Preparation of boldenone by sequential conversion of Arthrobacter simplex and genetically-engineered yeast strain
A technology of genetically engineered strains and Arthrobacter simplex is applied in the directions of genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, biochemical equipment and methods, etc. It can solve the problems such as the lack of Arthrobacter simplex and yeast strains, and achieve good application value and promotion prospects. Improve coenzyme utilization, easy to achieve effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
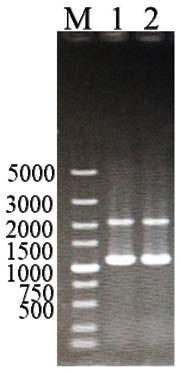
Image
Examples
Embodiment 117
[0064] Example 1 Acquisition of 17β carbonyl reductase gene and construction of Pichia pastoris genetic engineering strain
[0065] (1) Acquisition of 17β carbonyl reductase gene ayr1
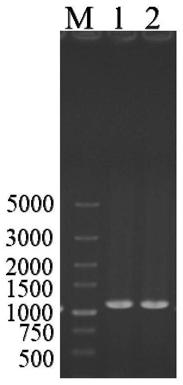
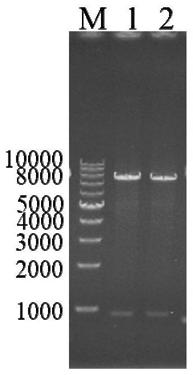
[0066] Using the Saccharomyces cerevisiae W303 genome as a template, amplify the 17β carbonyl reductase (GenBank number: KZV10489.1) encoding gene ayr1 (GeneID: 854682), design the primer pair as follows, and recover the PCR product with GelExtraction Kit (Omega, USA) , the recovered fragment was connected to the vector pPIC3.5K, the recombinant plasmid pPIC3.5K-ayr1 was constructed, and transformed into E.coli JM109 to obtain a genetically engineered strain containing the target gene. The bacteria solution PCR verification and double enzyme digestion verification showed that the recombinant plasmid pPIC3.5K-ayr1 was successfully constructed (such as figure 1 and figure 2 shown). By sequencing the above clones and comparing them with the obtained ayr1 sequence, the sequencing results were c...
Embodiment 2
[0086] The establishment of embodiment 2 double bacterium sequence catalytic system
[0087] In the following examples, the effects of Pichia genetically engineered strains on AD or ADD, the simultaneous transformation and sequential transformation of Arthrobacter simplex and Pichia genetically engineered strains on the synthesis of BD, and the effects of simple Arthrobacter reaction systems were investigated respectively in the following examples. Effect of inactivation on BD synthesis.
Embodiment 2-1
[0089] Pick Pichia pastoris genetic engineering strain P.pastoris GS115AYR1 S.c Single clone, inoculated into 30mL BMGY, 30°C, 200r / min, shake to OD 600 =5-6; Centrifuge at 1500g-3000g at room temperature for 5min, collect the cells, remove the supernatant, resuspend the cells with 30mL BMMY, and induce expression; every 24h, add methanol to a final concentration of 0.5% to continue induction for 4 days; after induction for 4 days Add 5g / L of substrate AD (or ADD) and HP-β-CD with a molar ratio of 1:1 to the fermented broth, 30°C, 200r / min to continue conversion for 4 days, sample 1mL, and equal volume of acetic acid Ethyl ester ultrasonic extraction, HPLC analysis. Such as Figure 5 As shown, Pichia pastoris genetic engineering strain P.pastoris GS115AYR1 S.c After the growing cells converted the substrates AD and ADD, the yields of the corresponding products TS (testosterone) and BD were 59% and 69%, respectively. This indicated that ADD was more suitable as a substrate ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com