Colon-targeted sinomenine hydrochloride slow-release nanofiber membrane and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of sinomenine hydrochloride and nanofiber membrane, applied in nanotechnology, nanomedicine, nanotechnology and other directions, can solve the problems of reducing the sudden release of water-soluble drugs and side effects of the digestive tract, so as to reduce the sudden release phenomenon and maintain the efficacy of the drug , reducing the effect of irritation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
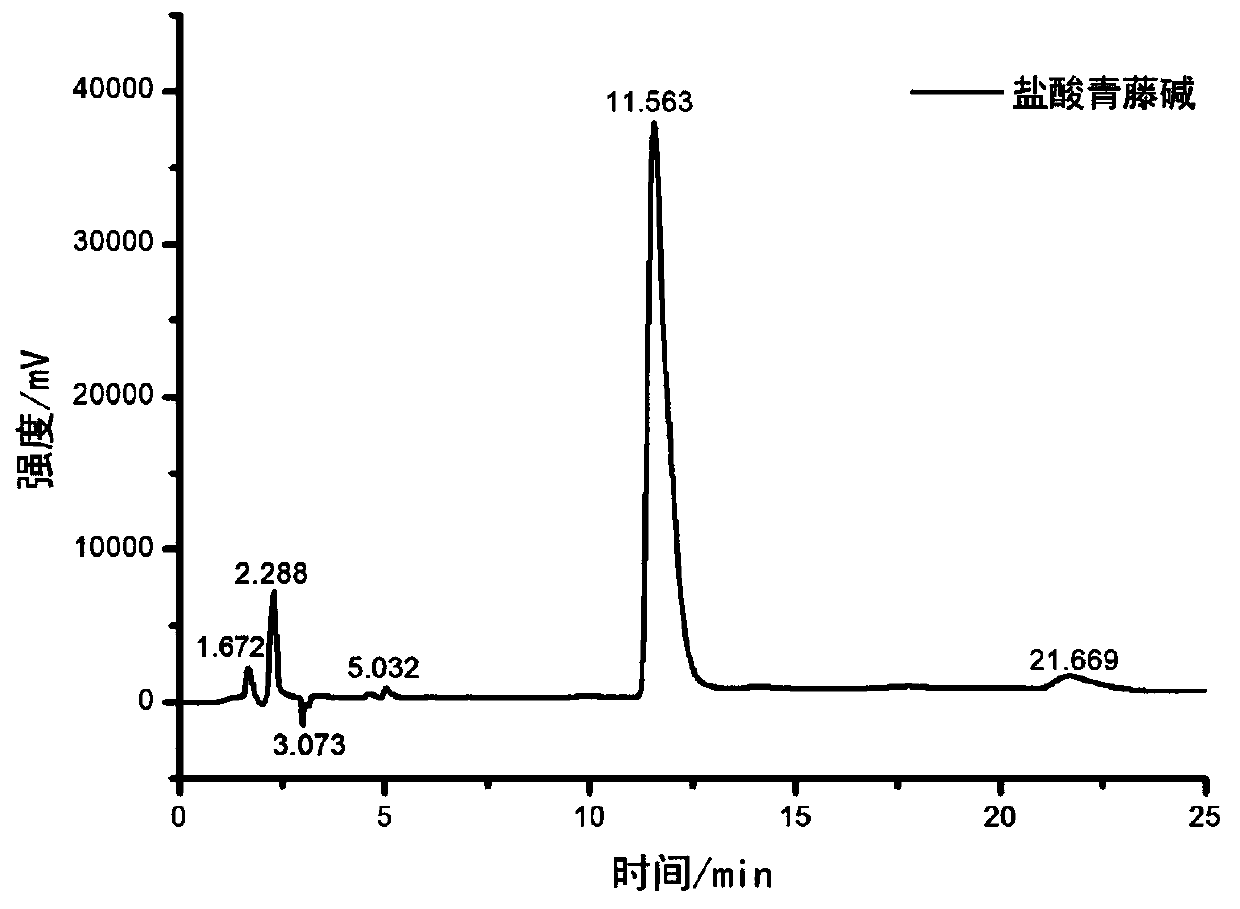
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] A method for preparing a colon-targeted sinomenine hydrochloride slow-release nanofibrous membrane, comprising:
[0035] (1) Weigh 2.2508g of polyacrylic resin Eudragit S100 with an analytical balance, add it to a mixed solution of 3.6430g N,N-dimethylacetamide and 9.110g of absolute ethanol, heat and stir to obtain a shell spinning solution . Wherein, the concentration of absolute ethanol is ≥99.7%, the concentration of N,N-dimethylacetamide is ≥99.5%, the heating temperature is 50°C, and the stirring time is 8h;
[0036] (2) Weigh 0.2503g of polyacrylic acid resin Eudragit RS100 and 0.3003g of sinomenine hydrochloride with an analytical balance, add them together to a mixed solution of 1.2720g of chloroform and 3.1781g of absolute ethanol, stir at room temperature to obtain a nuclear layer spinning solution. Wherein, the concentration of absolute ethanol is ≥99.7%, the concentration of chloroform is ≥99.0%; the stirring time is 4h;
Embodiment 2
[0046] A method for preparing a colon-targeted sinomenine hydrochloride slow-release nanofibrous membrane is basically the same as the method in Example 1, the difference being:
[0047] In step (1), the amount of polyacrylic resin Eudragit S100 is 2.2501 g; the solution is mixed with 6.3750 g of N,N-dimethylacetamide and 6.3750 g of absolute ethanol. The rest of the steps are the same.
[0048] In step (3), the positive electrode of the voltage in the electrospinning process is +17KV, the ambient temperature is 26° C., and the drug-loaded nanofiber membrane obtained has a drug-loading capacity of 20% to 30%.
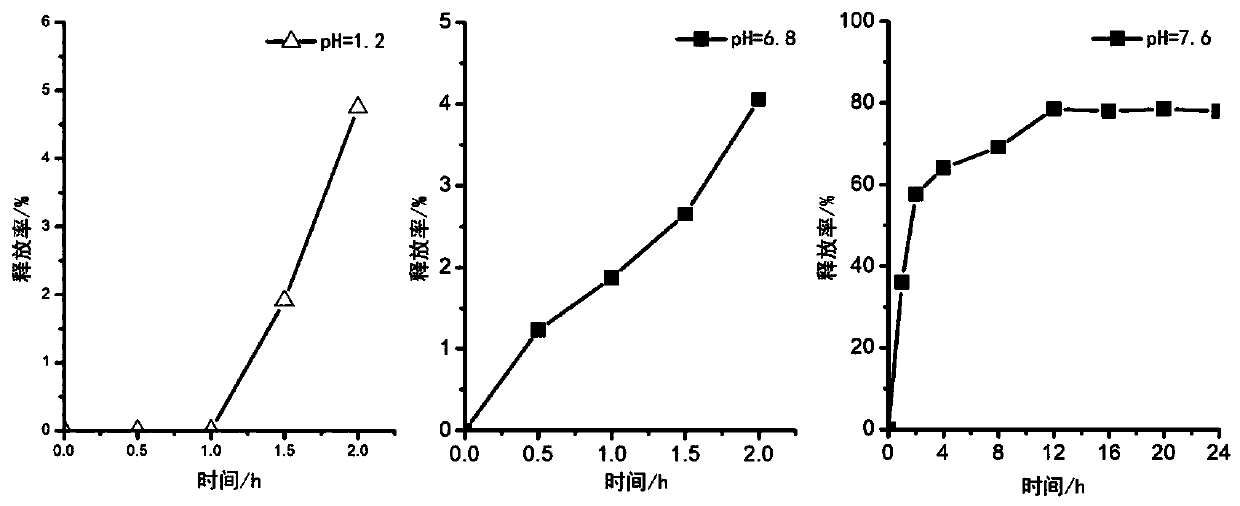
[0049] The same method as in Example 1 was used to measure the in vitro release of the coaxial drug-loaded sustained-release nanofiber membrane of Example 2. The nanofibrous membrane prepared in Example 2 of the present invention released only about 5% in two hours in a simulated stomach environment with a pH of 1.2, and only released about 4% in two hours in a simulat...
Embodiment 3
[0051] A method for preparing a colon-targeted sinomenine hydrochloride slow-release nanofibrous membrane is basically the same as the method in Example 1, the difference being:
[0052] In step (1), the amount of polyacrylic resin Eudragit S100 is 2.2498g; the solution is mixed with 6.3750g N,N-dimethylacetamide and 6.3750g absolute ethanol. The rest of the steps are the same.
[0053] In step (2), weigh the polyacrylic acid resin Eudragit RS100 of 0.2503g and 0.3003g sinomenine hydrochloride; add together in the mixed solution of 1.0556g chloroform and 3.6944g dehydrated alcohol, stir at room temperature to obtain the nuclear layer spinning solution . Wherein, the concentration of absolute ethanol is ≥99.7%, the concentration of chloroform is ≥99.0%; the stirring time is 4h;
[0054] In step (3), the positive electrode of the voltage in the electrospinning process is +17KV, the ambient temperature is 26° C., and the drug-loaded nanofiber membrane obtained has a drug-loadin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com