Preparation of exosomes from dental epithelial cells, preparation and application of exosome implants
A technology of epithelial cells and exosomes, applied in the field of biomedical engineering, to achieve the effects of overcoming immunogenicity, avoiding immunogenic problems, and being easy to store and transport
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] A preparation of exosomes from dental epithelial cells,
[0047] (1) Treatment of engineered dental epithelial cells
[0048] The engineered dental epithelial cell line (HERS-H1) preserved in liquid nitrogen was revived with warm water at 45°C, inoculated in a 10cm culture dish, added epithelial cell medium medium containing 2% fetal bovine serum, and stored at 37°C. 5%CO 2 After 28 hours, the medium was changed, and the cells were subcultured with trypsin after they were fused to 90%. When the cells in each dish expand to 90-95% of its volume, the extraction of the engineered dental epithelial cell line extract is carried out.
[0049] (2), acquisition of engineered dental epithelial cell extract
[0050] After sufficient cells have been amplified in step (1), inoculate the epithelial cell line obtained in step (1) into a T75 culture flask, and when it reaches 70% confluence, discard the medium, and wash the cells twice with PBS , add epithelial cell medium medium ...
Embodiment 2
[0054] This embodiment is on the basis of embodiment 1,
[0055] Identification of engineered dental epithelial cell-derived exosomes:
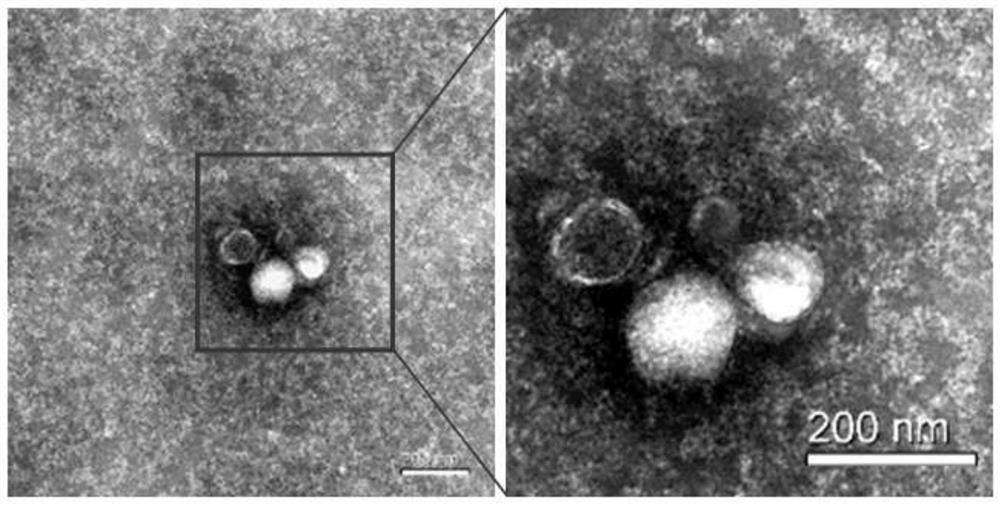
[0056] Step 1. Morphological Identification by Transmission Electron Microscopy
[0057] Exosomes were fixed with 1% glutaraldehyde, overnight at 4°C. After washing off the fixative, the mixed exosomes were dropped onto the sample-loading copper grid, and then water phosphotungstic acid was added dropwise to negatively stain the exosomes for 1 min. Transmission electron microscopy (Hitachi H-7650) imaged and photographed, a circular vesicle-like structure with a diameter of 50-150nm can be seen ( figure 1 ).
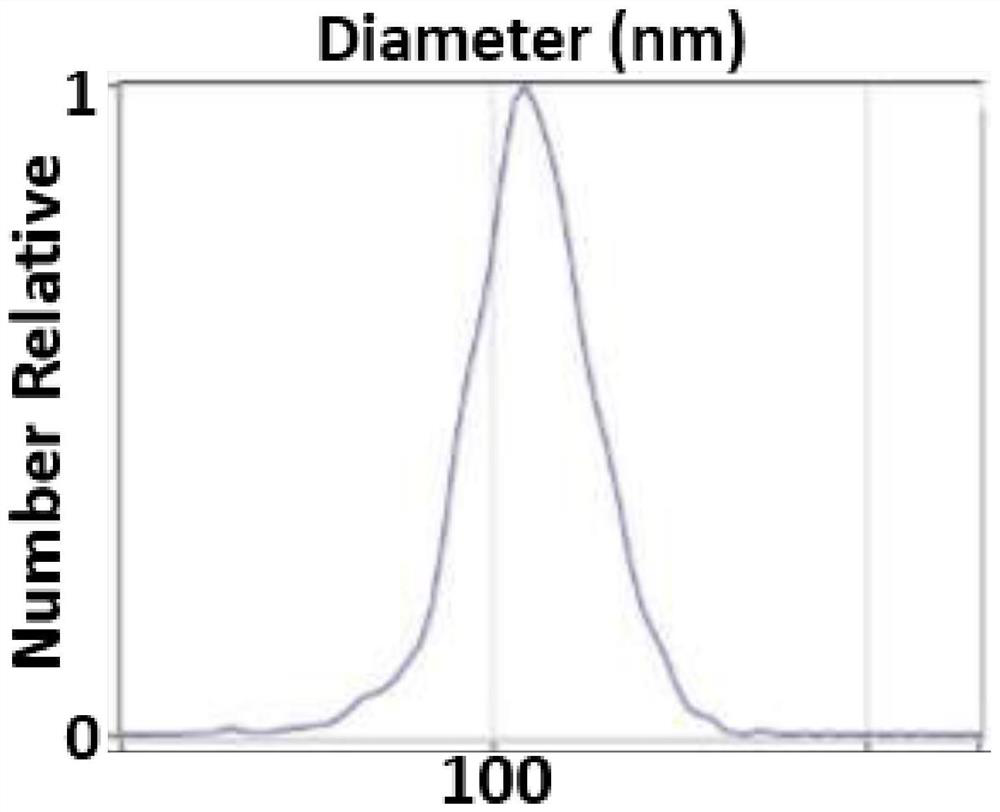
[0058] Step 2. Particle size distribution identification
[0059] Take 50 microliters of sample and inject it into a special channel to measure the particle size distribution of exosomes. It can be seen that the peak of the particle size distribution is around 110nm, and the particle size is mainly distributed between 60-150nm ( fi...
Embodiment 3
[0061] A collagen gel composite engineered dental epithelial cell-derived exosome implant was prepared. The standard type of collagen gel was placed on ice, and the required tip was pre-cooled at the same time. Add collagen gel, 10×basic medium and buffer to pre-cooled glass centrifuge tubes at a ratio of 8:1:1. The buffer composition was 2.2% sodium bicarbonate, 0.05N sodium hydroxide and 200M hydroxyethylpiperazine ethanesulfonic acid. Take 800 micrograms of exosome pellets and resuspend them with 400 microliters of liquid collagen gel mixture (the final concentration of exosomes is 2 mg / ml), and transfer the obtained liquid collagen gel mixed with engineered dental epithelial cell-derived exosomes to Put it into a pre-cooled centrifuge tube, and put it on ice for later use, to ensure that the solvent is in a liquid state and the time is cut off before the in vivo experimental model is stacked, within 0.5h. The standard type of collagen gel refers to the basic type of colla...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com