Saccharide-based water reducing agent and preparation method thereof
A water-reducing agent and sugar-based technology, applied in the field of sugar-based water-reducing agent and its preparation, can solve the problems of running pulp, increasing the ineffective adsorption of water-reducing agent, workability and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
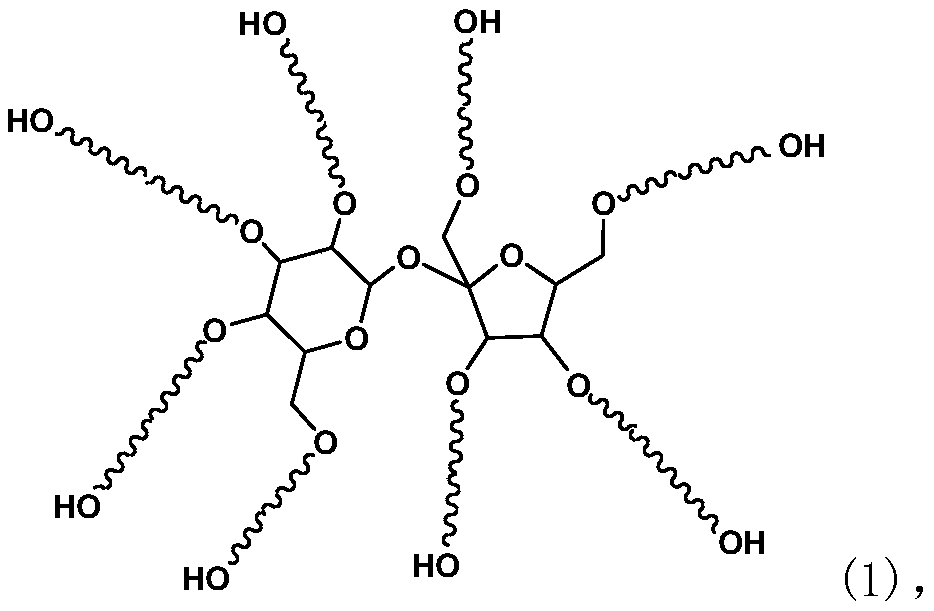
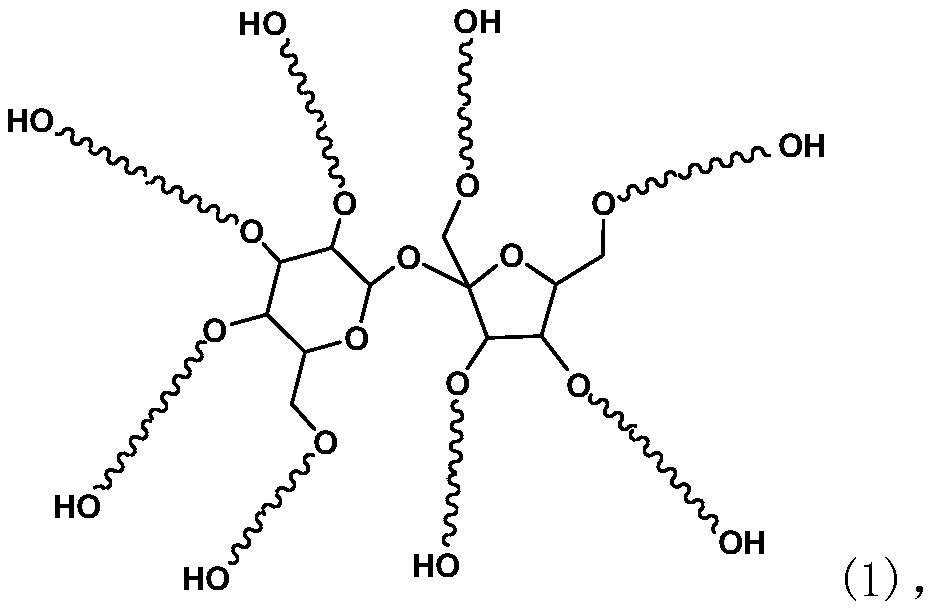
[0044] (1) Preparation of glycosyl polyether P:
[0045] Weigh 100 parts of sucrose into the reactor, add 0.2 parts of sodium hydroxide and 20 parts of ethylene glycol dimethyl ether in sequence, seal the reaction kettle, start the mechanical stirring, and replace with nitrogen three times. Then raise the temperature to 100°C, feed 20 parts of ethylene oxide, and after the induced reaction in the reactor starts (temperature rises, pressure drops), control the temperature of the reactor between 100 and 130°C, and the pressure of the reactor ≤0.4MPa, Continue to feed 464 parts of ethylene oxide. After feeding, keep warm for 30 minutes, cool down to 80°C and discharge to obtain 601 parts of light brown polyether, which is marked as P-1. The weight average molecular weight of the polyether is 1984 after testing.
[0046] In the same way, the following sugar-based polyethers were prepared for the synthesis of sugar-based water reducers.
[0047] Preparation of glycosyl polyether ...
preparation example 1
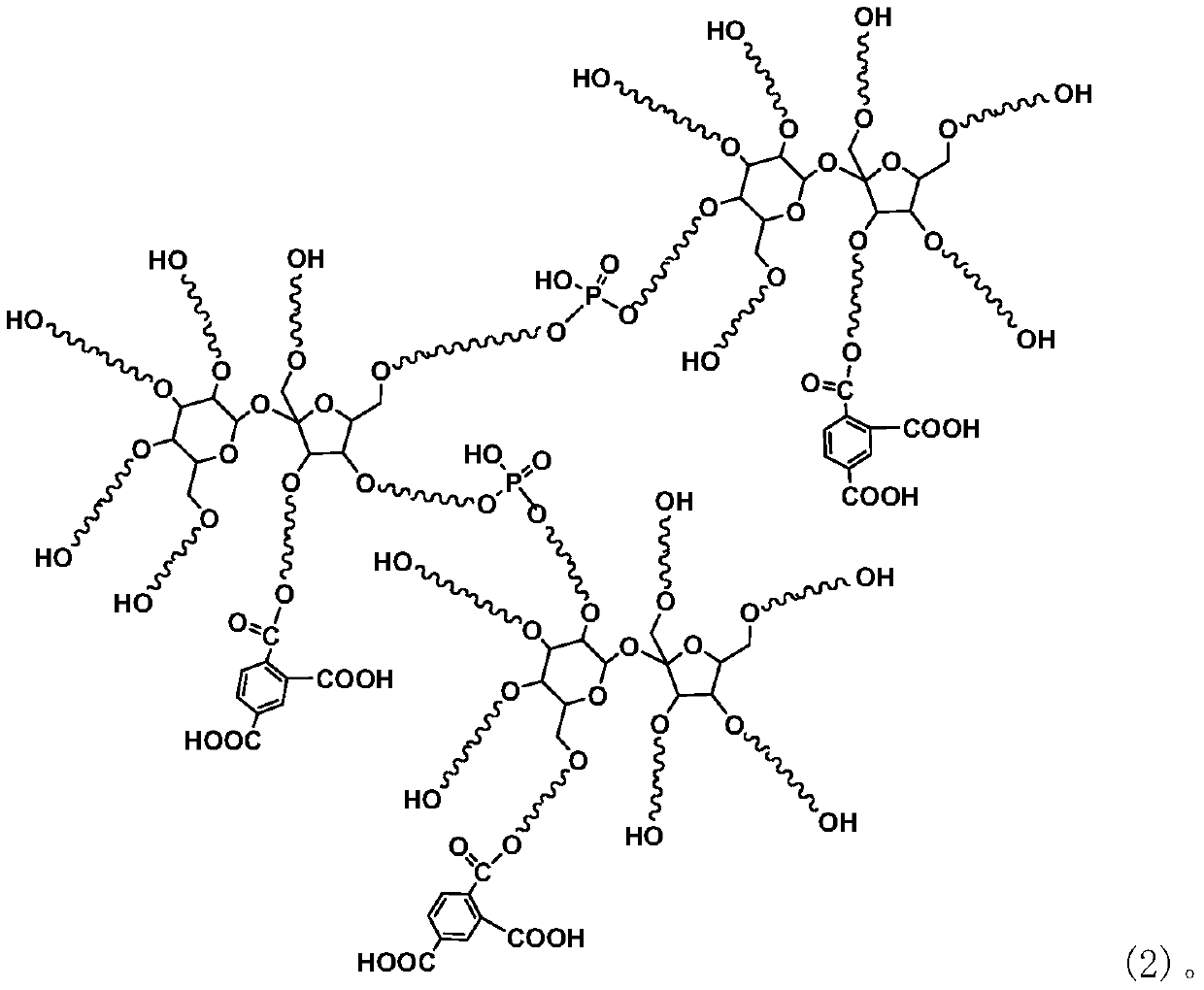
[0054] Weigh 100.0 parts of glycosyl polyether P-1 into the reactor, add 1.0 part of cross-linking agent phosphoric acid (85%), seal the reactor, and start mechanical stirring. Raise and keep the temperature at about 100°C, and react for 3.0h under the condition of vacuum degree of -0.08~-0.1MPa. Then add 10.0 parts of maleic anhydride, control the temperature of the reactor at 120° C., and react for 5.0 hours under normal pressure. Cool down to 50°C and discharge, neutralize with 32% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution to pH = 6-7 and dilute to 40-50% to obtain a light wine red sugar-based water reducer, which is designated as TJS-1. The tested sugar-based water reducer has a weight average molecular weight of 5394 and a molecular weight distribution of 1.54.
preparation example 2
[0056] Weigh 100.0 parts of glycosyl polyether P-2 into the reactor, add 3.0 parts of cross-linking agent polyphosphoric acid, seal the reactor, and start mechanical stirring. Raise and keep the temperature at about 120°C, and react for 4.0h under the condition of vacuum degree of -0.08~-0.1MPa. Then add 20.0 parts of phthalic anhydride, control the temperature of the reactor at 105° C., and react for 7.0 hours under normal pressure. Cool down to 50°C and discharge, neutralize with 32% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution to pH = 6-7 and dilute to 40-50% to obtain a light wine red sugar-based water reducer, which is designated as TJS-2. The tested sugar-based water reducer has a weight average molecular weight of 7579 and a molecular weight distribution of 1.47.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com