Method for detecting activity of laccase in litter
A litter and activity technology, applied in the field of enzyme activity detection, can solve the problems of non-degrading microbial colonization of surface litter, large variation in calculation time, too long detection time, etc., and achieves cumbersome operation steps, improved sensitivity, Precise results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Embodiment 1: establish the method for detecting litter laccase activity
[0036] 1. Reagent preparation:
[0037] 1M sodium hydroxide solution: 9.999g sodium hydroxide, dilute to 250mL with deionized water to prepare, store at room temperature.
[0038] Universal buffer stock solution: Prepare with 3.025g Tris, 3.9g maleic acid, 3.5g citric acid (3.825g citric acid monohydrate), 1.56g boric acid, and 122mL sodium hydroxide (1M) to 250mL with deionized water .
[0039] Culture buffer: adjust 100mL of universal buffer stock solution to pH 4.5 with hydrochloric acid, dilute to 1000mL with deionized water, and store at 4°C after sterilization.
[0040] 1330 μM ABTS working solution: Weigh 73.17 mg ABTS and dissolve it in 100 mL culture buffer, store at 4°C in the dark for 4 weeks before use.
[0041] 2. Operation steps for detection of litter laccase activity:
[0042] 1) After the litter samples to be tested were cut into pieces and passed through a 2mm sieve, weigh 3...
Embodiment 2
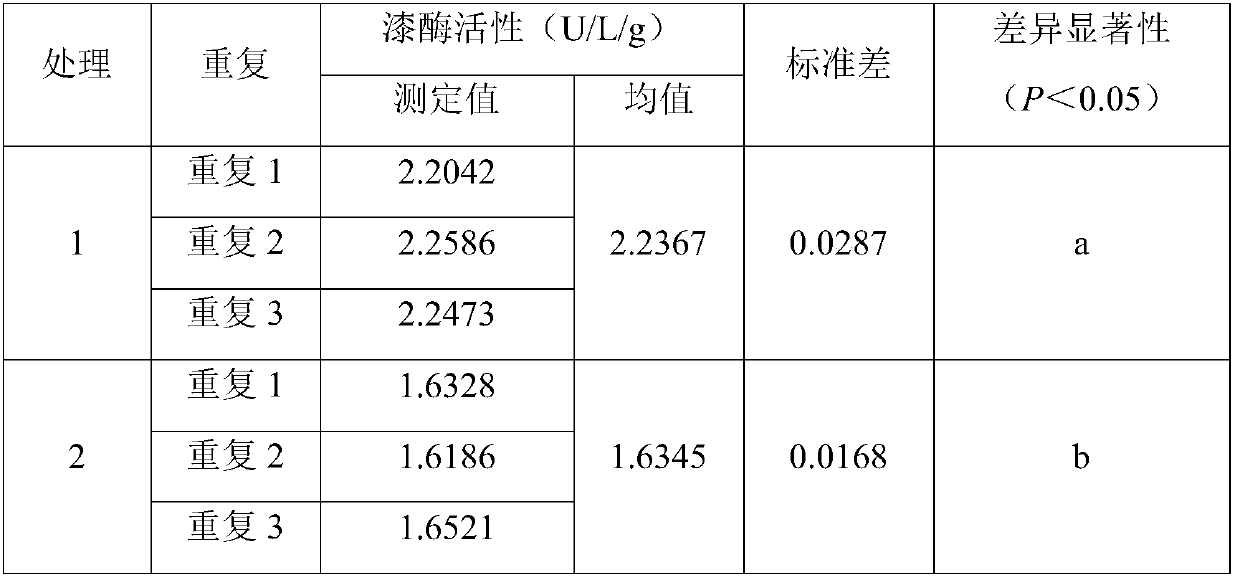
[0051] The litter branches used in this example were collected from the pure sweetgum forest and the mixed forest of sweetgum black pine at the southwestern foot of Zijin Mountain (32°04'N, 118°50'E) in Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province. The collected liquidambar branches with a diameter of 5 mm were killed at 105°C for 15 minutes, dried continuously at 80°C for 48 hours, and 7g of dry weight was weighed and put into a 300-mesh (0.050mm aperture) 10cm*8cm nylon decomposition bag. Nylon decomposition bags containing dried sweetgum branches were respectively buried in the pure sweetgum forest and the mixed sweetgum black pine forest, and covered with the original surface soil (0-10cm) about 1m away from the main trunk of the tree and compacted lightly. After 1 year of burial, the semi-degraded litter branches were taken out, and impurities such as sediment were removed. Treatment 1 was the litter branches of sweetgum pure forest, and treatment 2 was the litter branches of liquidamba...
Embodiment 3
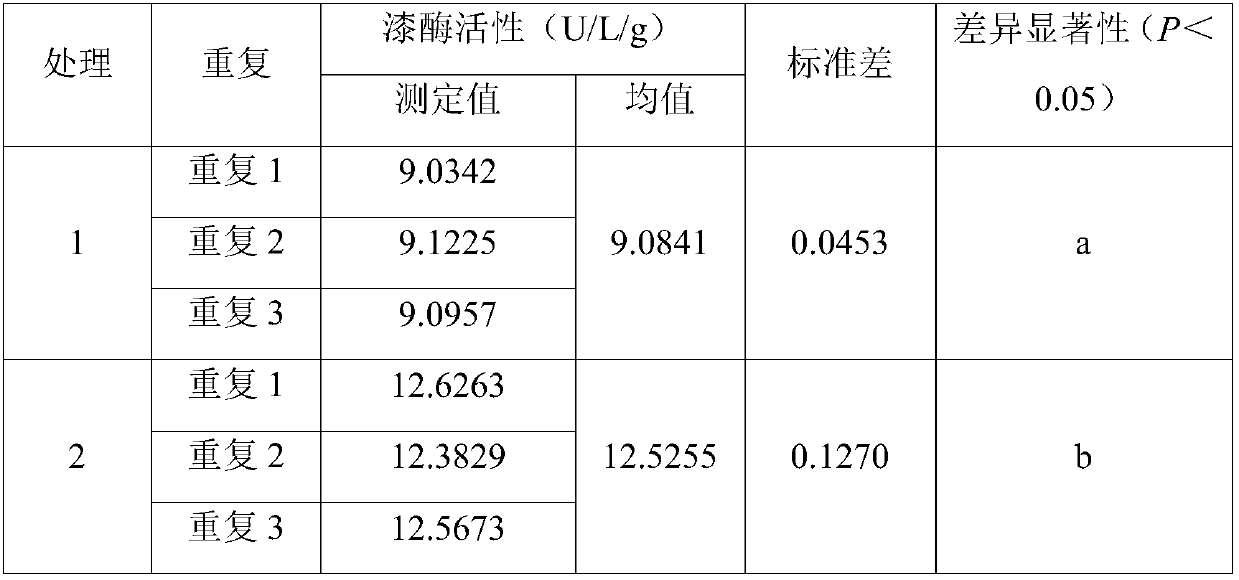
[0064] The litter and dead branches used in this example were collected from the 4-year-old and 9-year-old Eucalyptus grandis plantations in the southern seedling base (21°27'N, 110°11'E) of Zhanjiang City, Guangdong Province. The collected dead branches of Eucalyptus grandis litter with a diameter of 5mm were killed at 105°C for 15min, dried continuously at 80°C for 48h, and 10g of dry weight was weighed and put into a 300 mesh (0.05mm aperture) 10cm*8cm nylon decomposition bag. The nylon mesh bags containing the dried dead branches of Eucalyptus grandis were respectively buried in the 4-year-old and 9-year-old Eucalyptus grandis plantations, covered with the original surface soil (0-10cm) about 1m away from the main trunk of the tree and compacted lightly. After 4 months of burial, the semi-degraded litter was taken out, and impurities such as sediment were removed. Treatment 1 was the litter branches of the 4-year-old Eucalyptus grandis plantation, and treatment 2 was the li...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com