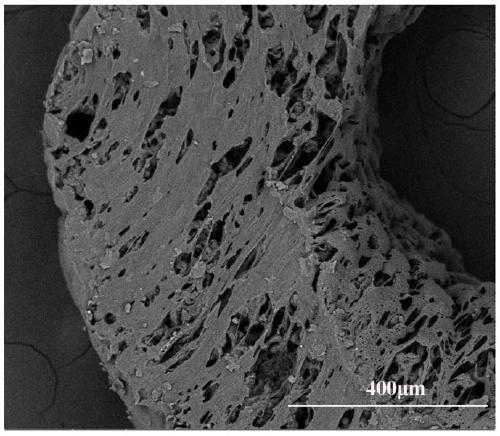
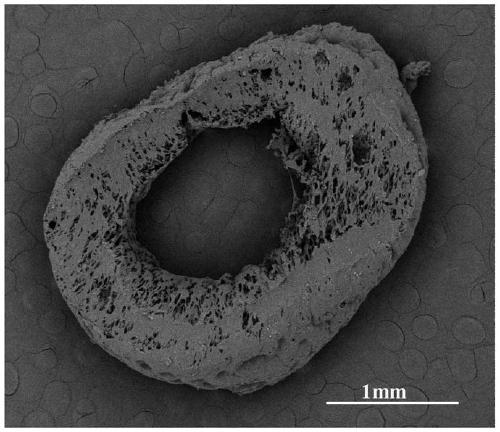
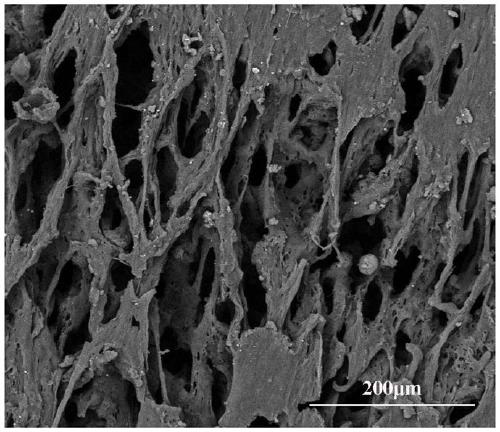
Nerve film and preparation method thereof
A nerve and thin film technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of cells not easy to adhere, cells not attractive, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0025] A preparation method of a nerve film, comprising: mixing polycaprolactone and isocyanate substances to react at a temperature of 60-80°C, and then adding a chain extender to react to obtain a polyurethane prepolymer.
[0026] Polycaprolactone reacts with isocyanate substances to generate polyurethane prepolymer under the action of chain extender. Under the action of the chain extender, the molecular chain of the generated polyurethane prepolymer is extended and the molecular weight is increased, which improves the mechanical properties (for example, twisting and folding properties) of the polyurethane prepolymer. Optionally, the polycaprolactone has a molecular weight of 2000.
[0027] In some optional embodiments, the chain extender includes ethyl lysine dihydrochloride, 1,4-butanediol, m-phenylenediamine, 1,2-ethylenediamine ethyl lysine dihydrochloride salt, ethylenediamine, carbamate, DL-lactic acid, and ascorbic acid. Among them, ethylenediamine is non-toxic and ...
Embodiment 1
[0042] The present embodiment provides a nerve membrane, which is prepared by the following steps:
[0043] Add 30.0g of polycaprolactone (molecular weight: 2000) into a 150ml small beaker. After the polycaprolactone is completely dissolved, add 7.8g of isophorone diisocyanate, react at 70°C for 2 hours, and add the catalyst stannous octoate dropwise. 0.1mL, continue to react for 2 hours, add chain extender lysine ethyl ester dihydrochloride 3.7g, react for 2.5 hours to obtain medical polyurethane prepolymer.
[0044] Add 0.25g gastrodin to the medical polyurethane prepolymer, react for 3 hours to obtain the first primary product; add 0.2mL water to the first primary product and continue to react for 0.5 hour to obtain the second primary product; put the second primary product at 90°C Curing and drying in an oven for 18 hours to obtain a medical polyurethane nerve material.
[0045] Weigh 2.0g of the above-mentioned medical polyurethane nerve material, add 20mL of 1,4-dioxane...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The present embodiment provides a nerve membrane, which is prepared by the following steps:
[0049] Add 30.0g of polycaprolactone (molecular weight: 2000) into a 150ml small beaker. After the polycaprolactone is completely dissolved, add 7.8g of isophorone diisocyanate, react at 70°C for 2 hours, and add the catalyst stannous octoate dropwise. 0.1mL, continue to react for 2 hours, add chain extender lysine ethyl ester dihydrochloride 3.7g, react for 2.5 hours to obtain medical polyurethane prepolymer.
[0050] The medical polyurethane prepolymer and gastrodin were mixed according to the mass ratio of 100:1, and the first product was obtained in 2 hours after reaction; 0.2mL water was added to the first product and continued to react for 20min to obtain the second product; The primary product was cured and dried in an oven at 100°C for 20 hours to obtain a medical polyurethane nerve material.
[0051] Weigh 2.0 g of the above-mentioned medical polyurethane nerve materi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com