Tissue engineering soft repair scaffold with globular protein as pore-foaming agent and preparation method thereof
A globular protein and tissue engineering technology, applied in the direction of prosthesis, medical science, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, limited instrument accuracy, application limitations, etc., to achieve the effect of promoting the formation of cartilage tissue, compact appearance and rapid cartilage damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
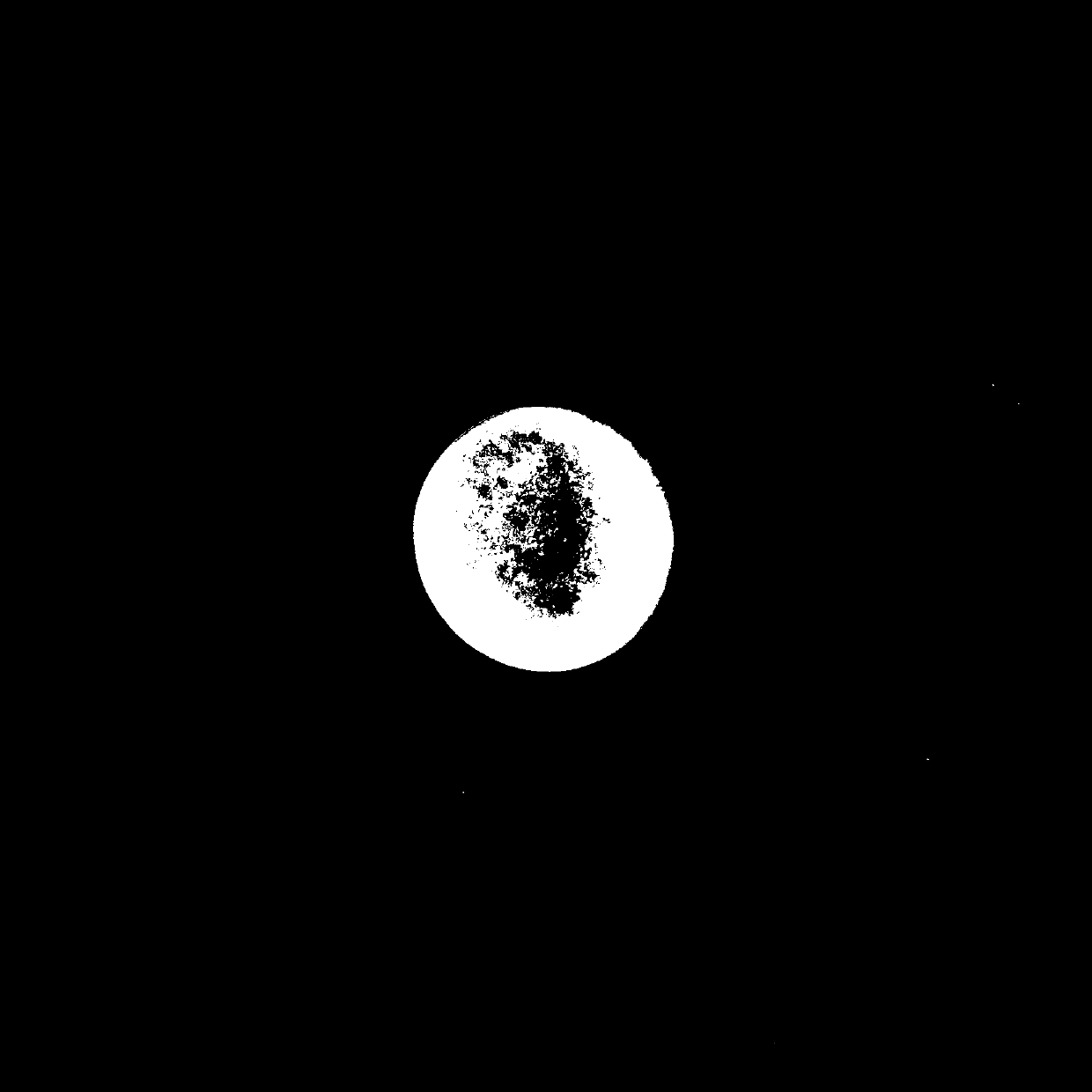
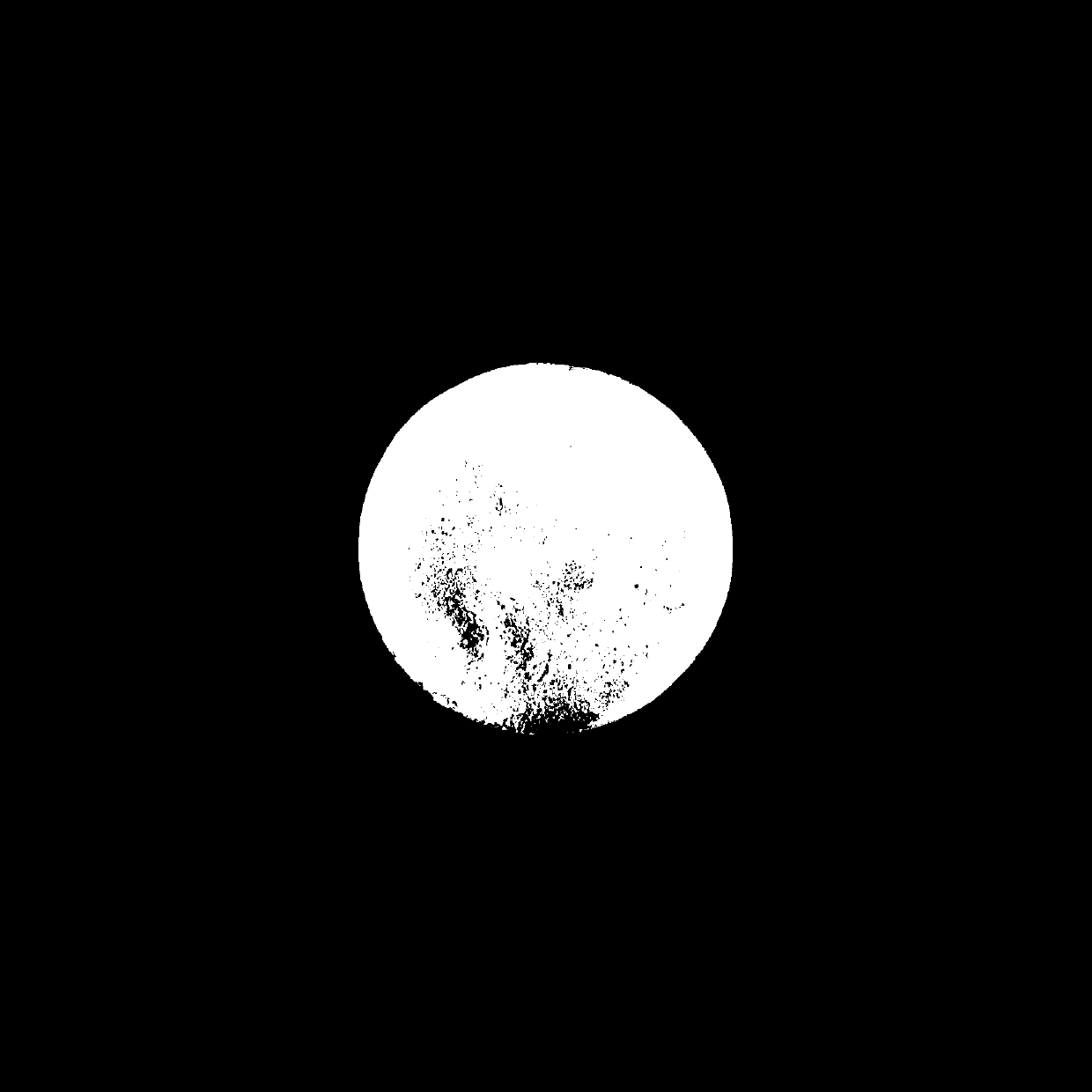
[0034] The present invention relates to a preparation method of a tissue engineering soft repair scaffold using globular protein as a porogen. Collagen (such as human-like collagen produced by high-density fermentation of genetically engineered bacteria BL21) is used as a raw material, and transglutaminase derived from microorganisms is used as a raw material. The cross-linking agent, globular protein and NaCl are porogens, and the tissue-engineered cartilage scaffold is prepared by biological cross-linking. The steps include: dissolving the collagen in the globular protein solution, and finally preparing the tissue engineered cartilage scaffold by using the pore-forming agent NaCl and the cross-linking agent glutamine transaminase.
[0035] Specifically include the following steps:
[0036] Step (a): dissolving the globular protein in double distilled water to obtain a globular protein solution with a mass fraction of 5%-15%;
[0037] Step (b): dissolving collagen in the glo...
Embodiment 1
[0047] Step (a): Weigh soybean protein and dissolve it in 5 mL double-distilled water to obtain a bovine serum albumin solution with a mass fraction of 5%;
[0048] Step (b): the human-like collagen is dissolved in the bovine serum albumin solution in step (a), so that its concentration is 15%;
[0049]Step (c): Put the protein mixture solution prepared in step (b) at 37°C to dissolve completely, add 4% NaCl, and stir to dissolve completely;
[0050] Step (d): Add transglutaminase with a content of 60 U / g collagen to the mixed solution prepared in step (c), and after completely dissolving, statically cross-link at 4°C for 24 h to obtain a human collagen cartilage scaffold ;
[0051] Step (e): The cartilage scaffold obtained in step (d) was washed in pyrogen-free water for 72 hours to remove the crosslinking agent and porogen, vacuum freeze-dried, and sterilized by Co60 irradiation to obtain a tissue engineered cartilage scaffold.
Embodiment 2
[0053] Step (a): Weigh bovine serum albumin and dissolve it in 5 mL double-distilled water to obtain a bovine serum albumin solution with a mass fraction of 5%;
[0054] Step (b): the human-like collagen is dissolved in the bovine serum albumin solution in step (a), so that its concentration is 15%;
[0055] Step (c): Put the protein mixture solution prepared in step (b) at 37°C to dissolve completely, add 1% NaCl, and stir to dissolve completely;
[0056] Step (d): Add transglutaminase with a content of 80 U / g collagen to the mixed solution prepared in step (c), and after complete dissolution, statically cross-link at 4°C for 24 h to obtain human collagen cartilage scaffolds ;
[0057] Step (e): The cartilage scaffold obtained in step (d) was washed in pyrogen-free water for 72 hours to remove the crosslinking agent and porogen, vacuum freeze-dried, and sterilized by Co60 irradiation to obtain a tissue engineered cartilage scaffold.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com