Application of Nano-MitoPBN in preparing medicines for resisting oxidation and treating diabetes
A diabetes drug and anti-oxidation technology, applied in the fields of biology and medicine, can solve problems such as unknown effects in the body, achieve the effects of reducing peripheral blood sugar levels, promoting mitochondrial function, and reducing oxidative stress levels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1: Nano-MitoPBN targeted removal of mitochondrial ROS improves blood sugar and abnormal glucose tolerance in diabetic mice
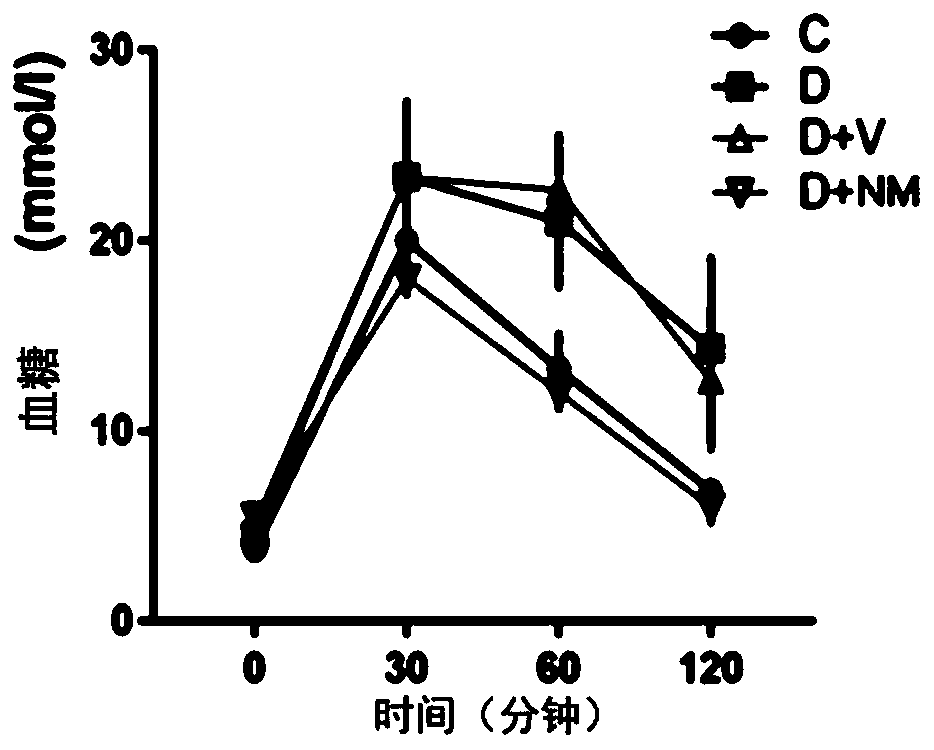
[0034] After 3 weeks of STZ stress mice, random blood glucose levels in diabetic mice were significantly increased, and Nano-MitoPBN intervention reduced the increase in blood glucose in diabetic mice caused by STZ. The results of intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test reflected the impaired glucose tolerance of diabetic mice, and Nano-MitoPBN intervention improved the impaired glucose tolerance of diabetic mice. See figure 1 As shown in the figure, C represents the normal control group, D represents the diabetic group (STZ+HFD), D+NM represents the diabetic Nano-MitoPBN intervention group, and D+V represents the diabetic + empty vector group.
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2: Nano-MitoPBN reduces the level of oxidative stress in diabetic mice
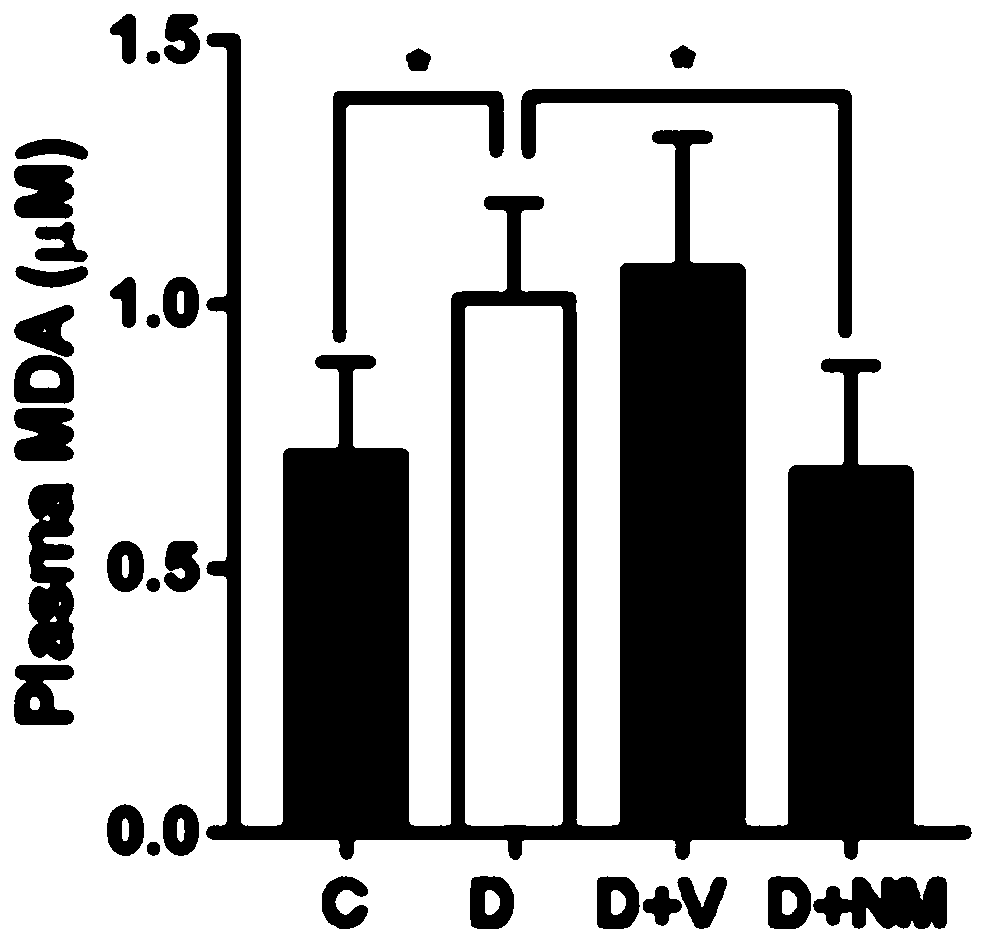
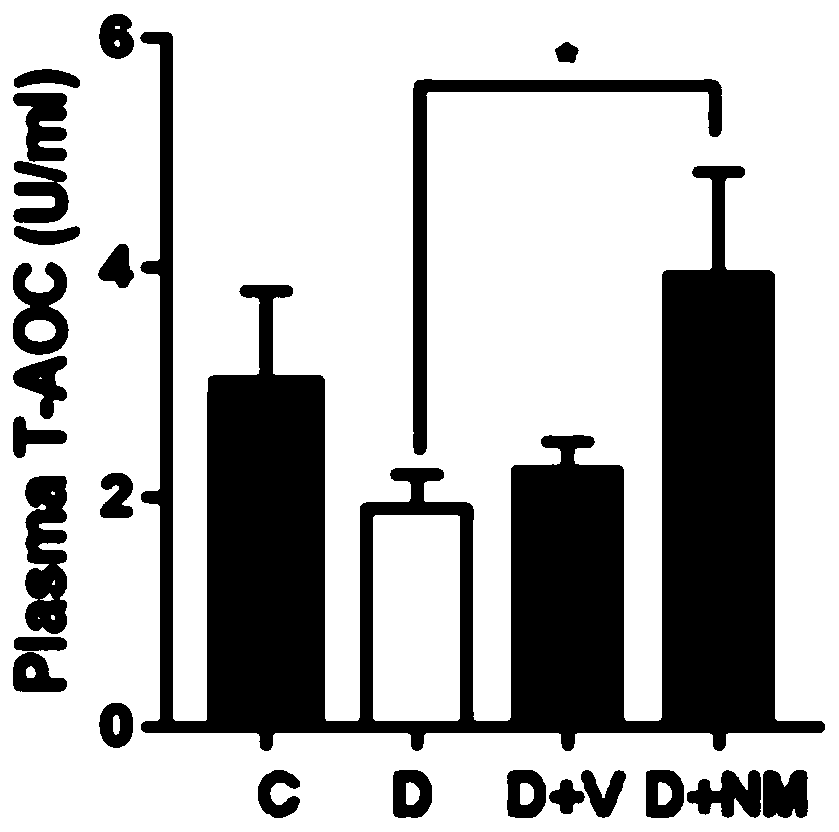
[0036] Oxidative stress in organisms is caused by the imbalance between oxidative damage and antioxidant system. Malondialdehyde (MDA) is an oxidation end product of free radicals acting on lipid peroxidation in organisms, and the level of MDA can reflect the level of oxidative damage in organisms. The results showed increased MDA content in diabetic mice (see figure 2 ), the total antioxidant capacity (TAOC) in the body was significantly reduced (see image 3 ), the expression of antioxidant enzymes in vivo weakened, indicating that there was a certain degree of oxidative damage in diabetic mice, and Nano-MitoPBN intervention significantly reduced the level of oxidative stress in diabetic mice. In the figure, C represents the normal control group, D represents the diabetic group (STZ+HFD), D+NM represents the diabetic Nano-MitoPBN intervention group, and D+V represents the diabetic + em...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3: Nano-MitoPBN improves liver cell mitochondrial function in diabetic mice
[0038] Mitochondrial respiratory control rate (RCR) reflects mitochondrial function and is commonly expressed as the ratio of respiration rate, which is the ratio of state 3 respiration rate to state 4 respiration rate, and is a sensitive indicator for evaluating the integrity of mitochondrial structure and coupling degree of oxidative phosphorylation. An increase in RCR indicates that the mitochondrial function is enhanced, and a decrease in RCR, the closer to 1, the more the mitochondrial respiratory chain is uncoupled from oxidative phosphorylation, and the mitochondrial function is impaired. Through the determination of mitochondrial RCR in mouse liver tissue, we found that the mitochondrial respiratory function of diabetic mice was significantly impaired, and the mitochondrial respiratory function of diabetic mice was restored after Nano-MitoPBN intervention (see Figure 4 ). ATP...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com