Method for removing heavy metals in shellfish enzymatic hydrolysate
An enzymatic hydrolyzate and heavy metal technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, food science, applications, etc., can solve problems such as the need to improve the adsorption effect, narrow pH range, difficult separation, etc. The effect of strong adsorption capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
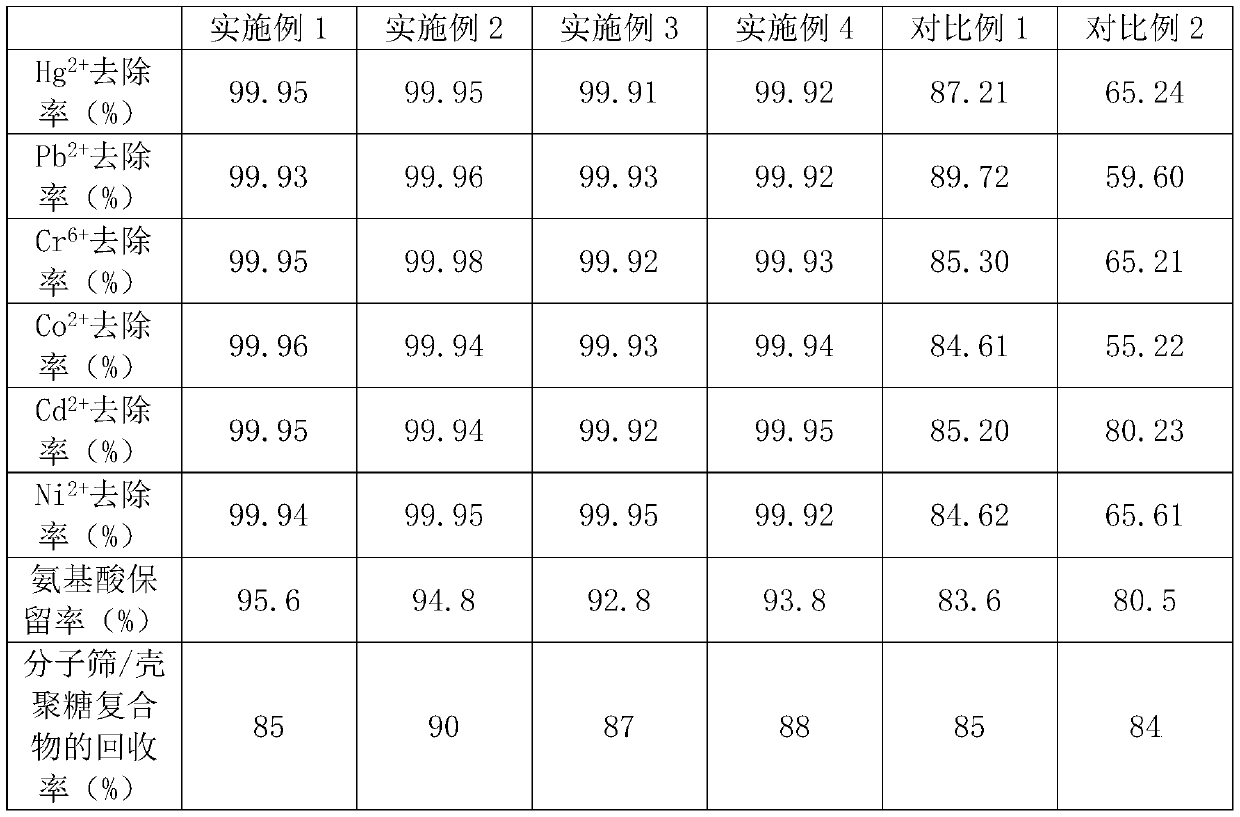
Embodiment 1
[0034] Step 1: Grind coal gangue to 300 mesh and place it in ash dish, add sodium carbonate to the ash dish, roast for 1 hour at a temperature of 1000° C. and then grind to obtain a pretreated sample. The sodium carbonate and coal gangue powder The mass ratio of the pretreated sample is 1:3. The pretreated sample is oxidized at 300°C for 1h, then added with a hydrochloric acid solution with a mass concentration of 15%, soaked at 50°C for 1h, and the filtrate and filter residue are collected after filtration. Add oxalic acid in, mix well, obtain mixed liquor, described oxalic acid and Fe in the filtrate 3+ The molar ratio is 2:1, wash the filter residue, add sodium hydroxide and grind it evenly, treat it at 600°C for 1h to obtain slag, add deionized water, and let it stand at 50°C for 2h to obtain a mixture. The mass of the sodium hydroxide and filter residue The ratio is 1:1, the molar ratio of deionized water to sodium hydroxide is 30:1, the mixed solution is added to the mix...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Step 1: Grind coal gangue to 350 mesh and place it in a gray dish, add sodium carbonate to the gray dish, roast at 1200°C for 2 hours and then grind to obtain a pretreated sample, the sodium carbonate and coal gangue powder The mass ratio of the pretreated sample is 1:4. The pretreated sample is oxidized at 350°C for 1.2h, then added with a hydrochloric acid solution with a mass concentration of 15%, soaked at 60°C for 1h, and the filtrate and filter residue are collected after filtration. Add oxalic acid in the filtrate, mix homogeneously, obtain mixed solution, described oxalic acid and Fe in the filtrate 3+ The molar ratio is 3:1, wash the filter residue, add sodium hydroxide and grind it evenly, treat it at 650°C for 1h to obtain slag, add deionized water, and let it stand at 50°C for 2h to obtain a mixture. The mass of the sodium hydroxide and filter residue The ratio is 1:1, the molar ratio of deionized water to sodium hydroxide is 30:1, the mixed solution is adde...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Step 1: Grind coal gangue to 400 mesh and place it in a gray dish, add sodium carbonate to the gray dish, roast it at 1100°C for 2 hours and then grind it to obtain a pretreated sample, the sodium carbonate and coal gangue powder The mass ratio of the sample is 1:4. The pretreated sample is oxidized at 350°C for 1.2h, then added with a hydrochloric acid solution with a mass concentration of 15%, soaked at 60°C for 1.5h, and the filtrate and filter residue are collected after filtration. Add oxalic acid in the filtrate, mix homogeneously, obtain mixed solution, described oxalic acid and Fe in the filtrate 3+ The molar ratio is 3:1, wash the filter residue, add sodium hydroxide and grind it evenly, treat it at 650°C for 1h to obtain slag, add deionized water, and let it stand at 50°C for 2h to obtain a mixture. The mass of the sodium hydroxide and filter residue The ratio is 1:1, the molar ratio of deionized water to sodium hydroxide is 30:1, the mixed solution is added t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com