A dye anaerobic biological decolorization system and method
An anaerobic biological and dye technology, applied in water pollutants, anaerobic digestion treatment, sustainable biological treatment and other directions, can solve the problems of high cost of lactic acid, lack of macromolecular organic matter utilization ability, restricting practical application, etc. cost, solving the problem of carbon source cost, and the effect of efficient degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
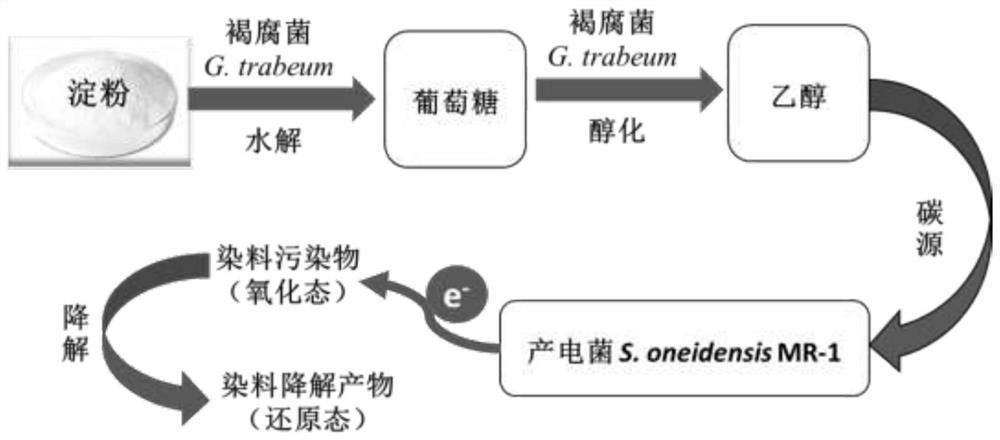
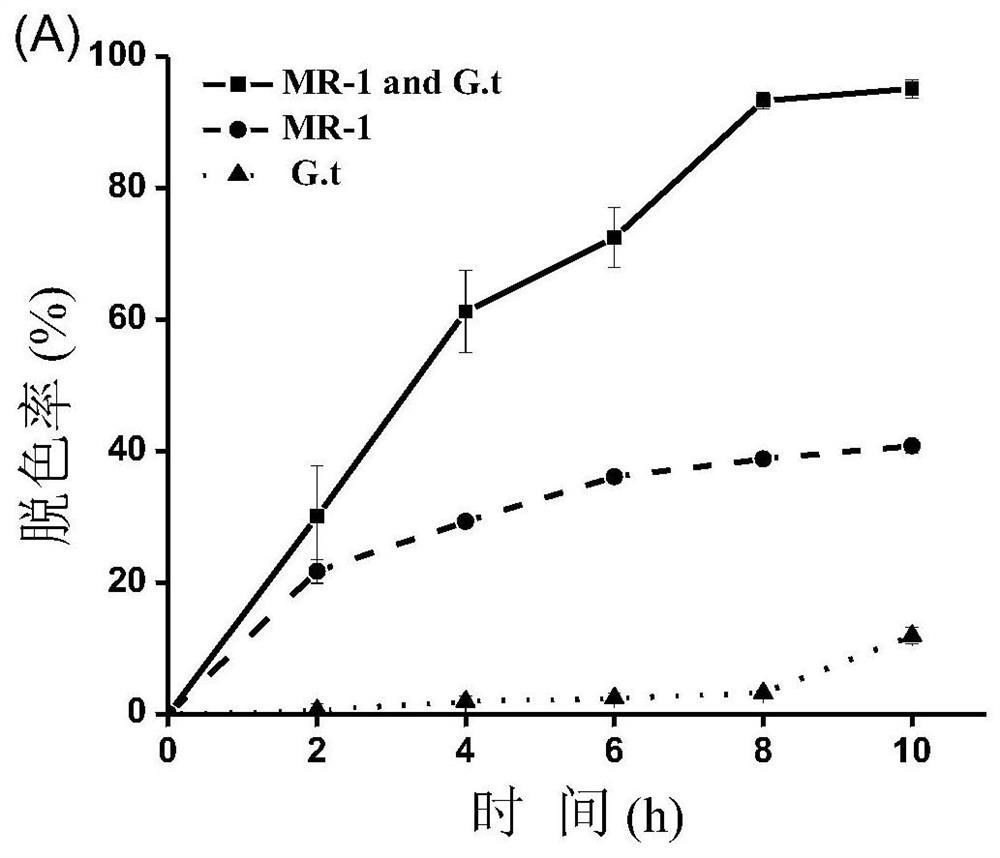
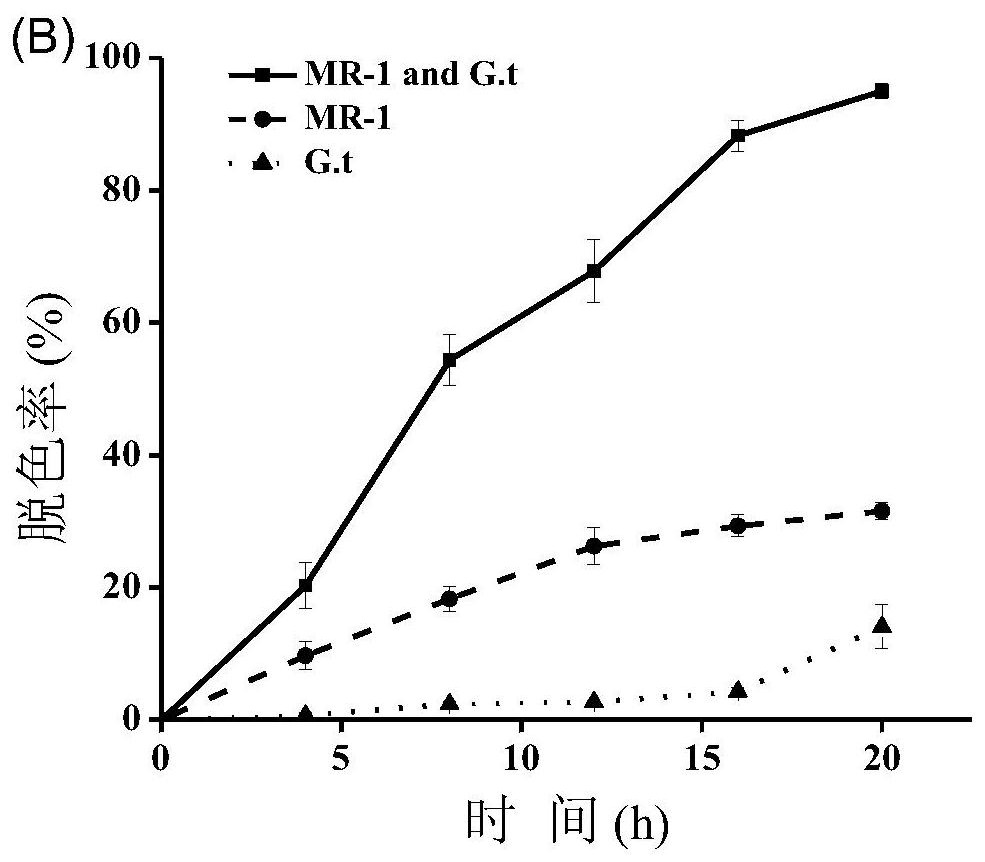
[0039] A low-carbon source cost dye anaerobic biological decolorization system, brown rot fungus G. trabeum First, the starch is hydrolyzed to generate glucose, and the glucose is further metabolized into small molecular organic compounds such as ethanol. Shewanella MR-1 utilizes ethanol and other anaerobic respiration and metabolism to release electrons, and finally transfers electrons to dye pollutants to achieve efficient degradation of pollutants.
[0040] The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0041] (1) Streak the MR-1 stored in glycerol on a solid plate LB medium (containing 5g / L of yeast extract, 10g / L of tryptone, 10g / L of sodium chloride, 2% agar) at 30°C Incubate overnight.
[0042] (2) Use a pipette to suck up the activated single colony, inoculate it in 50mL liquid LB medium, (30 ± 0.5) ℃, (200 ± 5) rpm and shake for 10 hours to the late logarithmic phase, and then in the late logarithmic phase The bacteria were collected by centrifugation at 7000...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com