Preparation method and application method of a heavy oil viscosity-reducing and degrading mixed bacterial agent
A technology of mixing bacterial agents and application methods, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, methods using microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of insignificant viscosity-reducing effect, high degradation efficiency, and low degradation efficiency, and achieve Realize the effects of efficient degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons, high degradation efficiency, and simple preparation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Acinetobacter sp.strain ZX-15, Achromobacter pulmonisstrain PI3-03, Acinetobacter sp.RS206 and Chrobactrum anthropisttrain CON21 domestication, screening and preparation of mixed bacterial agents:
[0049] (1) Take 3g of the soil that has been polluted by heavy oil for a long time in the heavy oil production area of Shengli Oilfield, add it to 150mL enrichment / degradation medium containing 1g / L heavy oil, and culture it in a constant temperature shaker at 37°C for 5 days (160 r / min) Afterwards, 3 mL of the supernatant was transferred to a new enrichment / degradation medium with a heavy oil content of 2 g / L, and cultured again for 5 days. By analogy, gradually increase the concentration of heavy oil to 5g / L, a total of five cycles of domestication.
[0050] (2) Take the culture solution of the last acclimatization cycle and smear the plate, pick colonies with different morphological characteristics, and repeat the streaking until it is confirmed that the colonies in the...
Embodiment 2
[0058] 2. Degradation and viscosity-reducing performance of mixed bacterial agents under different culture conditions
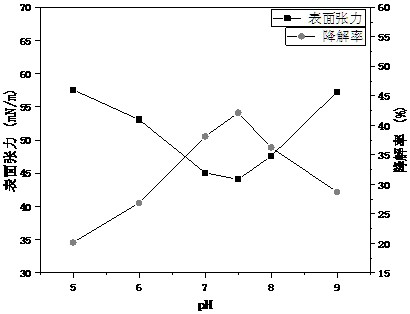
[0059] Inoculate Acinetobacter sp.strain ZX-15, Achromobacterpulmonis strain PI3-03, Acinetobacter sp.RS206 and Chrobacttrumanthropi strain CON21 in the seed medium respectively, at 37°C, 160r / min Shake at constant temperature for 24 hours to obtain the seed solution, then mix their seed solution according to the volume ratio of 2:2:1:1, inoculate in the degradation medium, and conduct the experiment of the following degradation conditions. Wherein, the degradation medium was 1.0 g of ammonium sulfate, 0.25 g of magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, 2.0 g of sodium nitrate, 4.0 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, and 7.6 g of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate were dissolved in 1000 mL of deionized water.
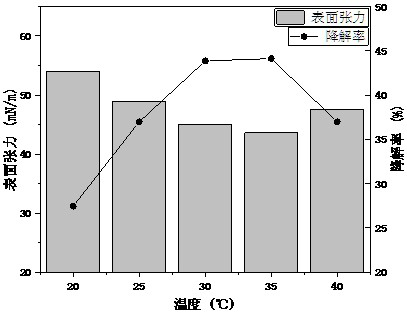
[0060] 1. Different temperature
[0061] Degradation conditions: pH7.5, heavy oil 2g / L, inoculation amount 5% (V / V), sodium chloride 4g / L; temperature: 20°C, 25°C...
Embodiment 3
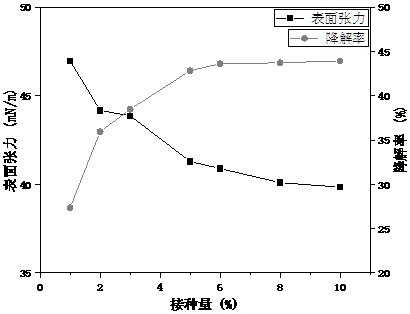
[0070] Degradation and Viscosity Reduction Performance of Bacteria Agents with Different Mixing Ratio
[0071] Inoculate Acinetobacter sp.strain ZX-15, Achromobacterpulmonis strain PI3-03, Acinetobacter sp.RS206 and Chrobacttrumanthropi strain CON21 in the seed medium, at 37°C, 160r / min Oscillate at constant temperature for 24 hours to obtain the seed liquid, and the seed liquid is mixed according to the volume ratio according to the following ratio:
[0072]
[0073] The results show that the degradation rate of petroleum hydrocarbons in combination D is the highest, which is 43.84%, and the surface tension is 41.2mN / m. The surface tension of combination E is the lowest, which is 38.7mN / m, and the degradation rate of petroleum hydrocarbons is 40.58%. The surface tension and degradation rate of the two combinations are relatively small. Combination D has the best degradation ability for heavy oil, and has a good viscosity-reducing effect. It is most suitable for biological ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface tension | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface tension | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface tension | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com