Cephalosporin C acylase mutant with high thermal stability
A technology of acylase mutant and cephalosporin, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of affecting industrial application, low stability and high production cost of 7-ACA
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
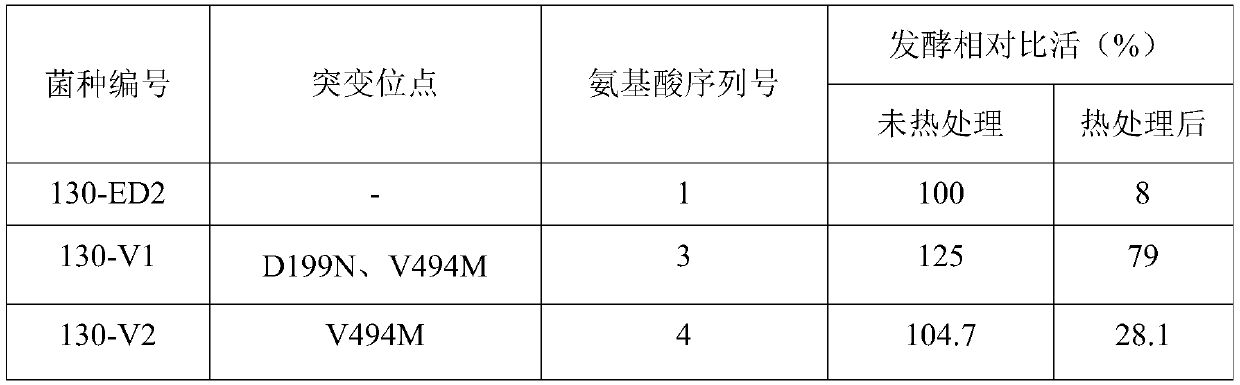
[0058] Example 1 Construction of initial CPC acylase 130-ED2 expression strain
[0059] According to the CPC acylase 130-ED2 coding gene (formerly SEQ ID NO: 13) published in PCT / CN2017 / 076688, the whole gene synthesis is carried out, here is the sequence SEQ ID NO: 2. Restriction endonuclease sites NdeI and XhoI were designed at both ends of the gene, and subcloned into the corresponding sites of the vector pET24a (Novagen) to obtain the recombinant plasmid pET24a-130ED2, which was transformed into the expression host Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3), and the expression initial The recombinant Escherichia coli of CPC acylase is still numbered 130-ED2.
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2 Error-prone PCR method constructs random mutation point library and screening
[0061] 2.1 Error-prone PCR method to construct random mutation point library
[0062] Using SEQ ID NO:2 as a template, an error-prone PCR technique was used to construct a random mutant library.
[0063] Forward primer C-F: 5'- CATATG GAACCGACCTCCACCCCGCAG-3',
[0064] Reverse primer C-R: 5'- CTCGAG CGGTTTGAAGTTGAACGGGGTACGTTC-3'.
[0065] 50μL error-prone PCR reaction system includes: 50ng plasmid template pET24a-13ED2, 30pmol pair of primers C-F and C-R, 1X Taq buffer, 0.2mM dGTP, 0.2mM dATP, 1mM dCTP, 1mM dTTP, 7mM MgCl 2 , (0mM, 0.05mM, 0.1mM, 0.15mM, 0.2mM) MnCl 2 , 2.5 units of Taq enzyme (Fermentas). The PCR reaction conditions are: 95°C for 5min; 94°C for 30s, 55°C for 30s, 72°C
[0066] 2min / kbp; 30 cycles; 10min at 72°C. The 2.0kb random mutation fragment was recovered from the gel as a large primer, and MegaPrimer PCR was performed with KOD-plus DNA polymerase:...
Embodiment 3
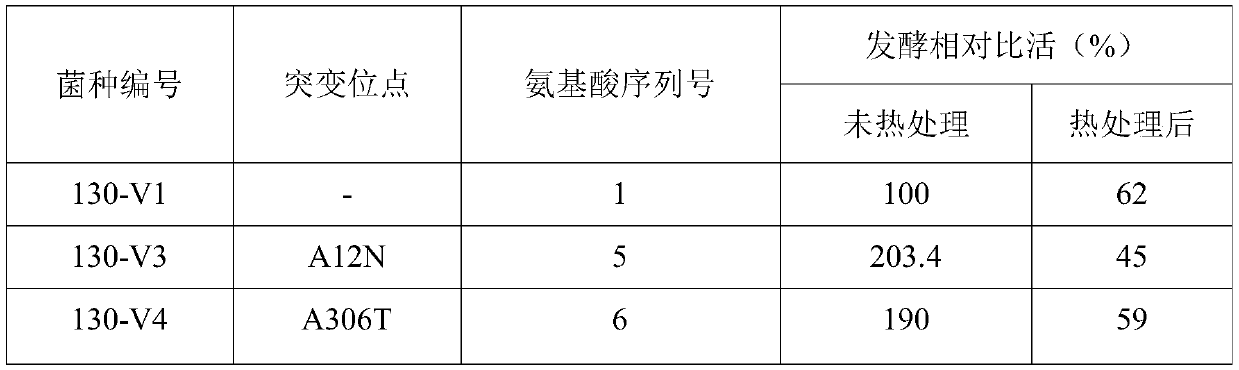
[0082] Embodiment 3 The second round of error-prone PCR method constructs random mutation point library and screening
[0083] 3.1 Error-prone PCR method to construct random mutation point library
[0084] Referring to the method of Example 2, the plasmid of the CPC acylase mutant strain 130-V1 strain obtained in Example 2 was extracted as a template, and a random mutant library was constructed by using error-prone PCR technology. The error-prone PCR system is the same as step 2.1 in Example 2, and the error-prone PCR is continued with the forward primer C-F and the reverse primer C-R.
[0085] 3.2 High-throughput screening, heat treatment and activity determination of mutant library
[0086] The method is the same as step 2.2, step 2.3 and step 2.4 of embodiment 2.
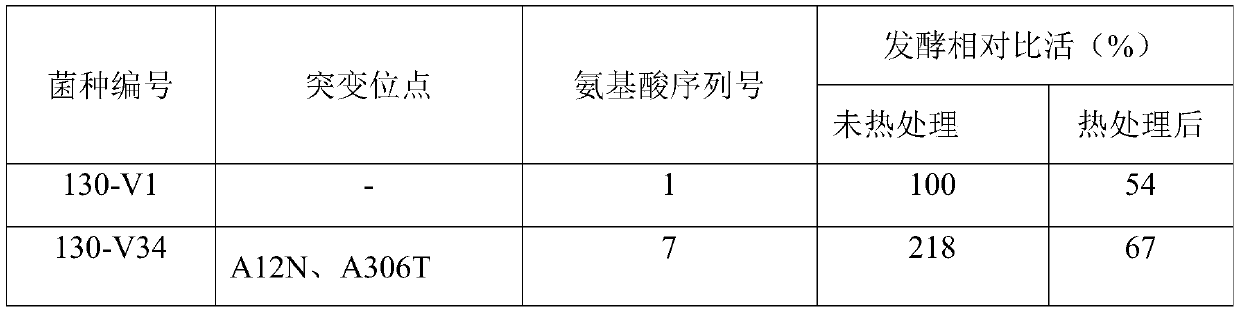
[0087] Through the screening of the random mutation library, two strains 130-V3 and 130-V4 were screened out with significantly improved activity relative to the CPC sodium salt substrate, but no improvement in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com