Aspergillus oryzae lipase mutant and application thereof
A technology of Aspergillus oryzae lipase and mutant, which is applied in the fields of enzyme engineering and genetic engineering, can solve the problems of low yield of Aspergillus oryzae lipase, unsatisfactory catalytic activity, and unsatisfactory stability, and achieves improved hydrolysis activity and good thermal stability. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Embodiment 1: Construction of Aspergillus oryzae lipase mutant library by random mutation
[0023] Utilize the error-prone PCR kit (the kit is purchased from Beijing Tianenze Gene Technology Co., Ltd.) in vitro to Aspergillus oryzae lipase gene aol-3 (nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2, amino acid sequence is SEQ ID shown in NO.1) to introduce nucleotide mutations.
[0024] Error-prone PCR reaction conditions and primers (30μL system):
[0025]Aspergillus oryzae lipase gene (SEQ ID NO.2) DNA template with a concentration of 1 ng / μL, 1 μL of primers 1F and 1R at a concentration of 10 μM, 3 μL of 10× error-prone PCR Mix, 3 μL of 10× dNTP for error-prone PCR, easy MnCl for wrong PCR 2 4 μL, 2 μL of dGTP for error-prone PCR, 0.5 μL of 5 U / μL Taq DNA polymerase for error-prone PCR, and 14.5 μL of ultrapure water.
[0026] Primer 1F: 5' TAAGAAGGAGATATA CCATGGCACATCTGGCCATTAAGAGCC 3'
[0027] Primer 1R: 5' GTGGTGGTGGTGGTG CTCGAGGTTGGCGGCTGCAACTG 3'
[0028] ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2: Mutant library screening
[0032] The transformant that embodiment 1 obtains is carried out as follows:
[0033] 1. Selection of mutants: Transfer the mutants obtained above to a new LB solid medium containing 100 μg / mL kanamycin, label each mutant, and culture at 37°C overnight.
[0034] 2. Plate screening of mutants: Add IPTG with a final concentration of 0.1 mM to the screening medium containing 100 μg / mL kanamycin, spot the labeled mutants on the screening plate, and ensure that the numbers correspond to each other. Cultivate in a 37°C incubator for 24h-48h. During this period, observe whether there is a hydrolysis circle and the size of the hydrolysis circle.
[0035] 3. Re-screening of mutants: Transfer the mutants with larger hydrolysis circle obtained from the primary screening to LB liquid medium, culture at 37°C for 10 hours, and transfer the culture solution to LB culture with an inoculum volume concentration of 1%. cultured at 37°C until OD 60...
Embodiment 3
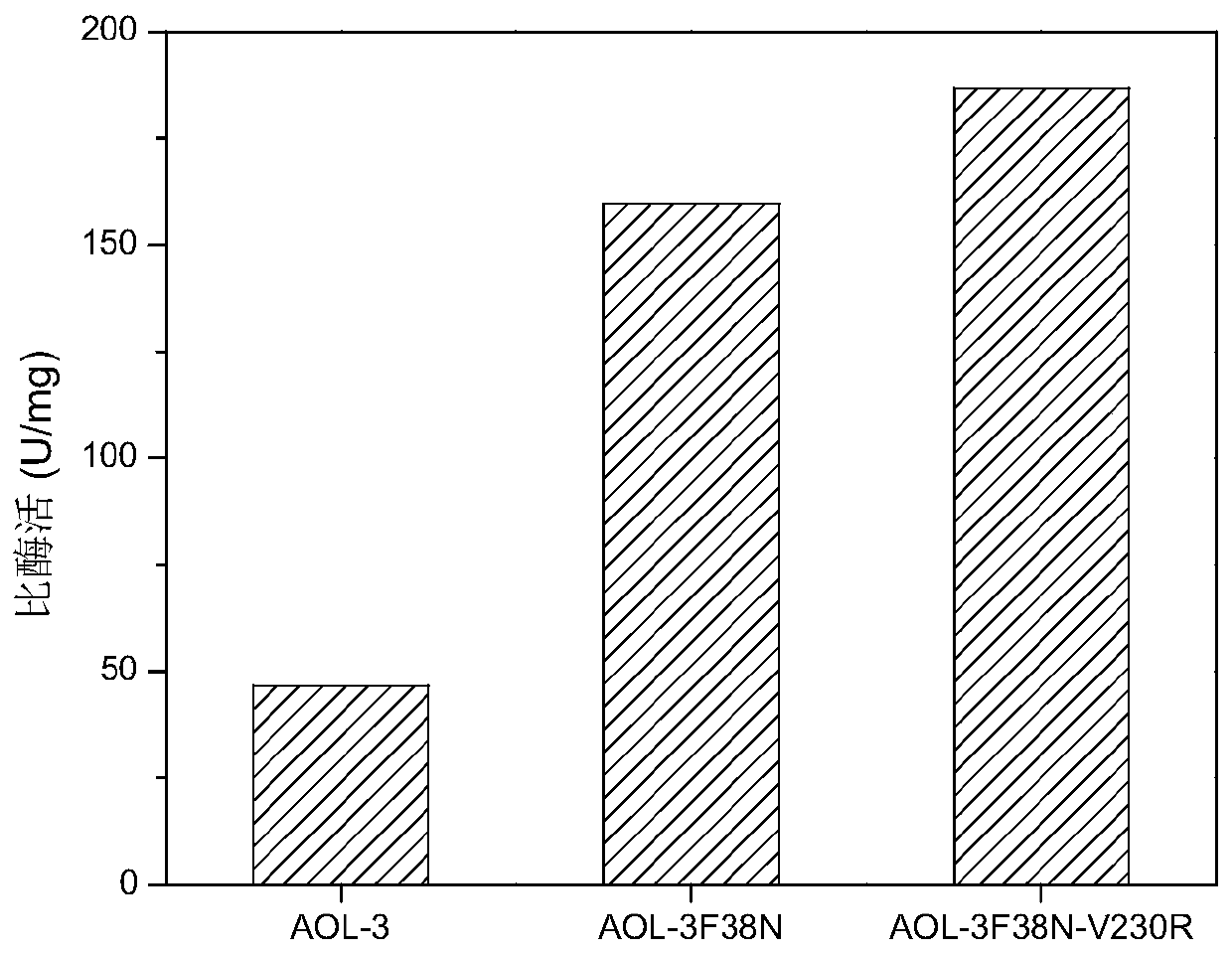
[0044] Example 3: Verification and purification of high-yield Aspergillus oryzae lipase production strain
[0045] The mutant bacteria AOL-3 in embodiment 2 were respectively F38N and mutant AOL-3 F38N-V230R Inoculate in LB liquid medium, cultivate at 37°C for 10 hours, inoculate the culture solution into LB medium with an inoculum volume concentration of 1%, and cultivate at 37°C until the cells grow to OD 600 When the concentration was 0.6, add IPTG with a final concentration of 0.1mM to induce, continue to culture at 28°C for 12h, collect the bacterial cells by centrifugation, resuspend with pH 7.5 phosphate buffer, and ultrasonically disrupt the cells for 10min with a sonicator (power 100W, Break for 2s, stop for 6s), the supernatant is the mutant strain AOL-3 F38N and AOL-3 F38N-V230R enzyme solution. According to the instructions of GE's 25mL nickel ion affinity chromatography filler and AKAT purification instrument, the supernatant was loaded onto a pre-equilibrated...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| optical purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com