Method for pretreating lignocellulose by using betaine eutectic solvent
A low eutectic solvent, lignocellulose technology, applied in the use of microorganism/enzyme cellulose treatment, cellulose raw material pulping, fiber raw material processing and other directions, can solve the problems of high toxicity, biodegradability, sensitivity, etc. Environmentally friendly, strong operability, and the effect of reducing dosage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
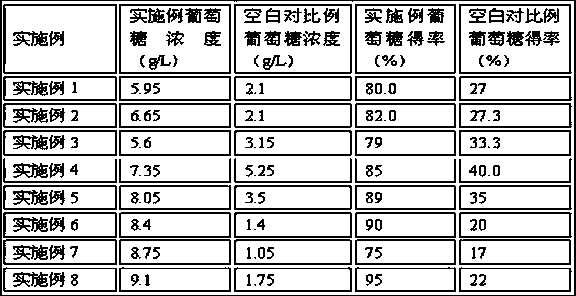
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] a) Preparation of 50 wt% [betaine][glycine] deep eutectic solvent: add betaine solution with a mass fraction of 46% to glycine aqueous solution drop by drop under stirring, the molar ratio of betaine and glycine is 1:5, React at 20°C for 12 h.
[0020] b) Pretreatment: Put the dried corncob powder and [betaine][glycine] deep eutectic solvent (moisture content: 50 wt%) in a 250 mL single-necked flask according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:5 Mix and stir at 50°C for 6 h; after the solid-liquid mixture is cooled to room temperature, add 1 times the volume of deionized water equal to the volume of the pretreatment solvent, mix, centrifuge to separate the solid and liquid, and then wash the solid with 3 times the volume of deionized water Repeat until the supernatant is colorless, then dry the solid to absolute dryness to obtain the pretreated corn cob.
[0021] c) Enzymatic hydrolysis: carry out enzymatic hydrolysis in 50 mL of acetate buffer (50 mM, pH 5.5), with a s...
Embodiment 2
[0023] a) Preparation of 60 wt% [betaine][lysine] deep eutectic solvent: add 46% betaine solution dropwise to aqueous lysine solution under stirring, moles of betaine and lysine The ratio was 1:10, and the reaction was carried out at 30°C for 24 h.
[0024] b) Pretreatment: According to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:10, dry corncob powder and [betaine][lysine] deep eutectic solvent (moisture content 40 wt%) in a 250 mL single-port Mix in a flask and stir at 70°C for 10 h; after the solid-liquid mixture is cooled to room temperature, add 1 times the volume of deionized water as the pretreatment solvent, mix, centrifuge to separate the solid and liquid, and then wash with 3 times the volume of deionized water The solid was washed several times until the supernatant was colorless, and then the solid was dried to absolute dryness to obtain pretreated corncobs.
[0025] c) Enzymatic hydrolysis: carry out enzymatic hydrolysis in 50 mL of acetate buffer (50 mM, pH 5.5), with a subs...
Embodiment 3
[0027] a) Preparation of 70 wt% [betaine][arginine] deep eutectic solvent: 46% betaine solution was added dropwise to arginine aqueous solution under stirring, the moles of betaine and arginine The ratio was 1:15, and the reaction was carried out at 40°C for 48 h.
[0028] b) Pretreatment: The dried corn stalk powder and [betaine][arginine] deep eutectic solvent (moisture content: 30 wt%) were mixed in a 250 mL single port according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:20. Mix in a flask and stir at 90°C for 12 h; after the solid-liquid mixture is cooled to room temperature, add 1 times the volume of deionized water as the pretreatment solvent, mix, centrifuge to separate the solid and liquid, and then wash with 3 times the volume of deionized water The solid was washed for several times until the supernatant was colorless, and then the solid was dried to absolute dryness to obtain pretreated corn stalks.
[0029] c) Enzymatic hydrolysis: carry out enzymatic hydrolysis in 50 mL ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com