Preparation of ferromagnetic nanoparticle and application thereof in extraction and removal of micro-plastics
A technology of ferromagnetic particles and nanoparticles, applied in the field of environmental pollution research, can solve the problems of secondary pollution of microplastics, inability to separate polymers with high density, etc., and achieve the effects of easy removal, environmentally friendly removal, and low cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
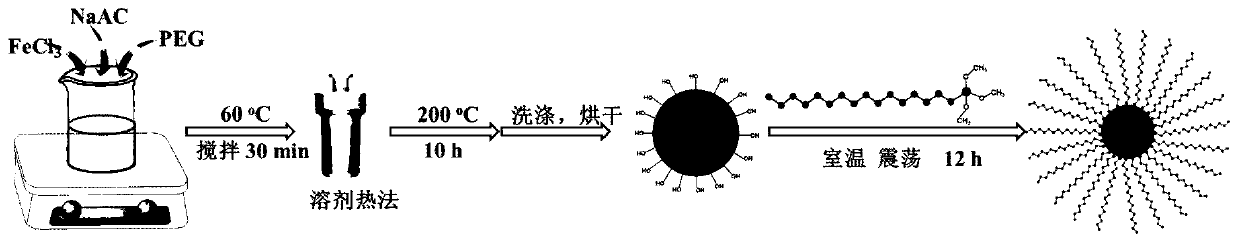
[0032] Embodiment 1: a kind of preparation method of hydrophobic ferromagnetic nanoparticles,
[0033] Such as figure 1 Perform the following steps in sequence as shown:
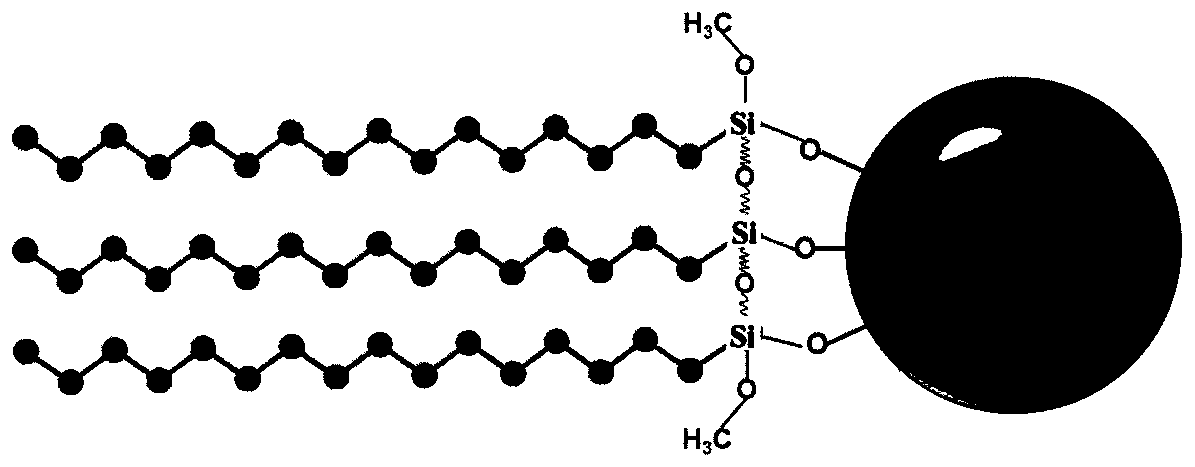
[0034]1), 1.35g iron trichloride (FeCl3 6H2O) is dissolved in 40ml ethylene glycol (EG), stirs and ultrasonic to dissolve completely; Add 3.6g anhydrous sodium acetate (NaAC) and 4g polyethylene glycol ( PEG) stirred, sonicated until dissolved; heated in a water bath at 60°C, mechanically stirred for 30 minutes, and then sonicated for 1 hour; after the solution was cooled to room temperature, pour the liquid into the reaction kettle, and blast at 200°C for 10 hours; pour off the supernatant from the black magnetic fluid solution, poured into a beaker and naturally settled; washed three times with distilled water and absolute ethanol, poured off the supernatant, and vacuum-dried at 60°C to constant weight to obtain ferromagnetic particles.
[0035] 2), adding 0.08g of ferromagnetic nanoparticles to 50mL of ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2: Extraction of microplastics in water using hydrophobic ferromagnetic nanoparticles obtained in the above examples
[0039] Add the microplastics to 50 mL of deionized water, add about 0.5 mL of the above-mentioned embodiment to obtain a suspension of hydrophobic iron nanoparticles, stir and mix with a glass rod for 2 min. Add the magnet into the beaker and stir slowly. After the magnetized microplastics are adsorbed on the magnet, take out the magnet. Apply 12V voltage to the magnet to demagnetize the magnet, rinse the magnet with a small amount of distilled water, rinse the microplastics on the magnet to a glass petri dish, and perform visual counting or stereoscopic microscope counting in the glass petri dish.
[0040] According to the method of the above steps, different sizes (large, medium and small) and different types (HDPE (high density polyethylene), LDPE (low density polyethylene), PP (polypropylene), PET (polyester), PVC (polyvinyl chloride) PE (p...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Example 3: Extraction of Microplastics in Sediments Using Hydrophobic Ferromagnetic Nanoparticles Obtained in the Examples Above
[0057] In order to prevent the impact of microplastics in the sediment on the recovery rate of the experiment, the sieved 5mm sediment was placed in a muffle furnace and burned at 450°C for 3h. Weigh 100g of sediment into a beaker, add different types of microplastics, stir evenly with a glass rod, then add 200mL of saturated sodium chloride solution, stir, mix evenly, and settle for 5 minutes. The supernatant was transferred to another beaker, and the remaining small amount of supernatant was transferred with a glass glue tip dropper, and this process was repeated 3 times. Add 2 mL of the hydrophobic iron nanoparticle suspension obtained in the example to the transferred supernatant, and stir and mix with a glass rod for 2 min. Add the magnet into the beaker and stir slowly. After the magnetized microplastics are adsorbed on the magnet, ta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com