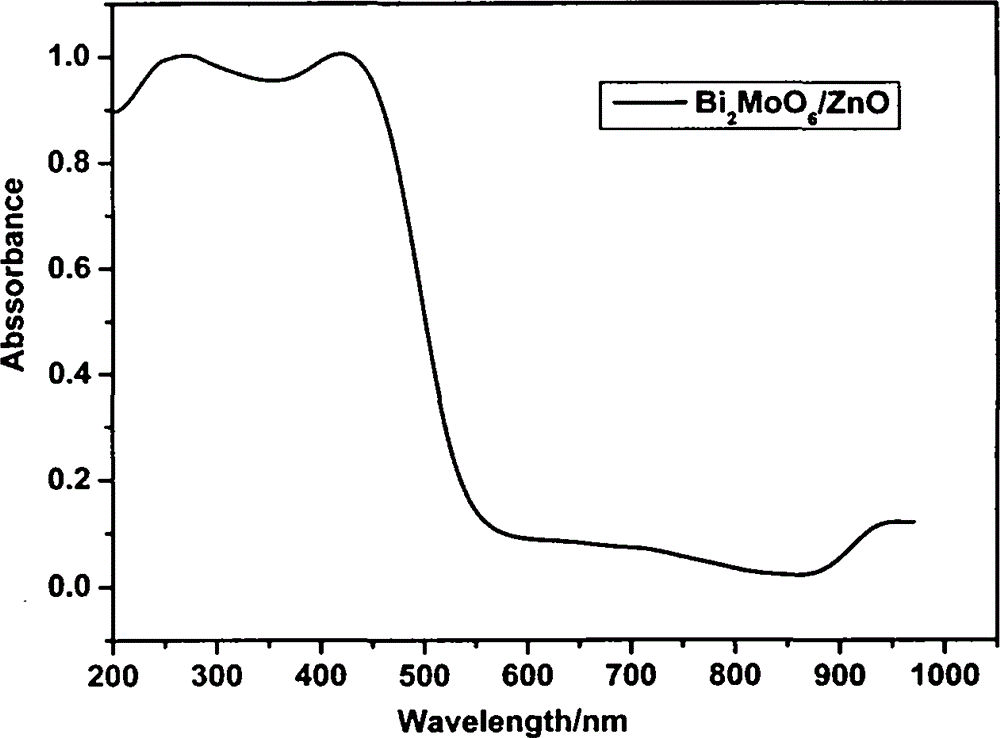
Bi2MoO6-ZnO composite photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104096558APromote absorptionGood photocatalytic degradation effectMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsSodium molybdateWavelength
The invention relates to a Bi2MoO6-ZnO composite photocatalyst and a preparation method thereof. The method mainly comprises the steps as follows: taking zinc acetate, bismuth nitrate and sodium molybdate in a certain proportion as raw materials, evenly mixing the materials through mechanical stirring in a certain order, adjusting the pH value of a solution, and then further preparing the Bi2MoO6-ZnO composite photocatalyst through a hydrothermal reaction. The Bi2MoO6-ZnO composite photocatalyst has the benefits as follows: the obtained composite visible-light-induced photocatalyst is formed by composition of Bi2MoO6 and ZnO, and the composite visible-light-induced photocatalyst has better absorption performance in ultraviolet-visible light regions with the wave length in a range of 320-580 nm; methyl orange has the good photocatalytic degradation effect under exposure to ultraviolet-visible light, the degradation rate exceeds 90% after 60 min, then the degradation effect tends to be gentle, and the total degradation rate of the methyl orange is 95% after 2 h.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
Ternary magnetic composite photocatalytic nanomaterial and preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN106732713AInhibitory complexExtend your lifePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationPhotocatalytic degradationSemiconductor
The invention provides a ternary magnetic composite photocatalytic nanomaterial and a preparation method and use thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: step 1, preparing a g-C3N4 photocatalyst; step 2, preparing WO3; and step 3, preparing the ternary magnetic composite photocatalytic nanomaterial. In the ternary magnetic composite photocatalytic nanomaterial prepared in the invention, the g-C3N4 photocatalyst is a novel organic visible-light-activated photocatalyst, and the Fe3O4 nanoparticles have excellent magnetism and electric conductivity. In addition, the WO3 as an inorganic semiconductor with good visible-light response has a band gap structure matching the g-C3N4. Therefore, according to the valence band theory and as reported in literatures, the WO3 can form a Z-type heterojunction photocatalyst having high photocatalytic activity with the g-C3N4. The composite material of such a special structure has improved photocatalytic effect such that the ternary magnetic composite photocatalytic nanomaterial prepared in the invention has excellent stability and photocatalytic degradation effect.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Porous graphene loaded titanium dioxide composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106215920AAvoid reunionImprove stabilityPhysical/chemical process catalystsCvd graphenePhotocatalytic degradation
The invention discloses a porous graphene loaded titanium dioxide composite material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes the steps: (1) preparing graphene quantum dot suspension liquid; (2) preparing loaded titanium dioxide graphene quantum dots; (3) performing surface treatment; (4) preparing the composite material. The graphene quantum dots are used as titanium dioxide carriers, nano titanium dioxide is finally attached onto porous graphene after surface treatment, can be more effectively loaded and fixed and can be prevented from agglomeration, stability of the nano titanium dioxide is remarkably improved, and agglomeration of the composite material is avoided, so that obtained porous graphene / titanium dioxide photocatalysts have excellent photocatalytic degradation performance and can be widely applied to the environmental protection field of sewage treatment and the like.
Owner:佛山市高明区尚润盈科技有限公司
Carbon nitride quantum dot-modified hierarchical-pore TiO2-SiO2 photocatalyst
ActiveCN108889329AAlleviate excessive hydrolysisImprove photocatalytic degradation performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationHigh concentrationWastewater
The invention relates to a carbon nitride quantum dot-modified hierarchical-pore TiO2-SiO2 photocatalyst and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method is mainly characterized in that the carbon nitride quantum dot-modified hierarchical-hole TiO2-SiO2 photocatalyst is prepared by introducing carbon nitride quantum dots in the process of synthesizing ordered hierarchical-pore TiO2-SiO2 bymeans of in-situ loading, and removing a template agent by means of calcining. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method used herein has good simplicity and operational convenience, enablesa raw material to be efficiently utilized, enables carbon nitride quantum dots to be loaded in pore walls of hierarchical-pore titania silica, thereby promoting the improvement of photocatalytic activity; the ordered hierarchical-pore structure also provides good passages for guest molecule diffusion and transfer and allows the prepared photocatalyst to provide good catalytic degrading activity for organic wastes, such as phenols and sulfadiazine, and antibiotic wastewater having actual high concentration.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Titanium dioxide/lignocellulose-based active carbon composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104549145AImprove adsorption capacityImprove photocatalytic degradation performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsOther chemical processesCellulosePhotocatalytic degradation
The invention relates to a titanium dioxide / lignocellulose-based active carbon composite material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, preparing faint yellow transparent TiO2 sol by using tetrabutyl titanate, then, dissolving tetrabutyl titanate into a prepared lignocellulose solution, sufficiently reacting tetrabutyl titanate, filtering a liquid on the upper layer after ending the reaction and settling, then, standing in the air for 12-36 hours, next, respectively and alternately washing and filtering by using distilled water and absolute ethyl alcohol until the filtrate is neutral, and drying a product in a vacuum drying oven to prepare a titanium dioxide / lignocellulose composite material; and then, pre-oxidizing, carbonizing and activating the composite material to prepare the titanium dioxide / lignocellulose-based active carbon composite material with efficient adsorption and catalysis performance. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple in process; and the obtained titanium dioxide / lignocellulose-based active carbon composite material has relatively-strong adsorption performance and relatively-good photocatalytic degradation performance and has the advantage of catalyzing organic pollutants in wastewater or air.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Method for preparing iron oxide nano granule modified titanium dioxide nano tube array
InactiveCN102002746AIncrease profitImprove absorbencySurface reaction electrolytic coatingCatalyst activation/preparationPhotocatalytic degradationBrown iron oxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing an iron oxide nano granule modified titanium dioxide nano tube array, and relates to a method for preparing a titanium dioxide nano tube array. The method comprises the following steps of: pre-treating a substrate, preparing electrolyte, performing electrochemical anodic oxidation on the substrate to form an ordered titanium dioxide nano tube array film with controllable size on the surface of the substrate, treating the film in Fe(NO3)3.9H2O by ultrasonic, and taking out and drying the film after standing; and thermally treating the dried composite film layer to obtain a product. By adopting the ultrasonic and chemical deposition combined method and controlling the concentration of the Fe(NO3)3 solution, the ultrasonic time and the dipping time, iron oxide nano granules can be controllably deposited on the surface of the titanium-based titanium dioxide nano tube array and in tubes, so that the photo-catalysis efficiency of the TiO2 can be improved, the photo-response of the TiO2 can be expanded to a visible light area, the utilization rate of the sunlight is improved, and the TiO2 applied to photo-catalysis can improve the absorptioncapability of an electrode on visible light and the photo-catalytic degradation capability on organic pollutants.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for preparing aluminum-doping zinc oxide nanometer sheet with photo-catalysis function
InactiveCN101717070AGood photocatalytic degradation effectPlay a role in environmental governanceNanostructure manufactureAluminum doped zinc oxidePhotocatalytic degradation
The invention belongs to the preparing technical field of nanometer material, in particular relates to a method for preparing aluminum-doping zinc oxide nanometer sheet with photo-catalysis function by electrochemical deposition. The invention uses water solution of zinc salt and aluminum salt as electrolyte solution; the electrochemical deposition process is carried out in a standard three-electrode system; electrolyte solution is poured in an electrolytic cell; platinum sheet is used as counter electrode, saturated calomel electrode is used as reference electrode, and an electric conductive base is used as work electrode; the electrolytic cell is heated with water; electrolyte solution in the electrolytic cell is kept at the temperature of 70-90 DEG C; the work electrode is applied with electric potential being -0.8 to -1.6 V relative to the reference electrode; after reaction, aluminum-doping zinc oxide nanometer sheet is obtained on the electric conductive base. The aluminum-doping zinc oxide nanometer sheet shows obvious photo-catalysis degradation effect upon methyl orange, and has great application foreground in the field of environmental improvement.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of porous ZnIn2S4 photo-catalyst
InactiveCN102836730AReduce chance of recombinationFully contactedPhysical/chemical process catalystsIndiumChemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of a porous ZnIn2S4 photo-catalyst, relating to a preparation method of a photo-catalyst and solving the problems of long consumed time of a preparation process and low porous ZnIn2S4 catalysis efficiency existing in the conventional ZnIn2S4 preparation method. The preparation method is realized through the following steps of: 1, adding bivalent zinc salt, trivalent indium salt and thioacetamide in bromoalkyl pyridine solution and adjusting pH value of reaction solution; 2, transferring reaction solution into a microwave reaction kettle, performing microwave hydrothermal treatment for 0.5-2 hours under the condition of 100-200 DEG C and then naturally cooling to room temperature; and 3, taking a sample out of the reaction kettle, washing with distilled water and absolute ethyl alcohol in sequence, and drying at certain temperature and under vacuum degree to prepare the porous ZnIn2S4 photo-catalyst. The porous ZnIn2S4 photo-catalyst prepared by the invention is suitable for treatment processes of industrial wastewater and toxic gas H2S.
Owner:INST OF PETROCHEM HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF SCI
Sulfur-doped carbon nitride photocatalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106669760ALarge specific surface areaMany reaction sitesPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationGraphite carbonPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a preparation method of a sulfur-doped carbon nitride photocatalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, calcining thiourea at 500 DEG C to 650 DEG C and keeping warm for 2h to 6h, so as to obtain sulfur-doped graphite carbon nitride; S2, grinding the sulfur-doped graphite carbon nitride obtained by the step S1 into powder; calcining at 400 DEG C to 550 DEG C again and keeping heat for 1h to 4h. The invention further discloses the sulfur-doped carbon nitride photocatalyst prepared by the preparation method of the sulfur-doped carbon nitride photocatalyst and application of the sulfur-doped carbon nitride photocatalyst. The sulfur-doped carbon nitride photocatalyst prepared by the invention has larger specific surface area and better photocatalytic activity; the steps of the preparation method are simple to operate and the catalyst has high activity and good stability.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION GUANGZHOU CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Molybdenum dioxide nanosheet/graphene-like carbon nitride photocatalytic material with visible-light response as well as preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN108786881AMany active sitesLarge specific surface areaPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationGlycol synthesisLight response
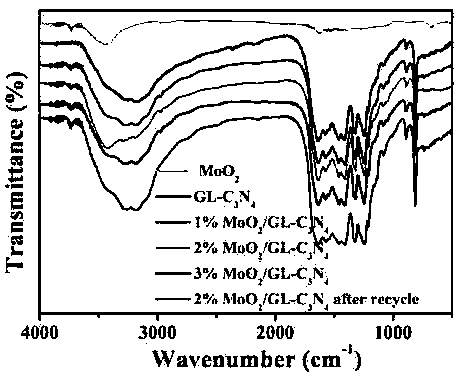
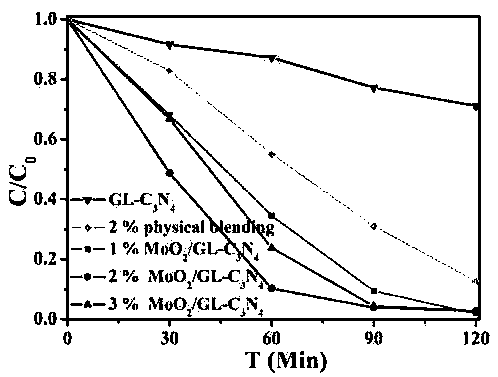
The invention relates to a preparation method of visible light responsive photocatalysts, in particular to a molybdenum dioxide nanosheet / graphene-like carbon nitride composite photocatalytic materialwhich can serve as an environment function material to be applied to the field of photocatalytic environment control. The composite photocatalyst is prepared by compounding molybdenum dioxide nanosheets (MoO2) and graphene-like carbon nitride (GL-C3N4) of a certain mass. The preparation method specifically comprises the following preparation steps: adding the prepared MoO2 and GL-C3N4 into ethylene glycol for performing stirred ultrasonic treatment, transferring the mixture into a reactor, and maintaining the temperature in a drying oven of 160-200 DEG C for 8-16 hours; finally, performing centrifugal washing and drying, so as to obtain the molybdenum dioxide nanosheet / graphene-like carbon nitride (MoO2 / GL-C3N4) composite photocatalyst. Experiments prove that compare with monomer carbon nitride, the composite photocatalyst has the advantage that the photocatalytic performance is obviously improved. In the preparation method provided by the invention, the raw materials are cheap, the process flow is simple, the reaction is mild, the whole synthetic process is green and environmental-friendly, the product cost is effectively reduced, and the composite photocatalyst has extremely high application prospects and application value in the aspects such as sewage treatment and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV +1
Porous tubular C3N4 photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109012734AImprove photocatalytic degradation performanceSave raw materialsPhysical/chemical process catalystsPhotocatalytic degradationPollutant
The invention discloses a porous tubular C3N4 photocatalyst. A preparation method of the porous tubular C3N4 photocatalyst comprises the following steps: (1) dispersing melamine in an acetic acid aqueous solution and performing a heating reflux reaction; (2) placing the solution, obtained by the heating reflux reaction, in a hydrothermal kettle for carrying out a hydrothermal reaction; (3) puttingan intermediate product, obtained by the hydrothermal reaction, into a calcination vessel, and calcining in a nitrogen atmosphere so as to obtain the porous tubular C3N4 photocatalyst. The porous tubular C3N4 photocatalyst having a one-dimensional hollow structure and a rich porous structure is prepared by adopting a molecular self-assembly method; the photocatalyst provided by the invention hasgood photocatalytic degradation performance for pollutants.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Hydrangea flower-cluster-shaped bismuth tungstate/biocarbon composite photocatalytic material, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107349927AHigh catalytic activityImprove controllabilityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOther chemical processesTungstateSurface-active agents
The invention relates to a hydrangea flower-cluster-shaped bismuth tungstate / biocarbon composite photocatalytic material, a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly adding biocarbon, Bi(NO3)3.5H2O and Na2WO4.2H2O into water, mixing uniformly, then adding a surface active agent to mix uniformly, and thus obtaining reaction precursor solution, wherein the proportion among Bi(NO3)3.5H2O, Na2WO4.2H2O, biocarbon and the surface active agent is (3-5)mmol:(1-3)mmol:(0.1-0.3)g:(1.2-1.8)mmol; adjusting the pH value of the reaction precursor solution to 1-3; carrying out hydrothermal reaction on the reaction precursor solution with adjusted pH value; and after the hydrothermal reaction is finished, taking out products, washing, drying and grinding to obtain the hydrangea flower-cluster-shaped bismuth tungstate / biocarbon composite photocatalytic material. The hydrangea flower-cluster-shaped bismuth tungstate / biocarbon composite photocatalytic material, the preparation method and the application have the advantages that by introduction of the biocarbon, not only can the cost be reduced and the process be simplified, but also the photocatalytic activity of the material can be improved and the degrading effect for organic pollutants is good.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
g-C3N4/Bi2O3 composite powder as well as preparation method and application thereof
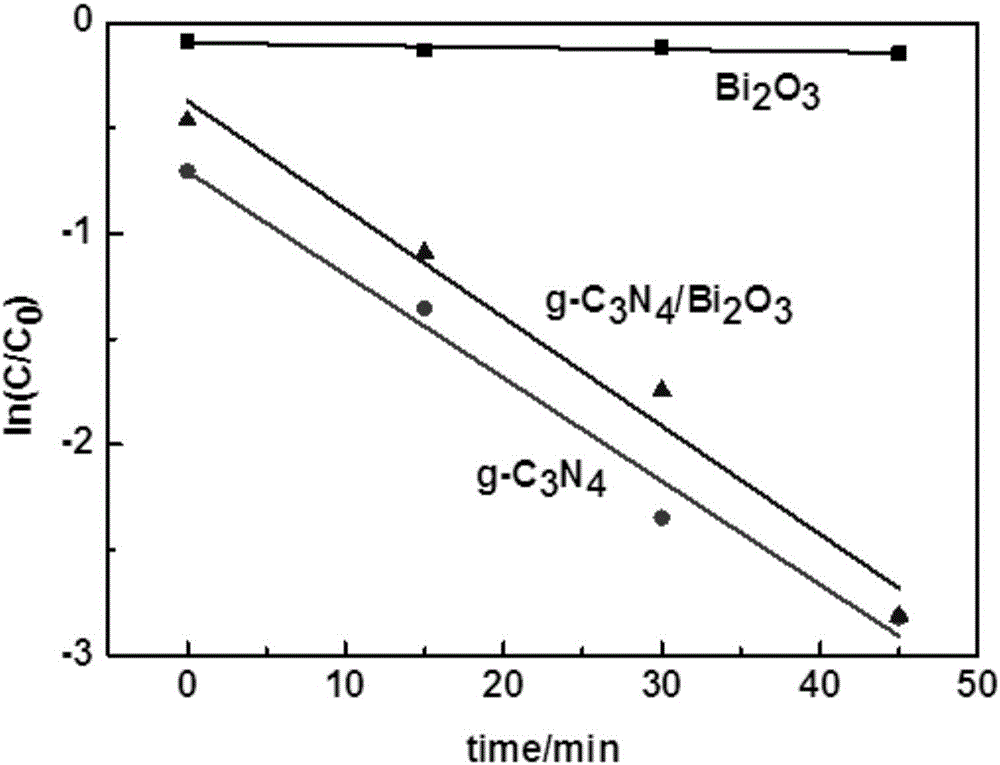
ActiveCN106694016AShort reaction timeShort processPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationEngineeringOrganopónicos
The invention provides g-C3N4 / Bi2O3 composite powder as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: preparing a precursor solution by adopting Bi(NO3)3.5H2O and NH4VO3 as raw materials, and preparing cubic-phase Bi2O3 microcrystals by virtue of a hydrothermal method; then preparing g-C3N4 from urea serving as a raw material by virtue of a calcining method; and finally, mixing the g-C3N4 and the Bi2O3, adding methanol, and performing an ultrasonic reaction, thus obtaining the g-C3N4 / Bi2O3 composite powder. According to the invention, the g-C3N4 / Bi2O3 composite powder is prepared by combing the traditional hydrothermal method, calcining method and ultrasonic synthesis method, and the prepared g-C3N4 / Bi2O3 composite powder has high absorption performance and photocatalytic performance, has high photocatalytic effect on organic pollutants under the irradiation of visible light, can be used for greatly improving the photocatalytic effect of the pure-phase Bi2O3, and has good application prospect in the aspects such as the environmental sewage treatment and the like.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
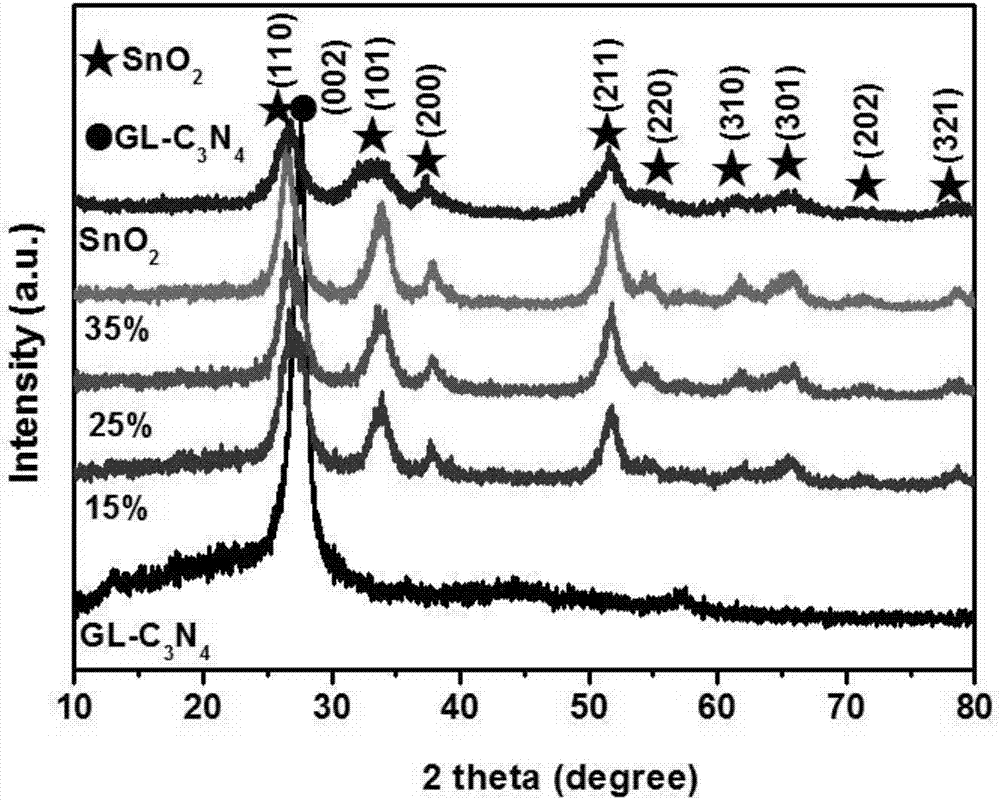
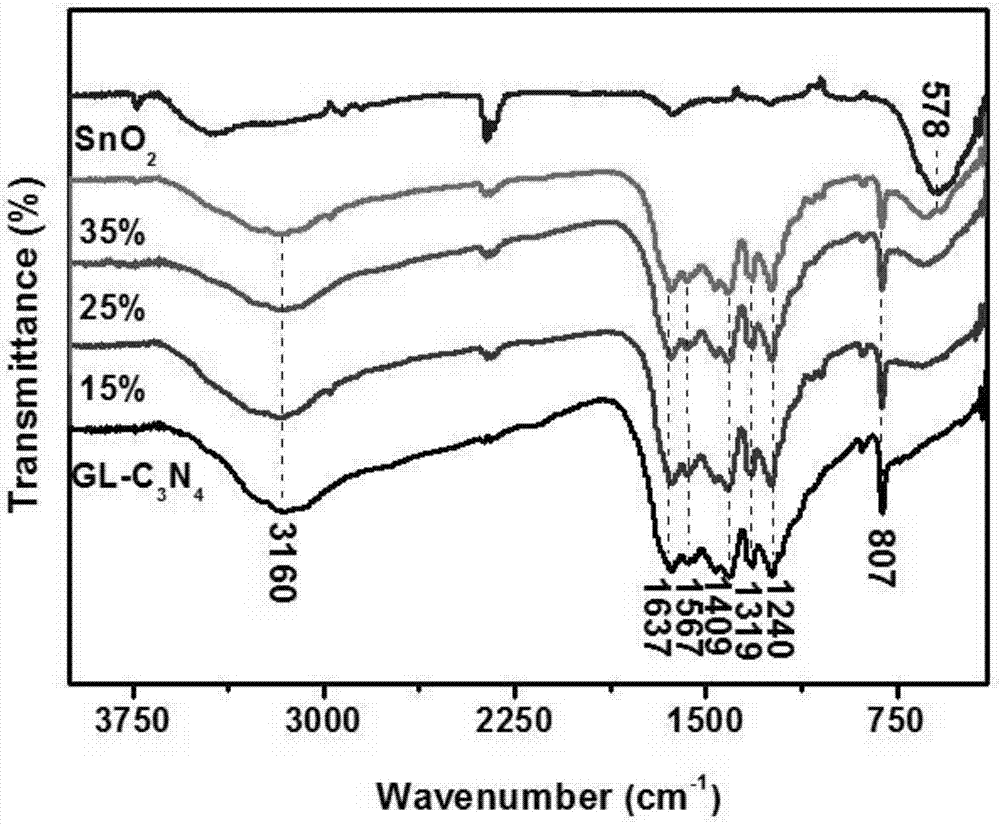
Stannic oxide/graphene carbon nitride composite photocatalytic material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107096558ASimple and fast operationLow costPhysical/chemical process catalystsTin dioxideGraphite carbon
The invention belongs to the field of photocatalysis and particularly relates to a stannic oxide / graphene carbon nitride composite photocatalytic material and a preparation method thereof. A composite photocatalyst is prepared by in-situ composition of stannic oxide (SnO2) and a certain mass of graphene carbon nitride (GL-C3N4) obtained by stripping graphite carbon nitride (g-C3N4) through ammonium chloride (NH4Cl). A photocatalytic performance experiment proves that the composite photocatalyst has relatively high photocatalytic activity in comparison with monomers carbon nitride and stannic oxide, and has good application prospect and economic benefit in the aspects of solar energy conversion and sewage treatment.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
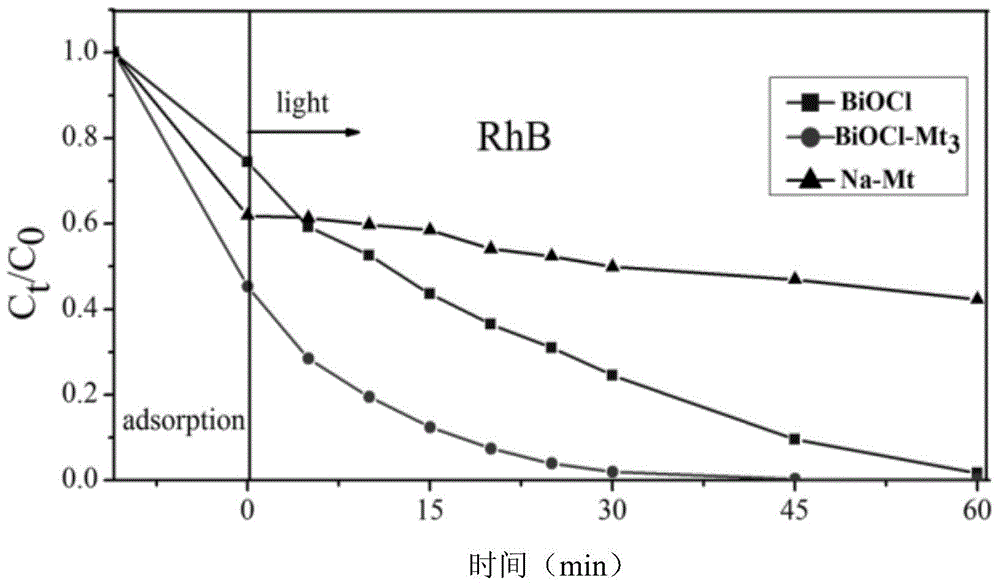
BiOCl/montmorillonite composite photocatalytic material and preparation method and application thereof
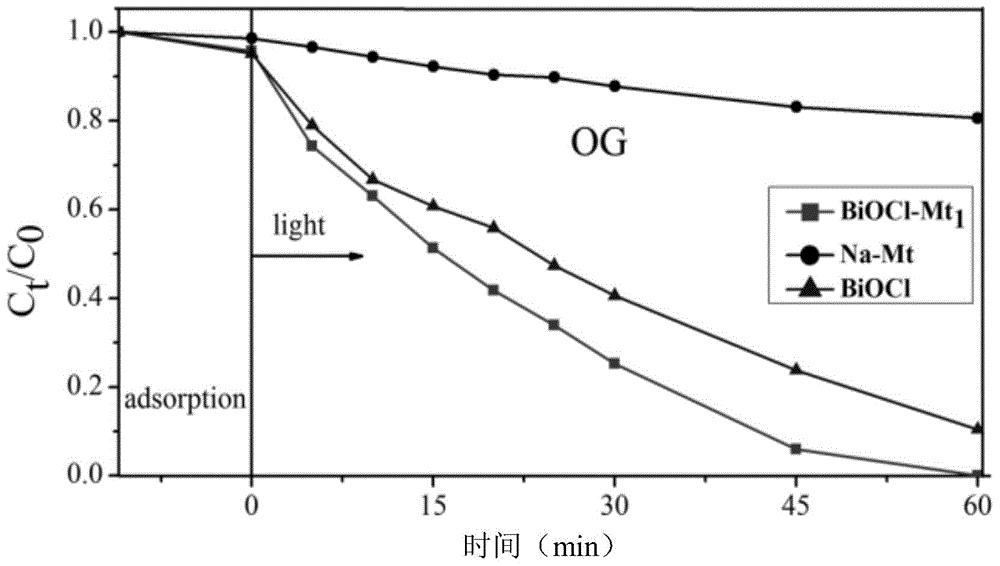
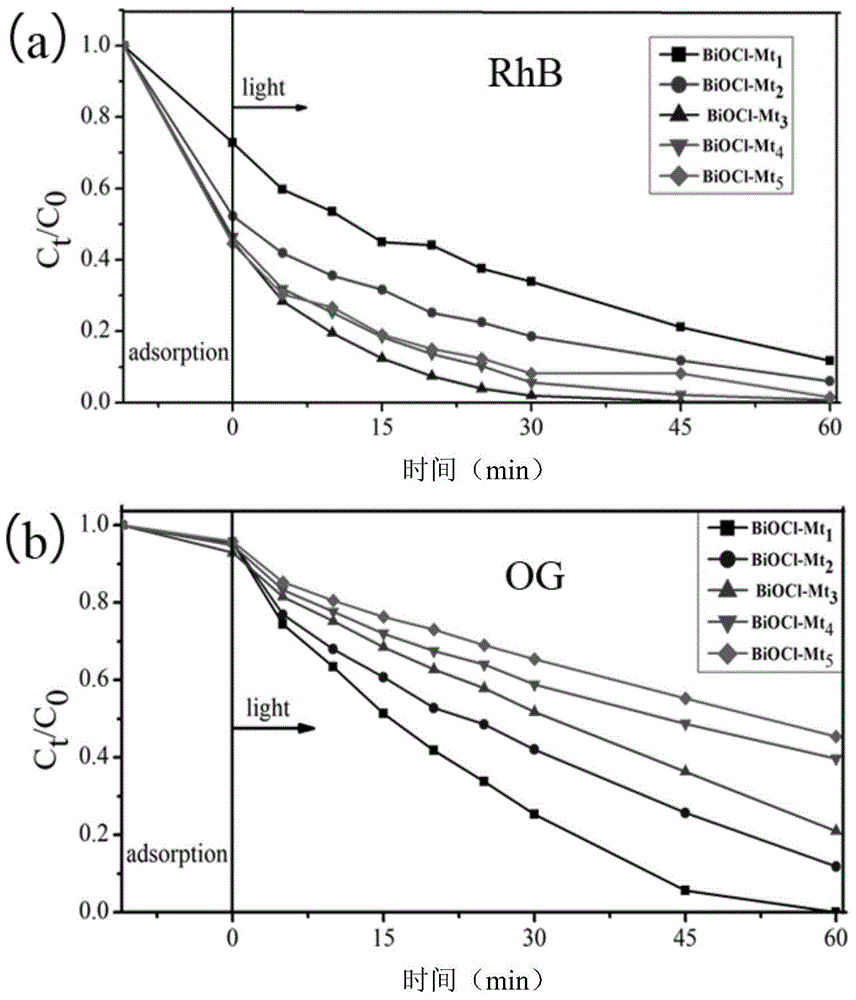
ActiveCN105013513AImprove adsorption capacityGood photocatalytic degradation effectPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationClearance rateMontmorillonite
The present invention discloses a BiOCl / montmorillonite composite photocatalytic material and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: during stirring, adding a 100 ml 3.0 wt% Bi(NO3)3 solution dropwise to a 100ml 1.0-5.0 wt% sodium-based montmorillonite suspension; after ultrasonic processing is performed, adjusting PH to 2; performing stirring for reaction for 8-16 h; centrifuging the mixed suspension; performing precipitation; washing the precipitate; drying and grinding the precipitate; and sieving the ground precipitate through a 200-mesh sieve to obtain the BiOCl / montmorillonite composite photocatalytic material. Under UV irradiation, the effect of adsorption and photocatalytic degradation is very significant for a cationic dye rhodamine B and an anionic dye orange G, and by using 0.15 g / L of the BiOCl / montmorillonite composite photocatalytic material, both the clearance rates of 40 mg / L of RhB and OG within a relatively short period, 1 h, are close to 100%.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing self-cleaning type surface raman-enhanced substrate
ActiveCN104357815AExcellent Raman scattering performanceImprove photocatalytic degradation performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsRaman scatteringThin membranePhotocatalytic degradation
The invention belongs to the technical field of inorganic functional materials, and discloses a method for preparing a Ag@AgCl / GO self-cleaning type surface raman-enhanced substrate. According to the method, silver nitrate serves as a precursor, PDDA serves as a modification reagent, C6H12O6 serves as a reducing agent, and hydrothermal reaction is performed to prepare Ag@AgCl sol; a Ag@AgCl / GO composite thin film is obtained through self-assembling and adsorbing Ag@AgCl nano particles with positive charges by using the fact GO carries negative charges, and has a high adsorption function and a temperature effect, and the Ag@AgCl / GO composite thin film is applied to the self-cleaning type surface raman-enhanced substrate. Compared with a conventional raman-enhanced substrate, the self-cleaning type surface raman-enhanced substrate has an excellent SERS (surface enhanced raman scattering) property, that a substrate material is recycled for multiple times is realized due to the excellent photocatalytic degradation performance, so that the self-cleaning type surface raman-enhanced substrate has a wide actual application prospect.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
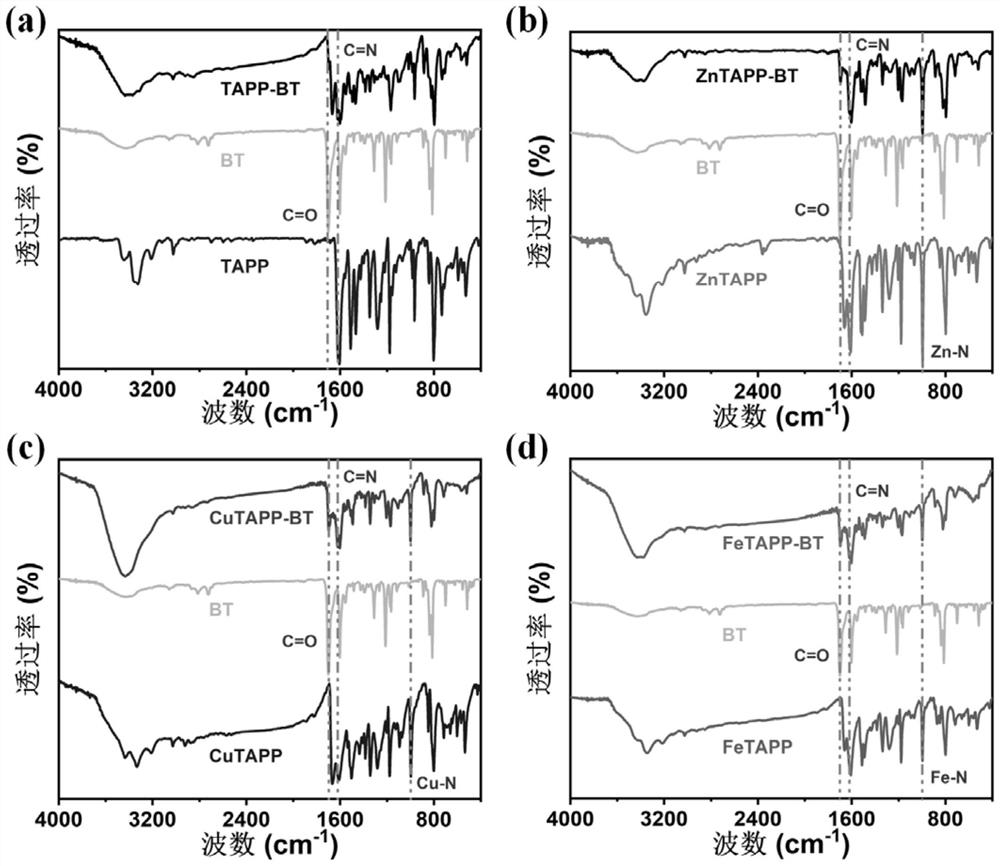
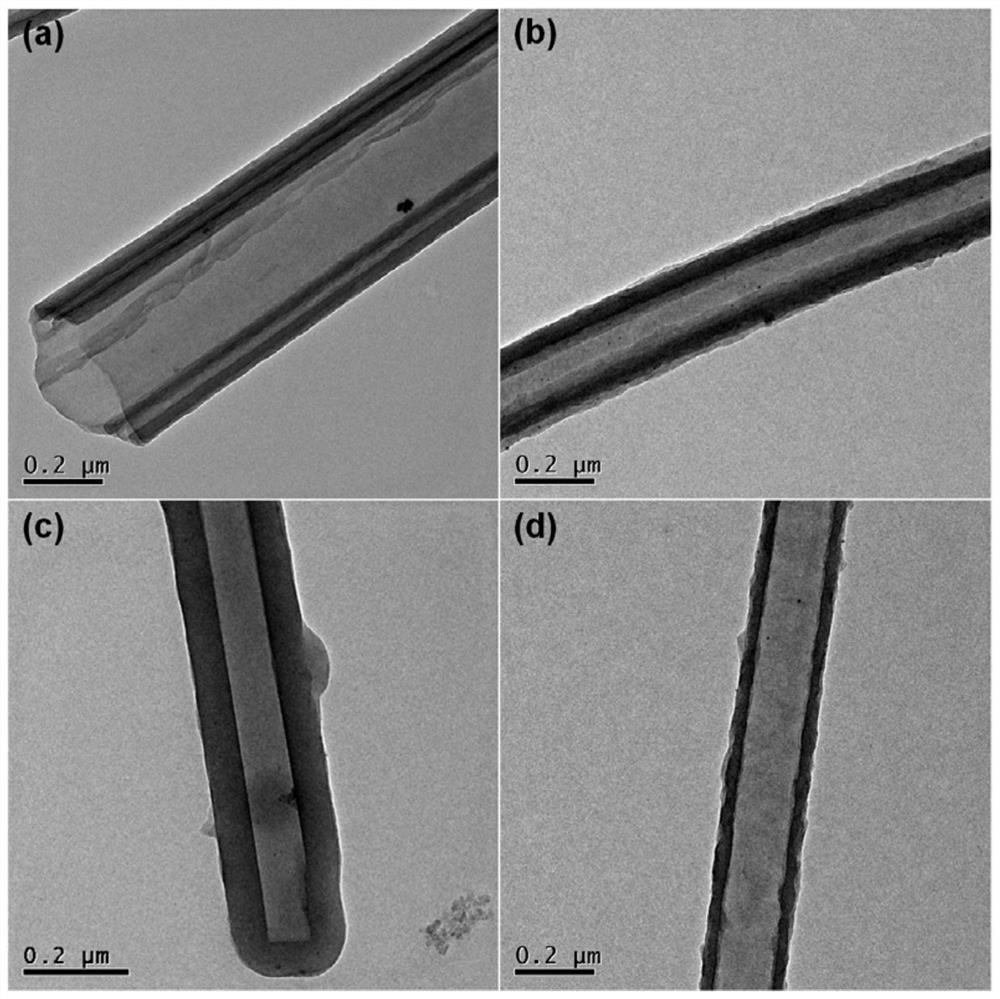
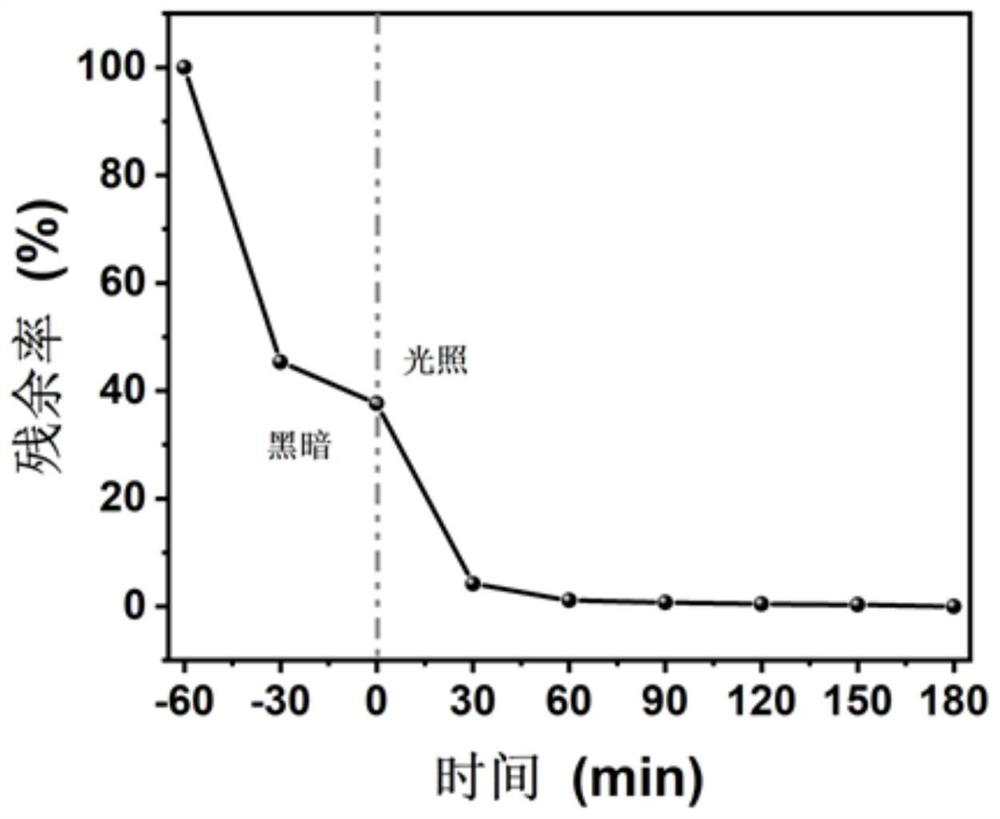
Metal coordination porphyrin-based conjugated polymer as well as preparation method and application thereof in photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants
ActiveCN112111070ASkeletal stabilityLow costWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsPtru catalystPhoto catalytic
The invention discloses a metal coordination porphyrin-based conjugated polymer as well as a preparation method and application thereof in photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. The catalyst provided by the invention has an approximately planar macrocyclic molecule with a 18pi conjugated skeleton, a stable rigid structure and a very stable highly conjugated system, so that the catalysthas excellent photoelectric conversion efficiency, a wide absorption spectrum range, strong oxidation-reduction capability and good chemical and thermal stability, metal coordination porphyrin is usedas an active center, a large number of derivatives can be derived, and the method has important application value in the aspects of photocatalytic degradation of environmental pollutants and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com